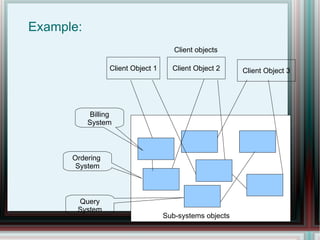
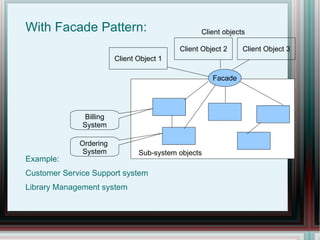
The document discusses various structural design patterns, including adapter, decorator, bridge, and facade patterns, which help in understanding class and object relationships. Each pattern is defined along with its purpose, use cases, and examples, emphasizing their roles in simplifying system complexity and enhancing reusability. The document also provides guidance on when to choose each pattern based on specific design needs.