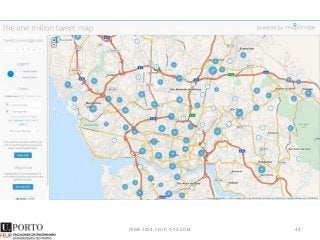
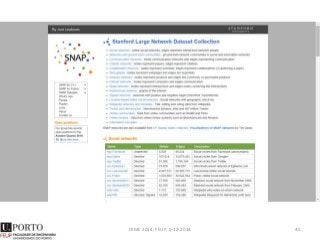
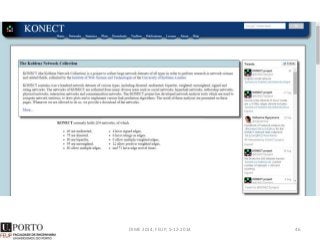
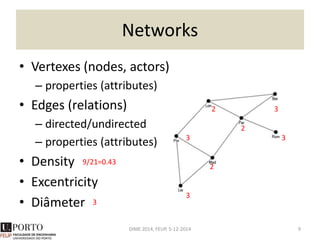
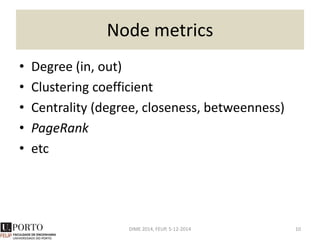
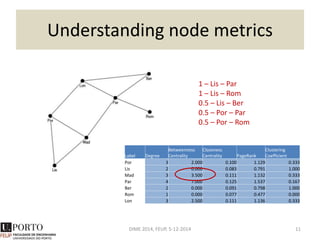
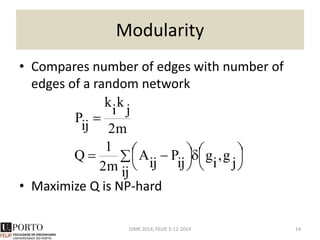
The document discusses network analysis and provides an overview of the topic. It covers that networks are found everywhere, from social and biological systems to financial networks. It also discusses complex networks, influential nodes, communities, and software tools for network analysis. A variety of network analysis methods and algorithms are presented, including approaches for identifying communities, central nodes, and other network properties. Examples of real-world networks and potential projects for network analysis are also mentioned.







![Chinese Whispers [Biemann]
• a
Randomized graph-clustering algorithm, which is time-linear in the
number of edges.
It can be viewed as a simulation of an agent-based social network.
DIME 2014, FEUP, 5-12-2014 20
Gephi plugin](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/networkanalysis-141202131214-conversion-gate02/85/Network-analysis-20-320.jpg)