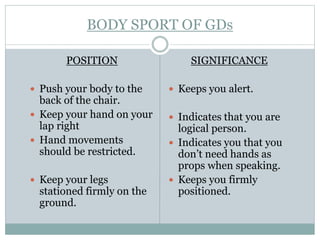
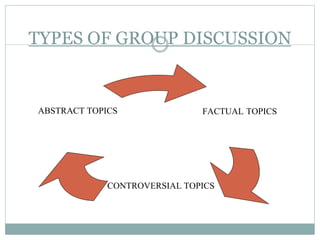
This document provides information about group discussions, including their purpose, types of topics, body language, personality traits assessed, tips, and dos and don'ts. Group discussions are used to assess candidates' personality traits and skills through discussion of a given topic among a group. They allow participants to think critically, solve problems, and make decisions as a group while improving listening, communication, and confidence. Factual, controversial, and abstract topics may be discussed. Proper body language and discussion techniques as well as traits like teamwork and leadership are important for success in group discussions.