Embed presentation
Download to read offline
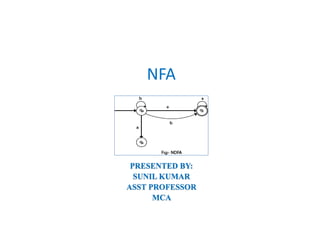
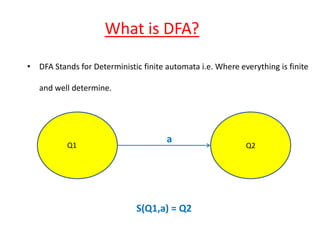




The document defines DFA and NFA, and discusses why NFA is studied. It provides definitions for both DFA and NFA, noting that DFA is deterministic with a single next state, while NFA is non-deterministic and can have multiple next states. NFA is easier to design but not practically implemented. The formal definition of NFA is given as a 5-tuple consisting of states, input symbols, initial state, final states, and a transition function that maps a state and input to a set of possible next states.





