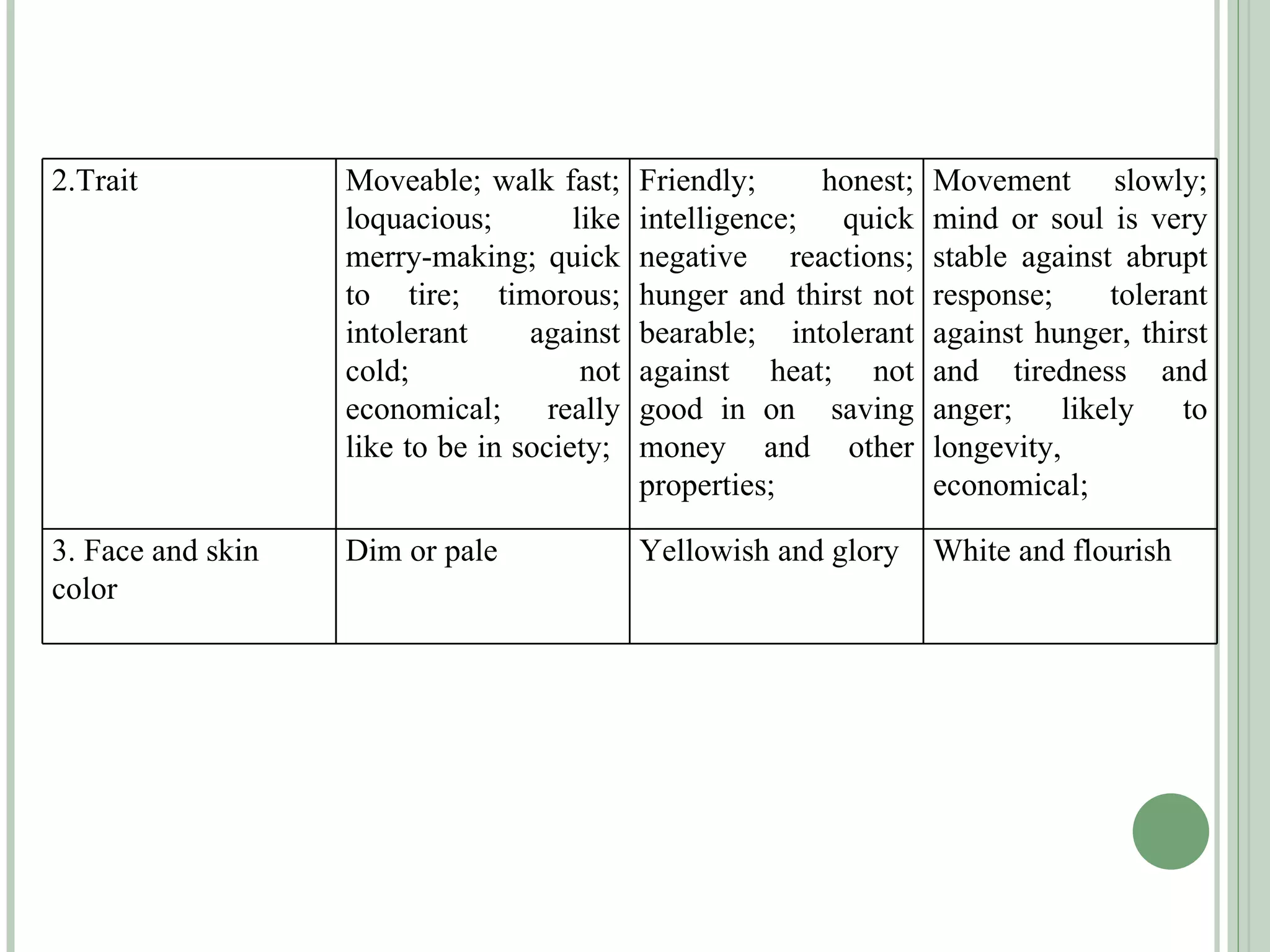
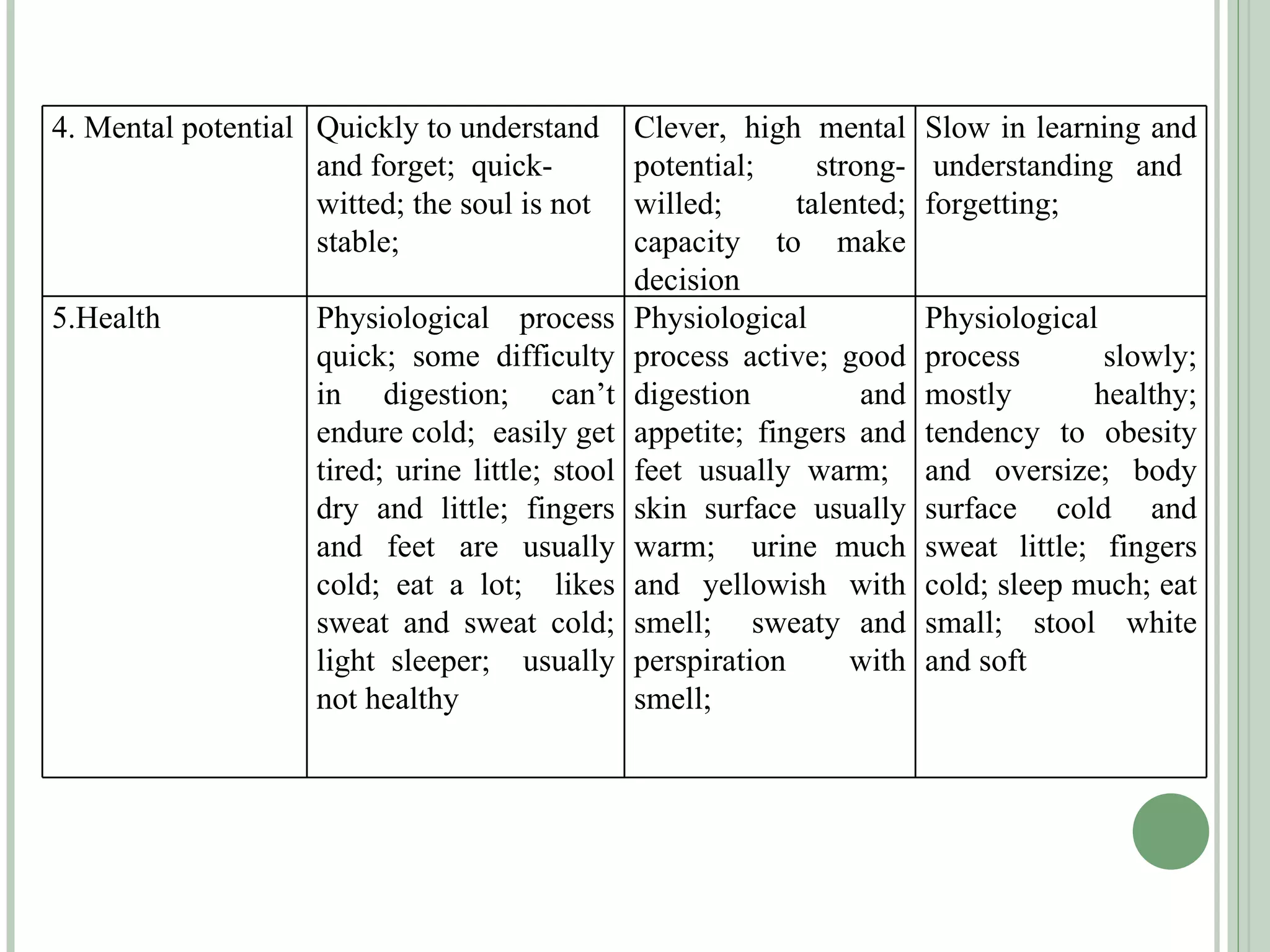
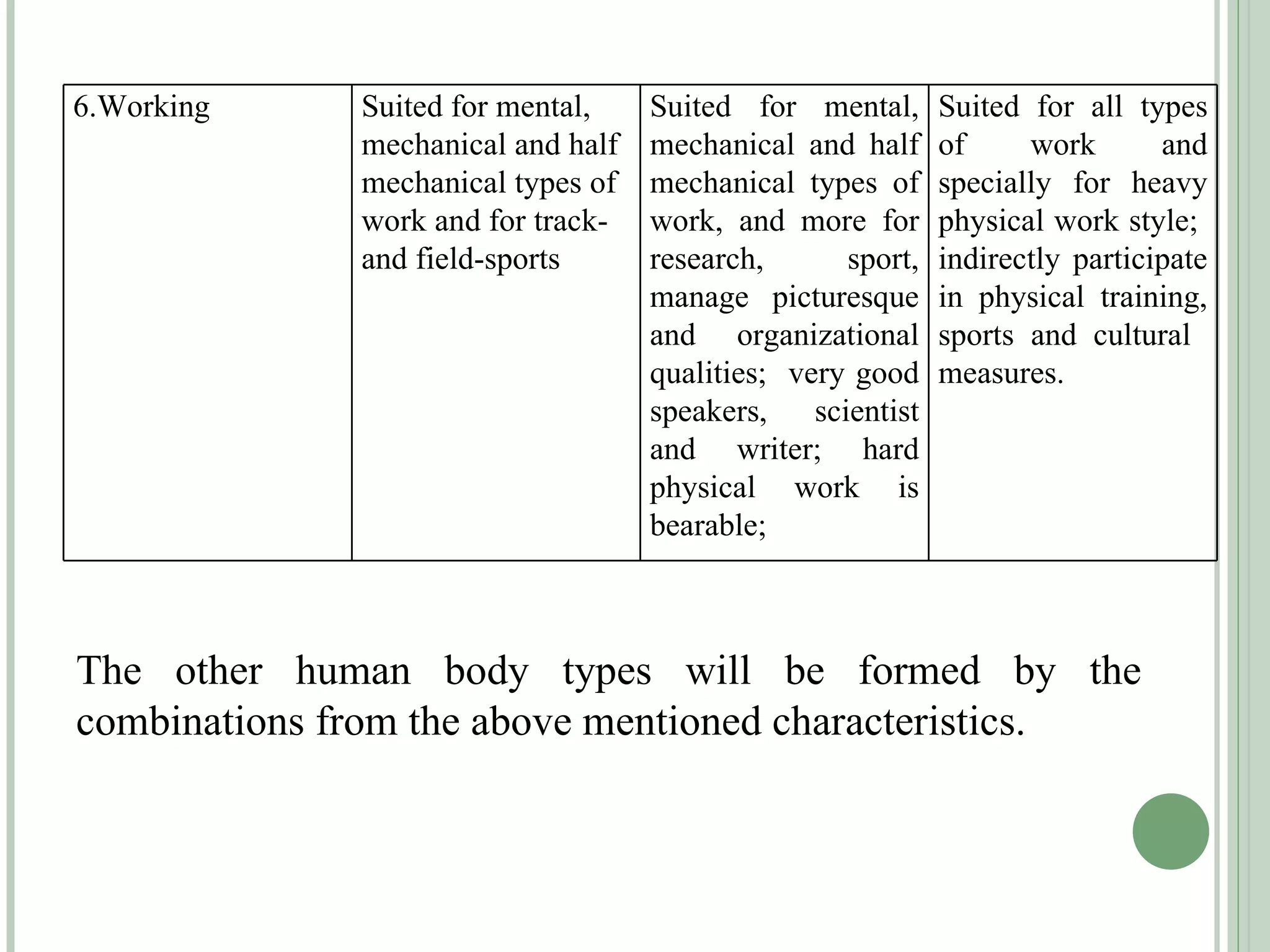
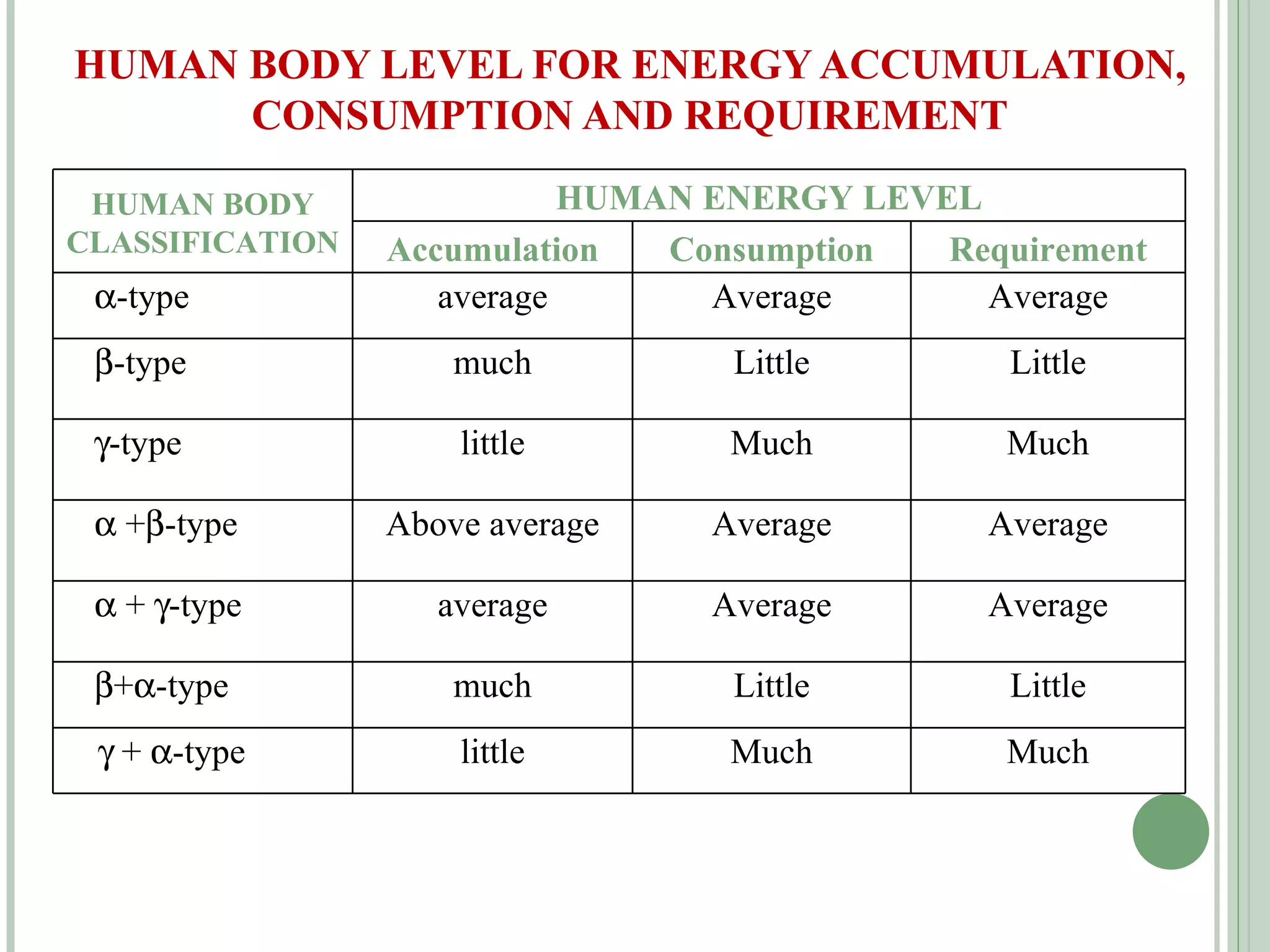
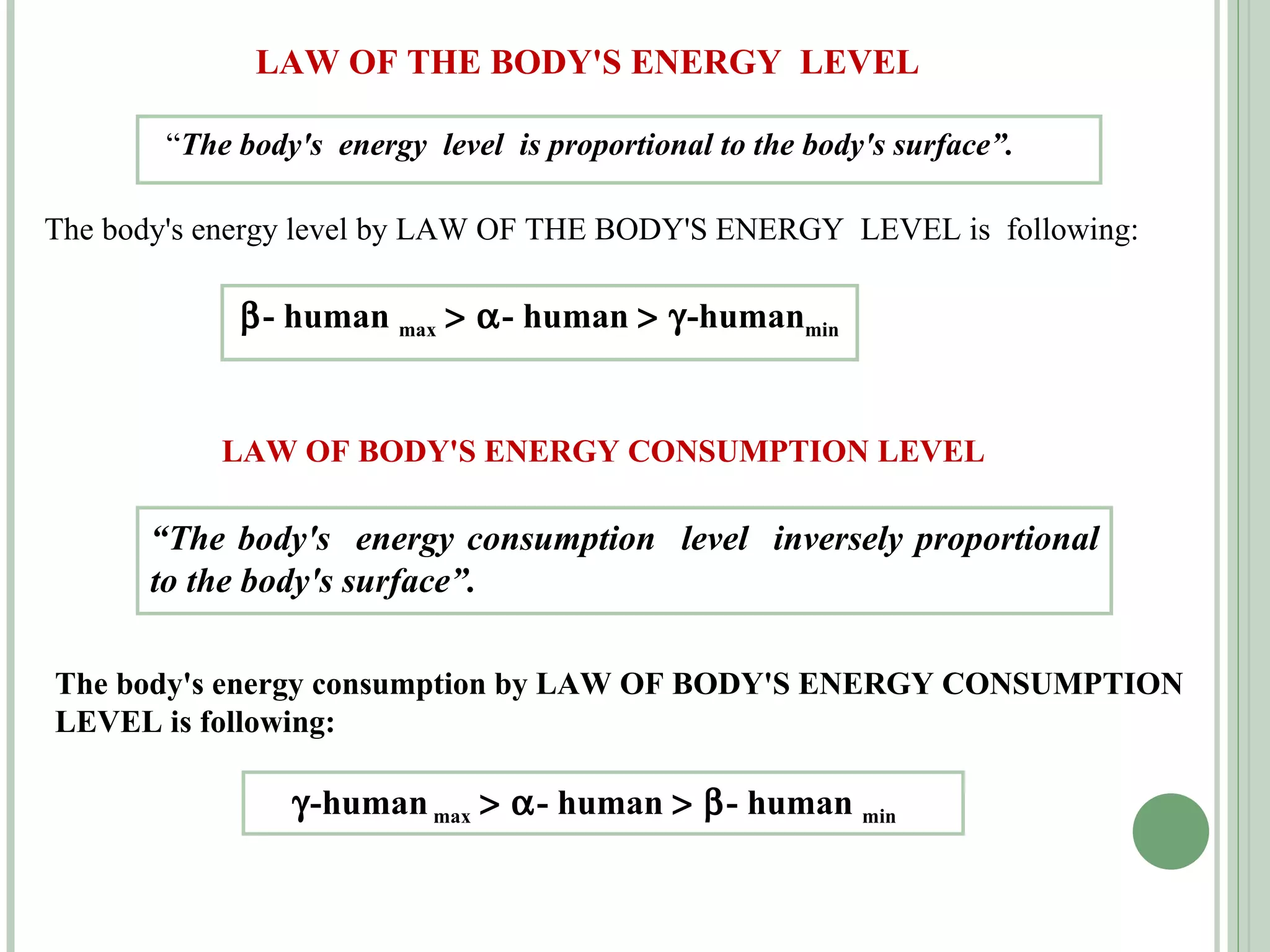
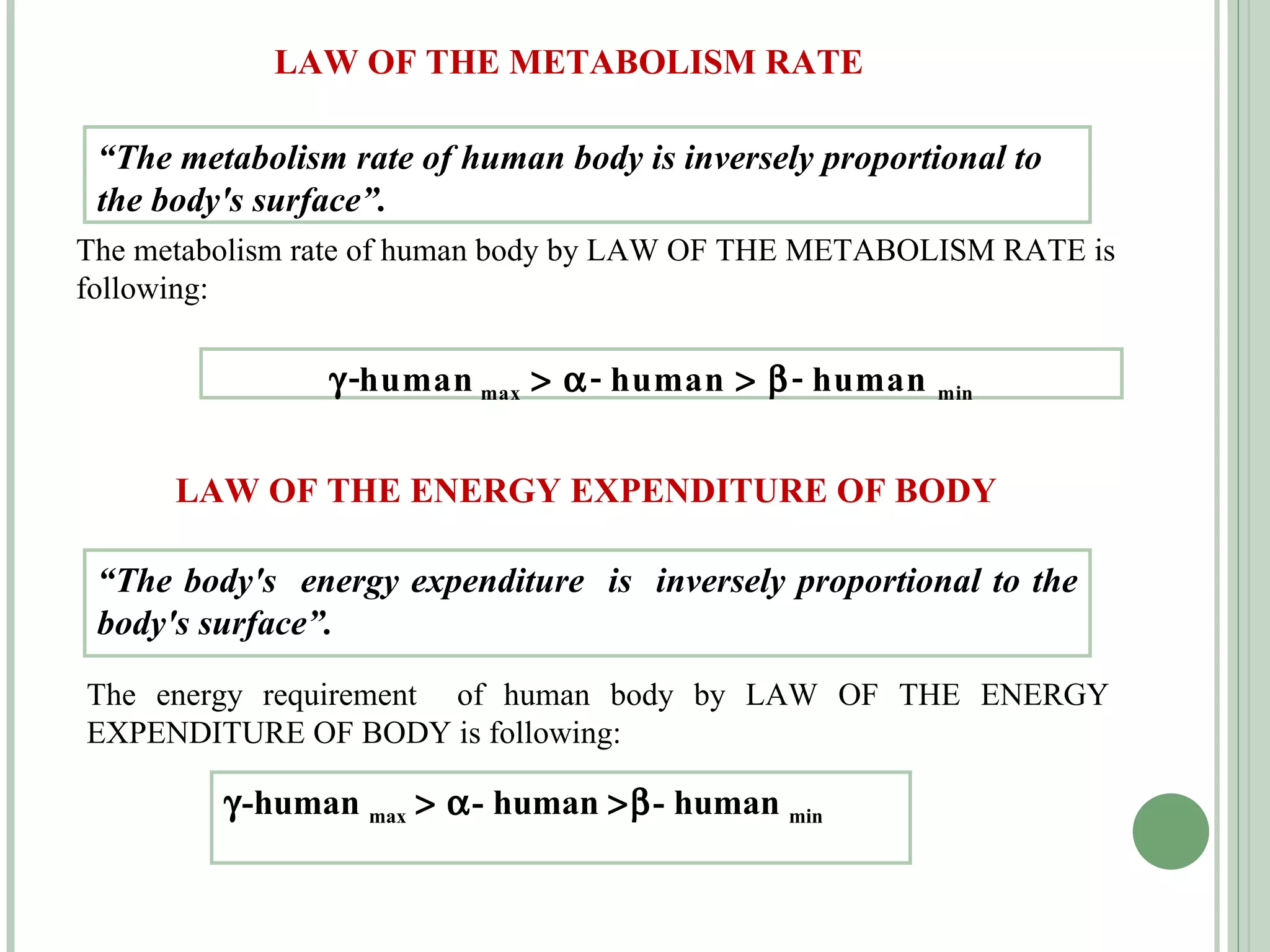
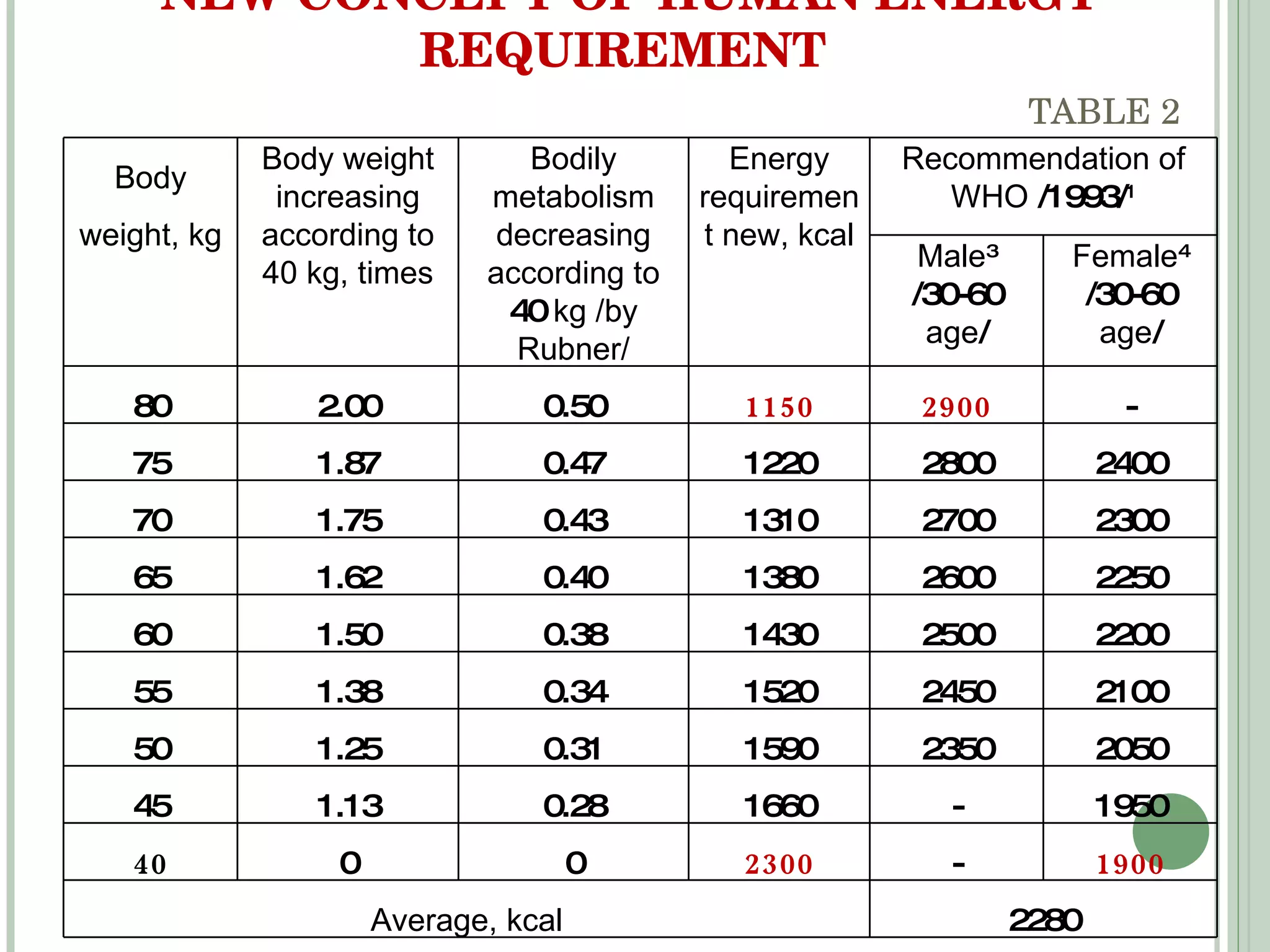
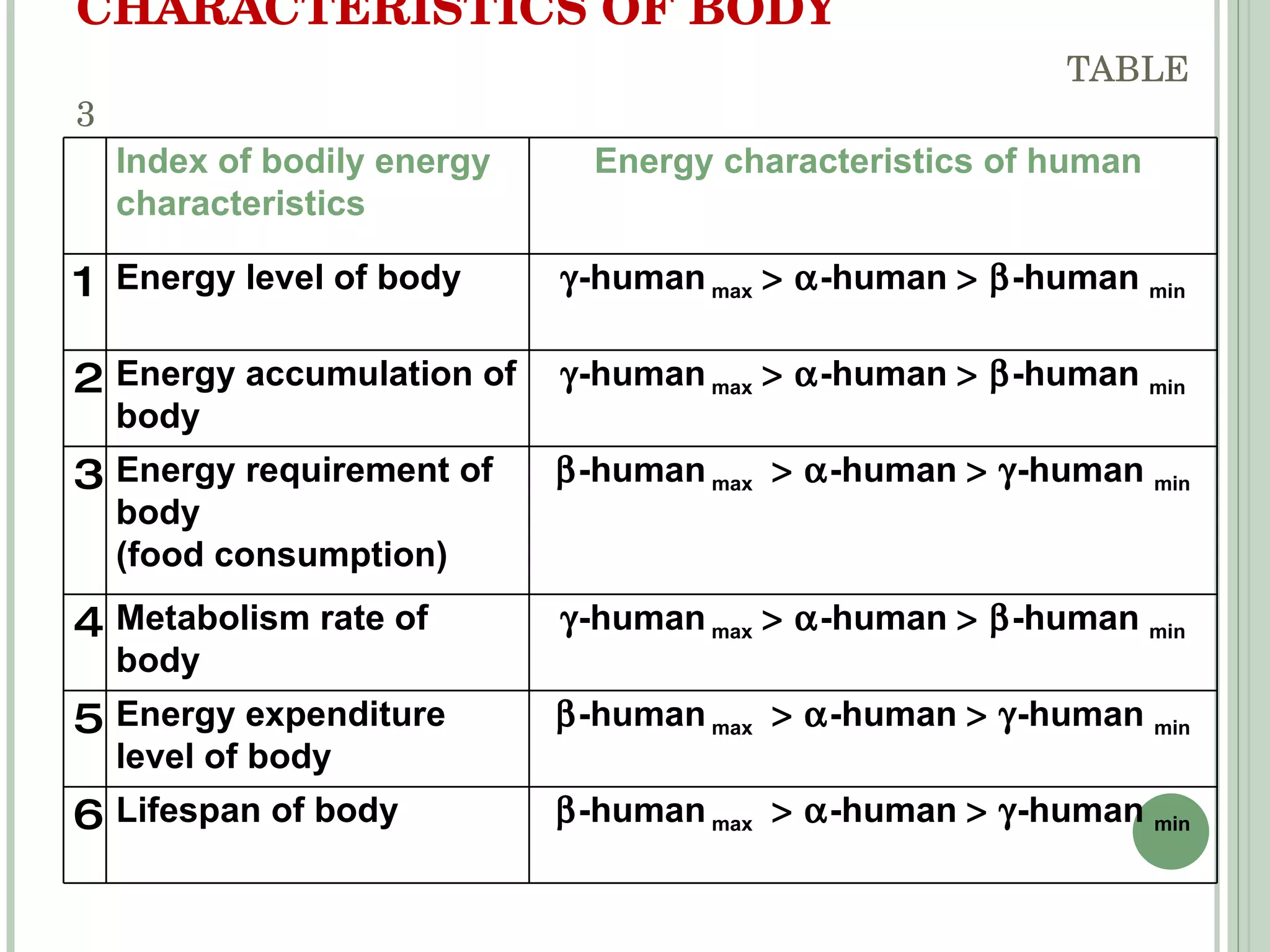
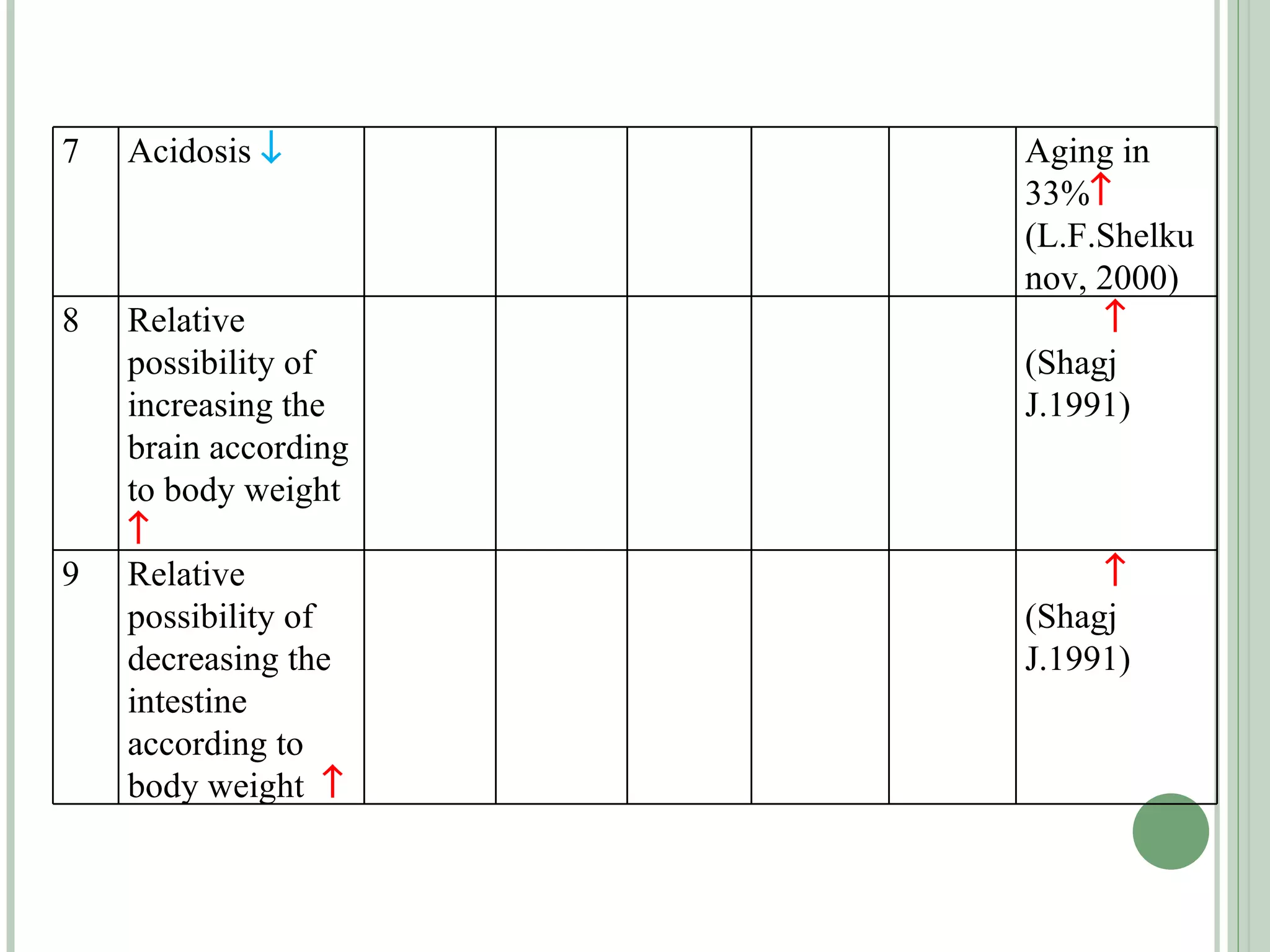
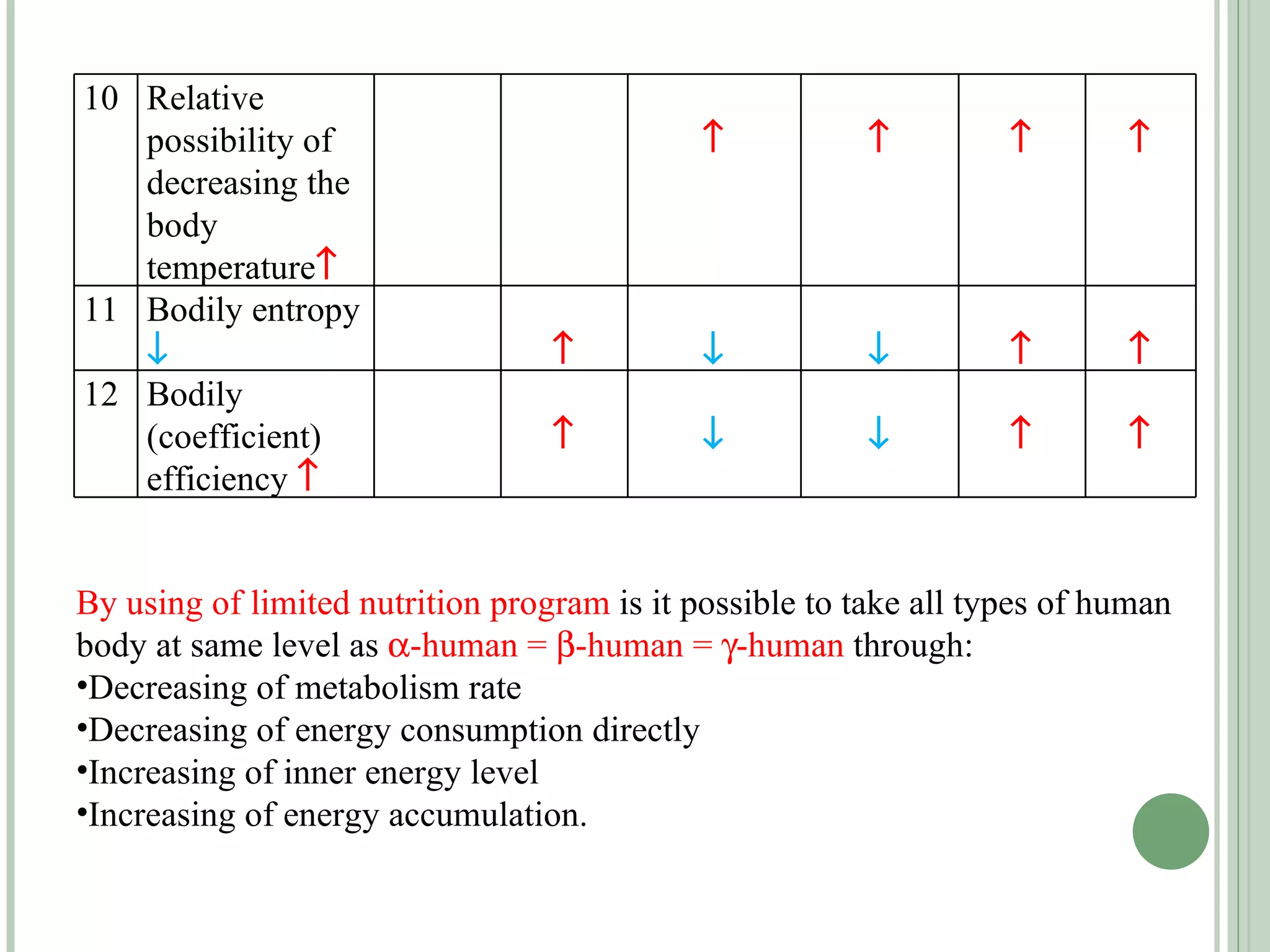
The document discusses new concepts in human development and nutrition based on the idea that humans consist of both an energy body and a physical body. It proposes that humans can be classified into alpha, beta, and gamma types based on their energy characteristics and levels. Various "laws" are presented regarding how these energy levels, metabolism rates, lifespans, and other factors differ depending on a human's classification. It suggests these energy characteristics can be balanced through limited nutrition programs.