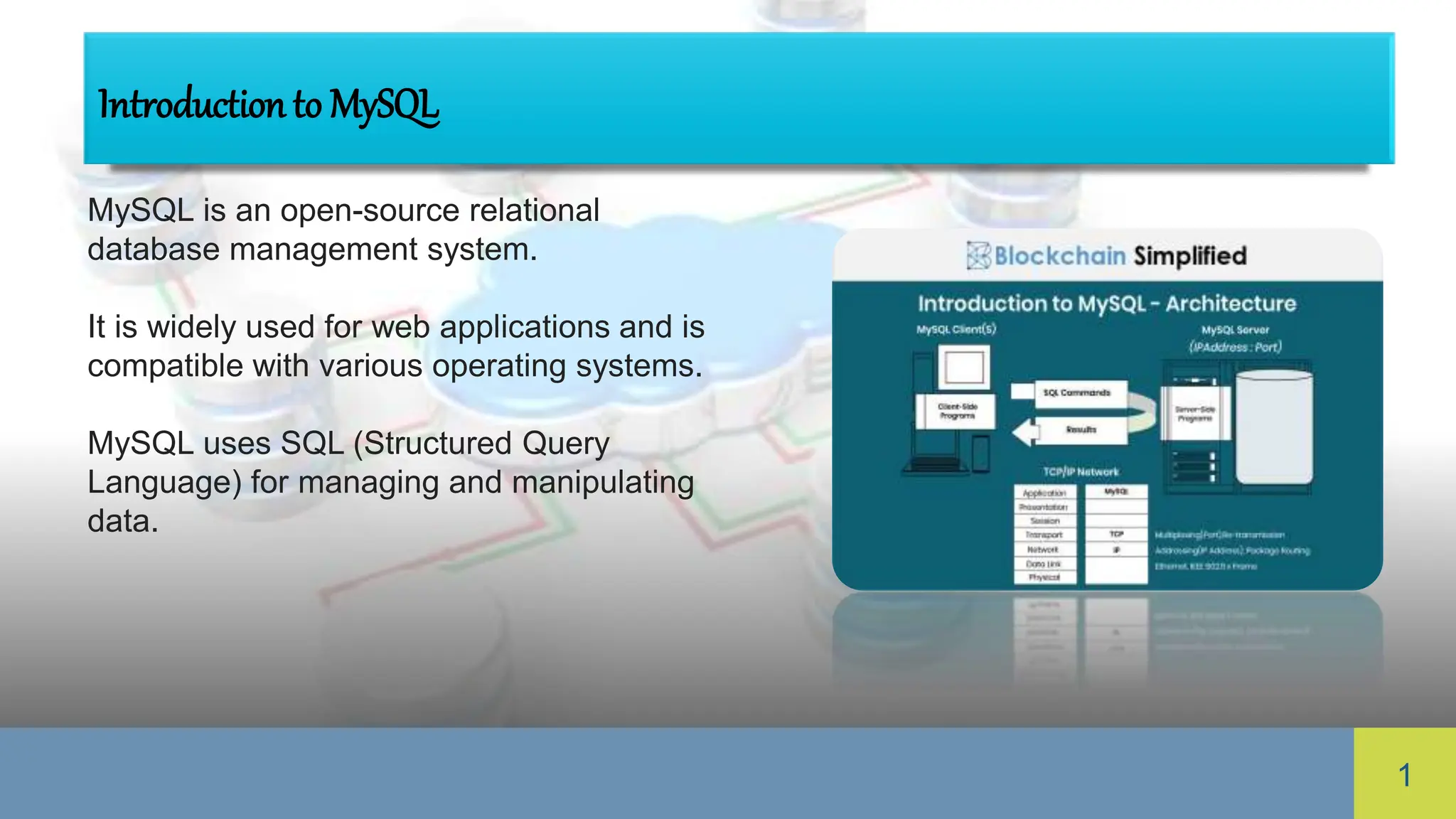
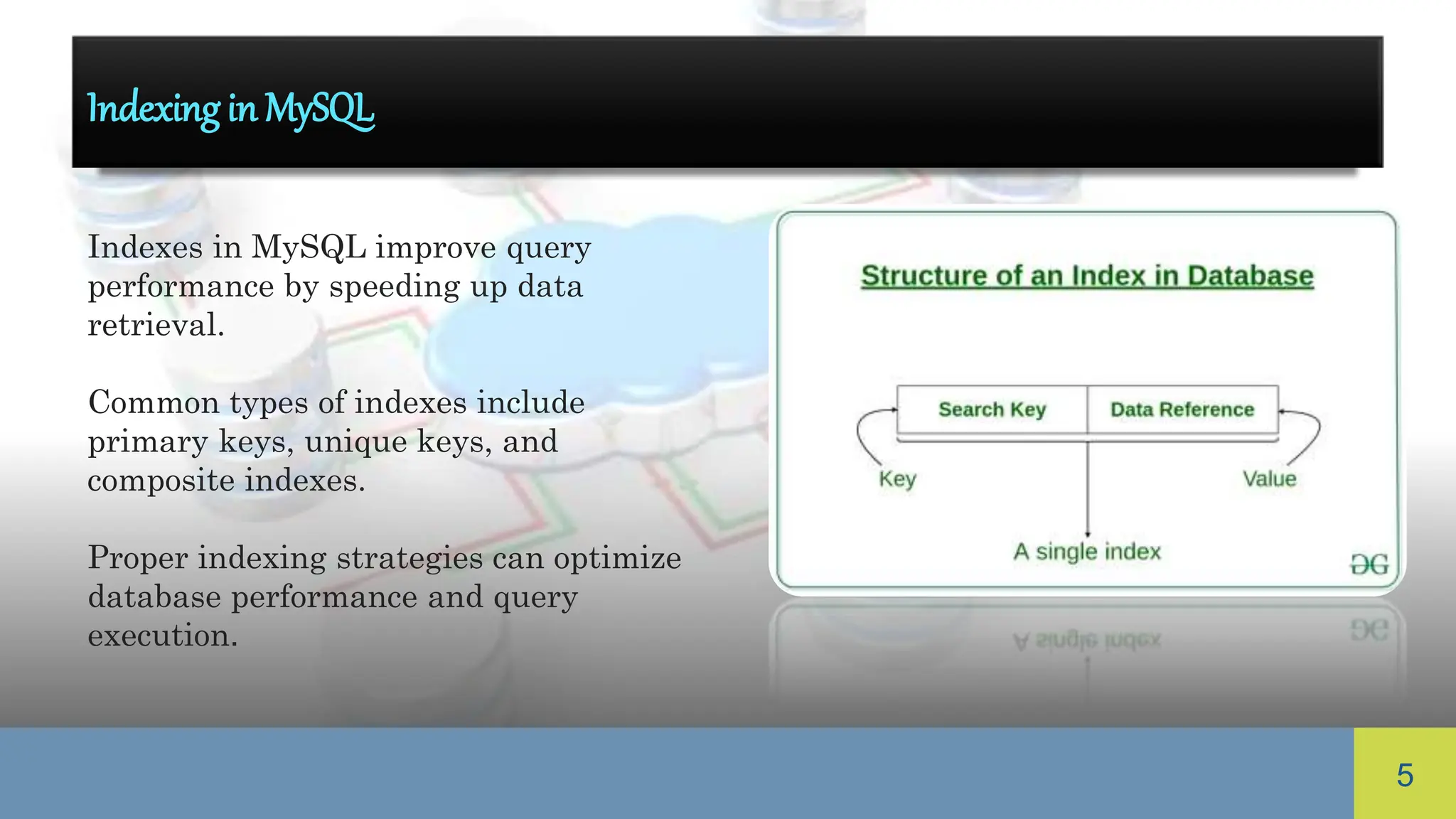
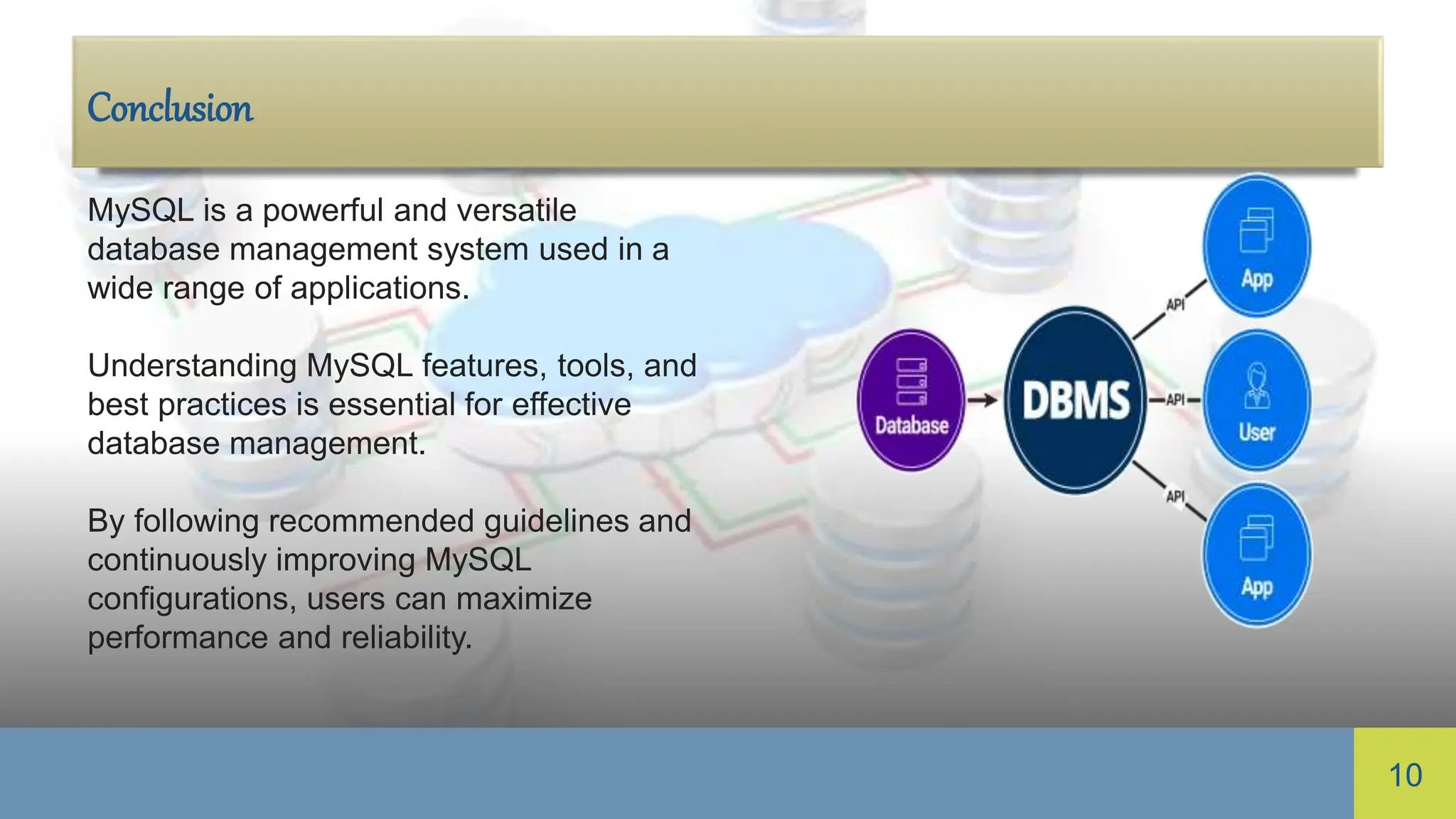
MySQL is an open-source relational database management system widely used for web applications, featuring multiple storage engines and strong data security. It includes MySQL Workbench for database administration and emphasizes data types, indexing, security best practices, replication, and performance tuning. Understanding these elements is crucial for effective management and optimizing MySQL's performance and reliability.