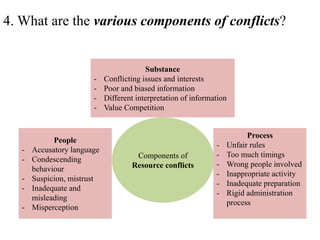
Resource conflicts arise from disputes over access to and control of natural resources due to incompatible interests, demographic changes, and poor governance. Key components include misunderstanding between parties, accusations, and inequity in resource distribution, with various actors such as local communities, NGOs, and government bodies involved. Effective conflict management strategies include negotiation, mediation, and use of legal systems, while examples of such conflicts can be seen in water resources, land issues, and illegal forestry activities.