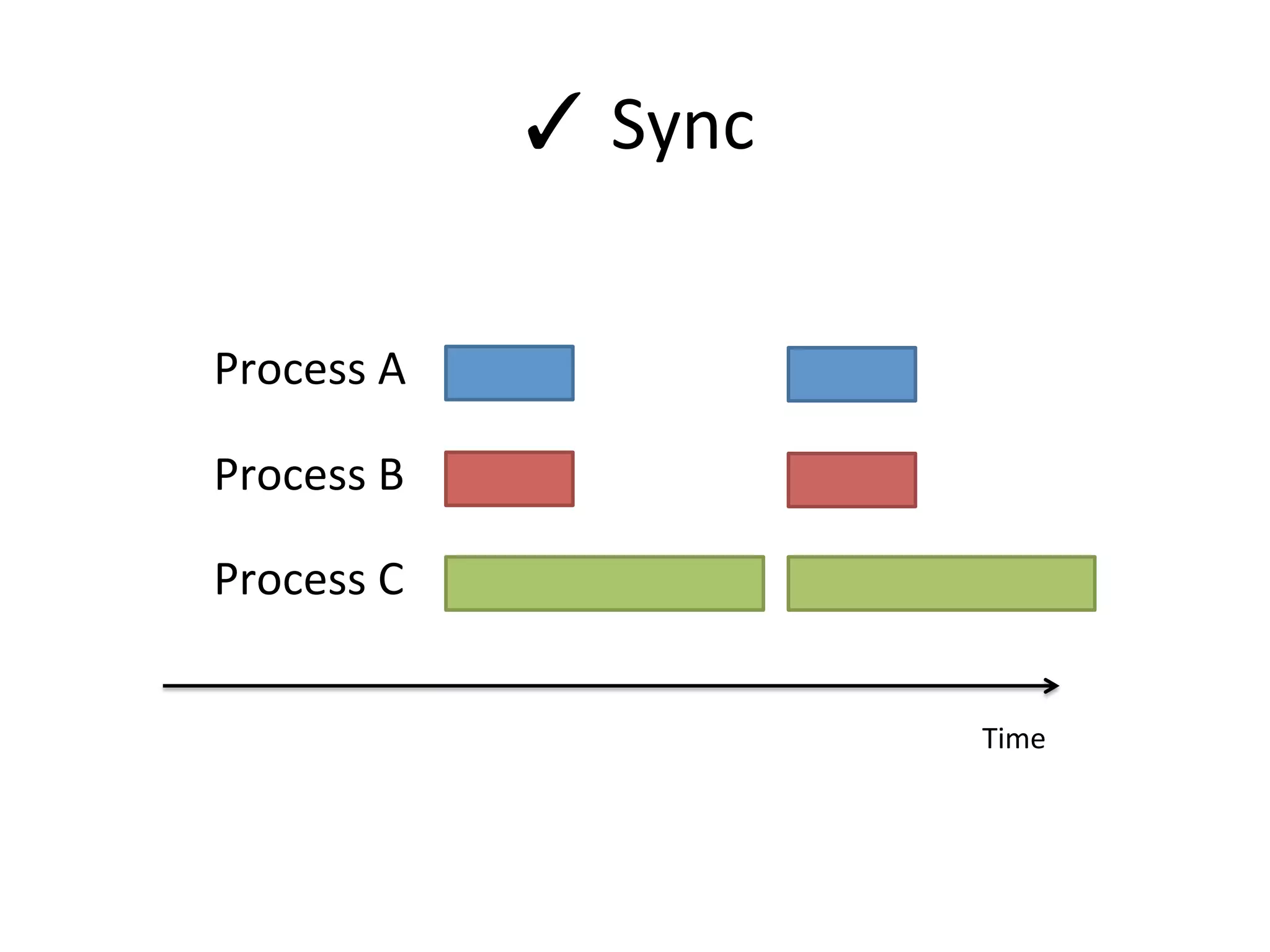
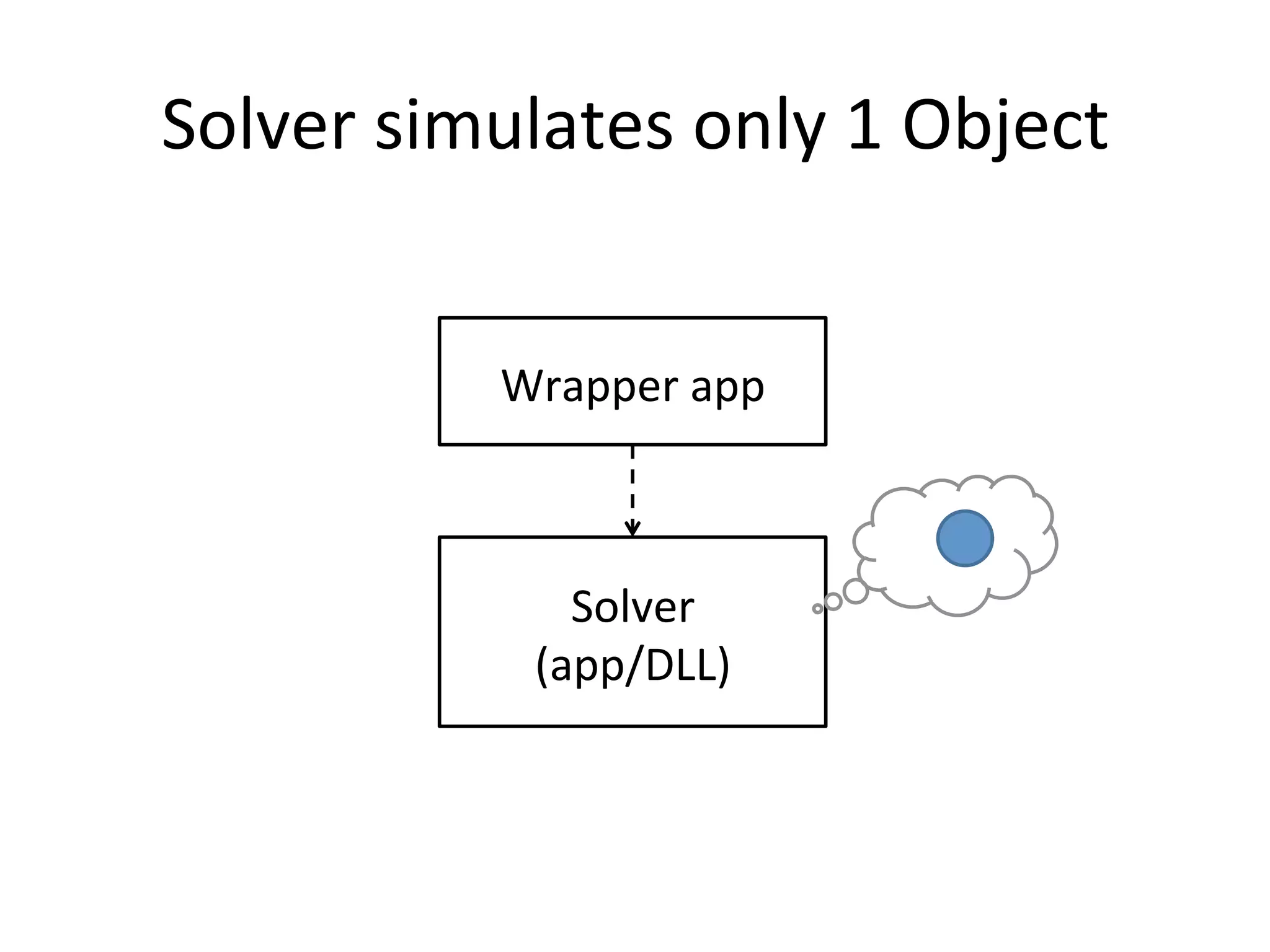
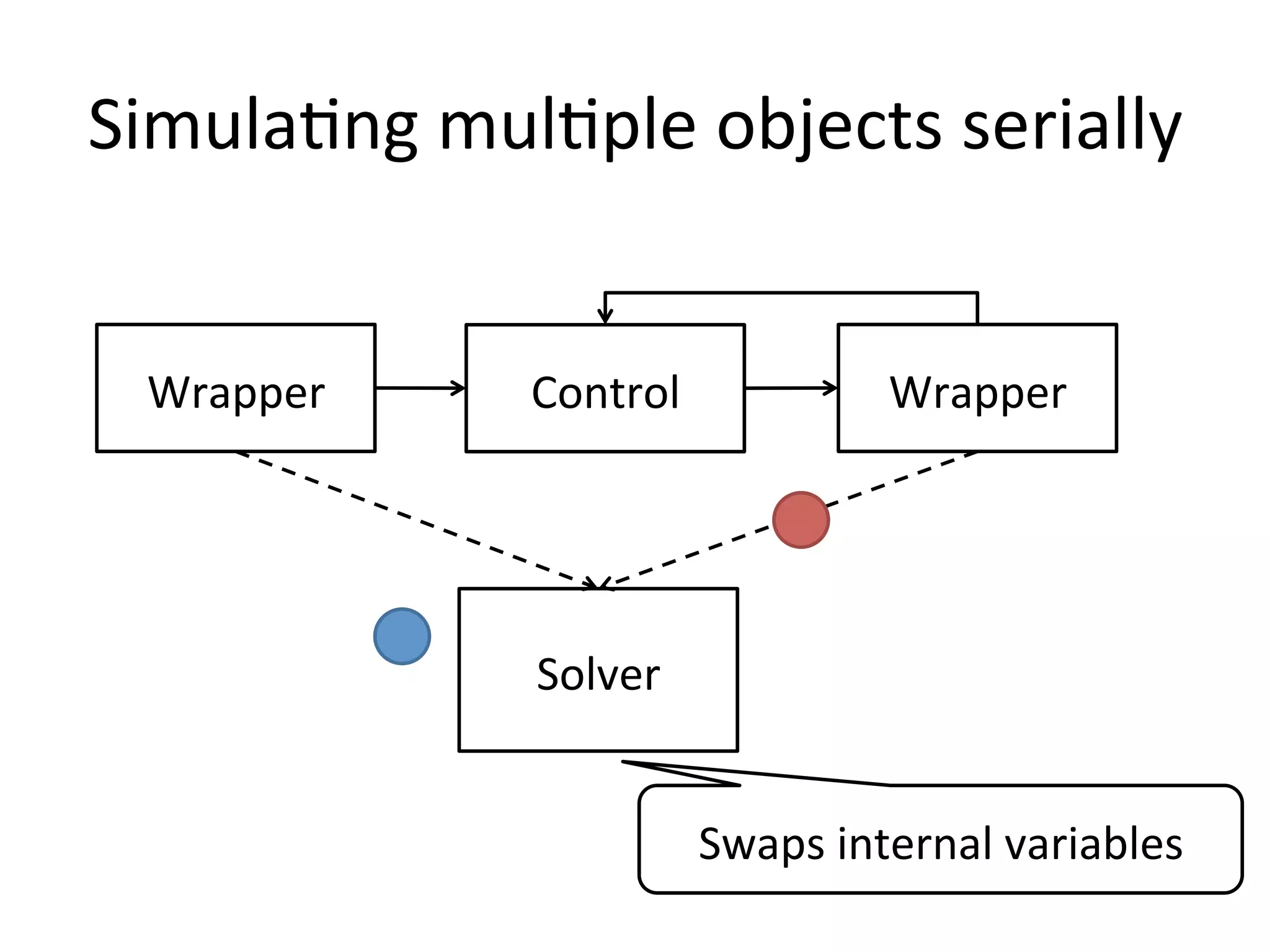
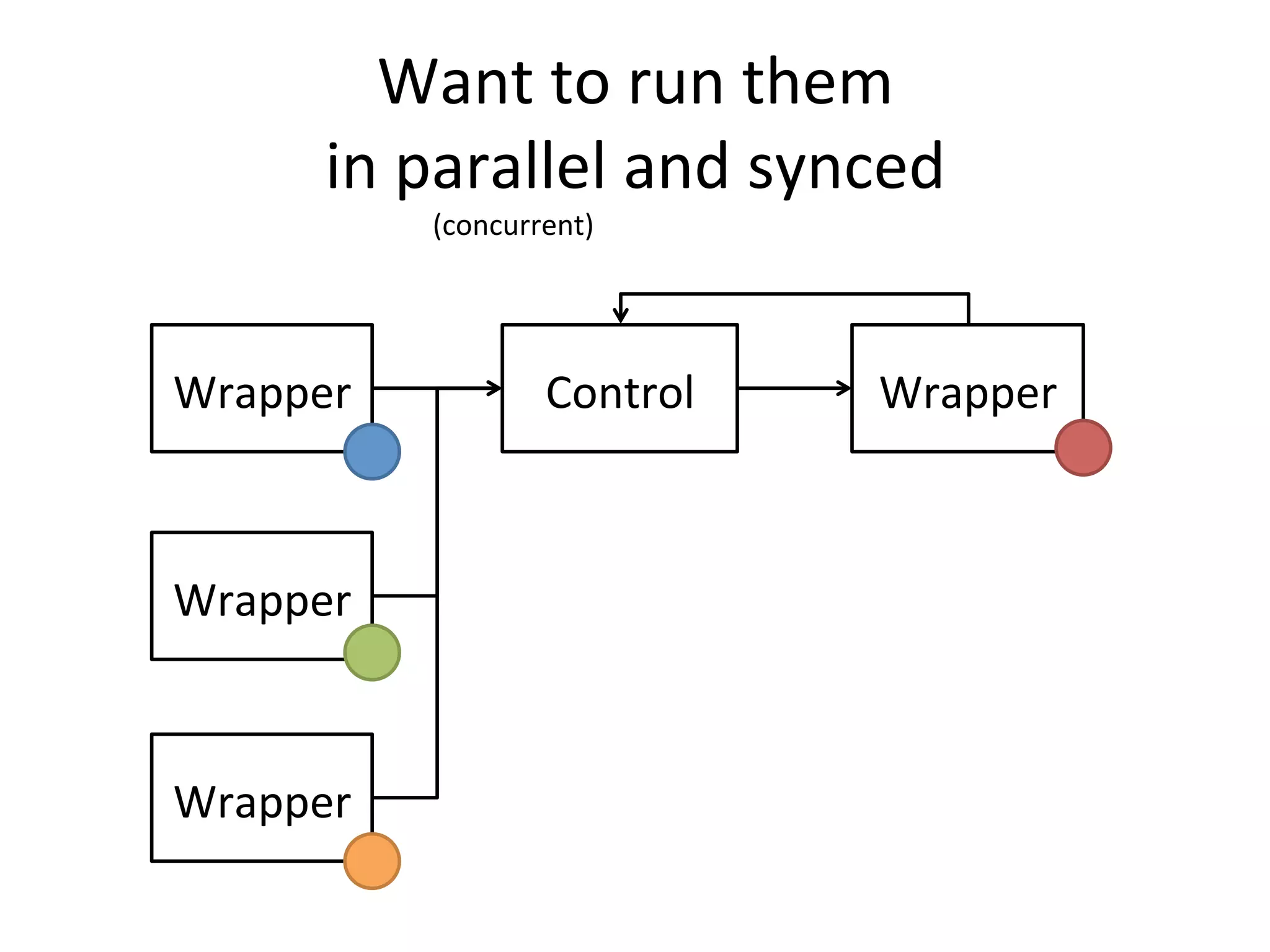
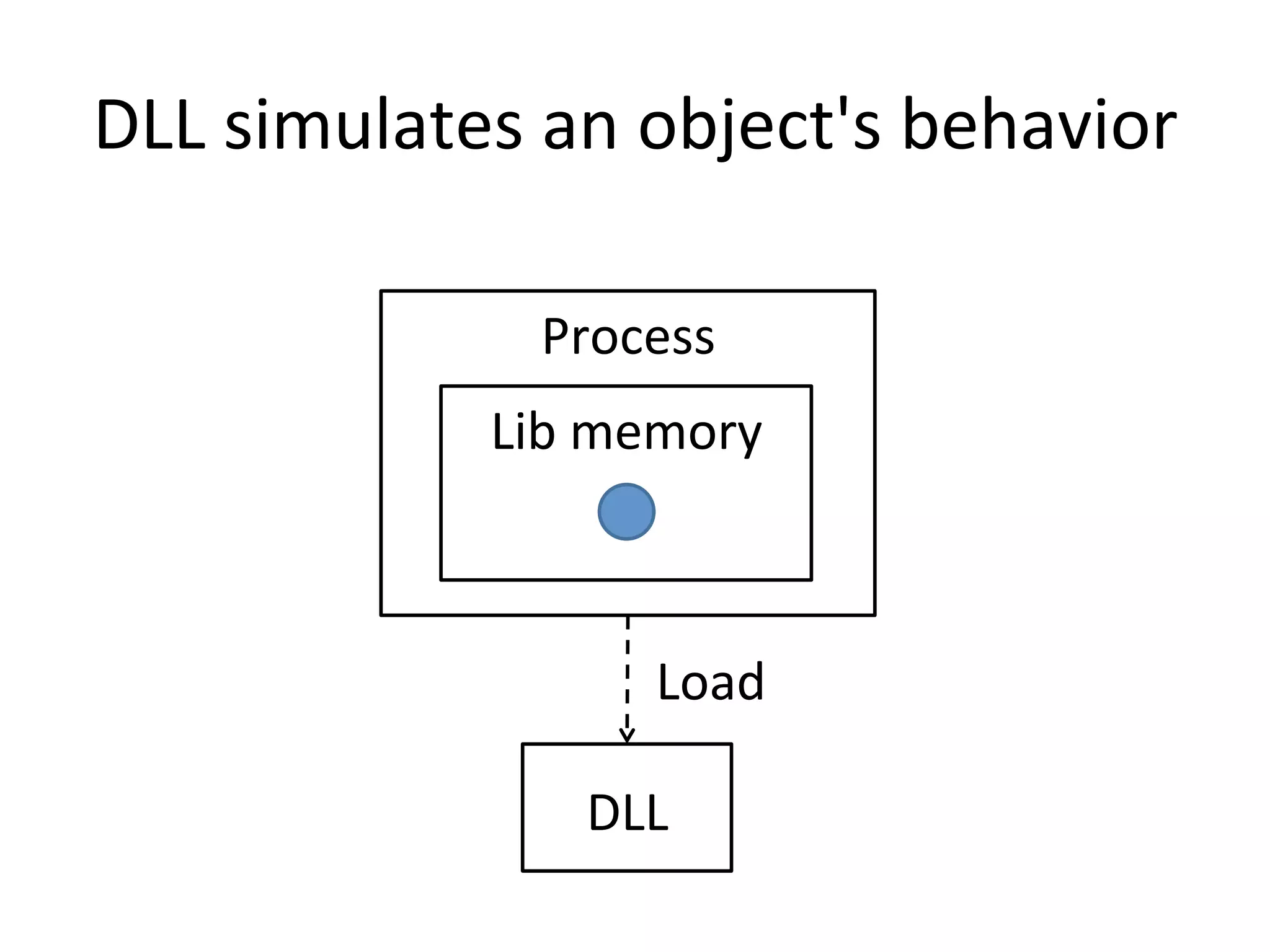
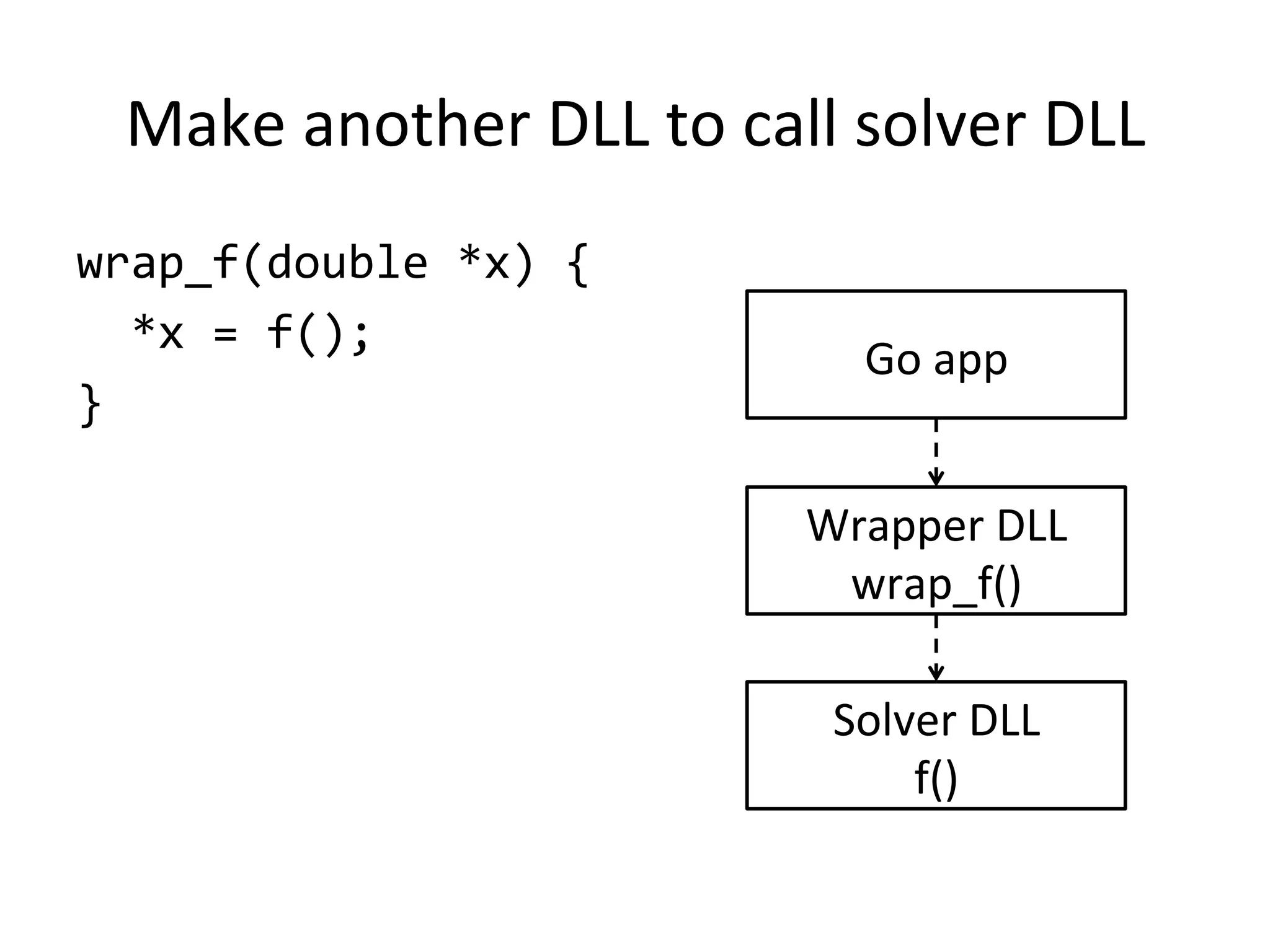
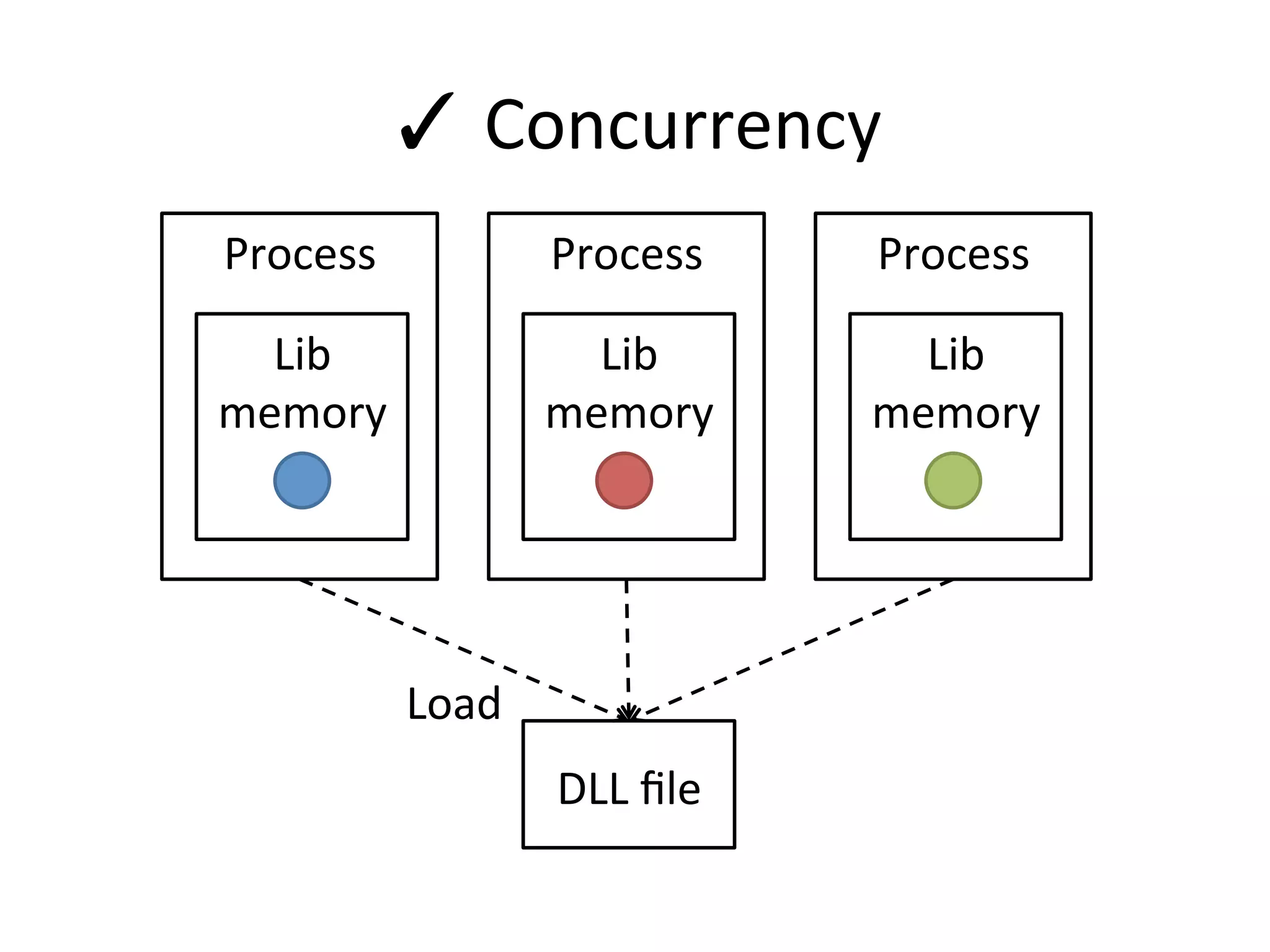
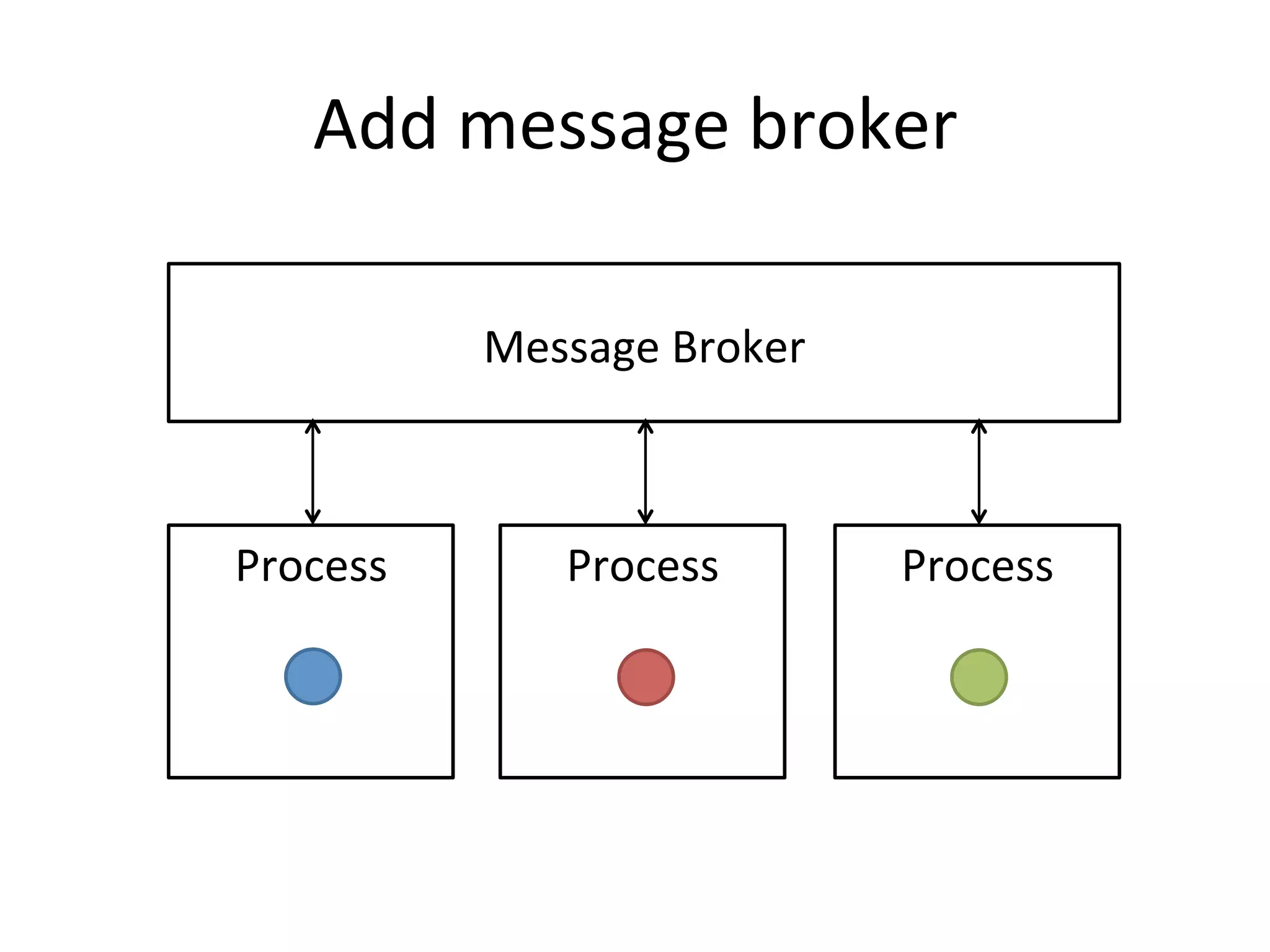
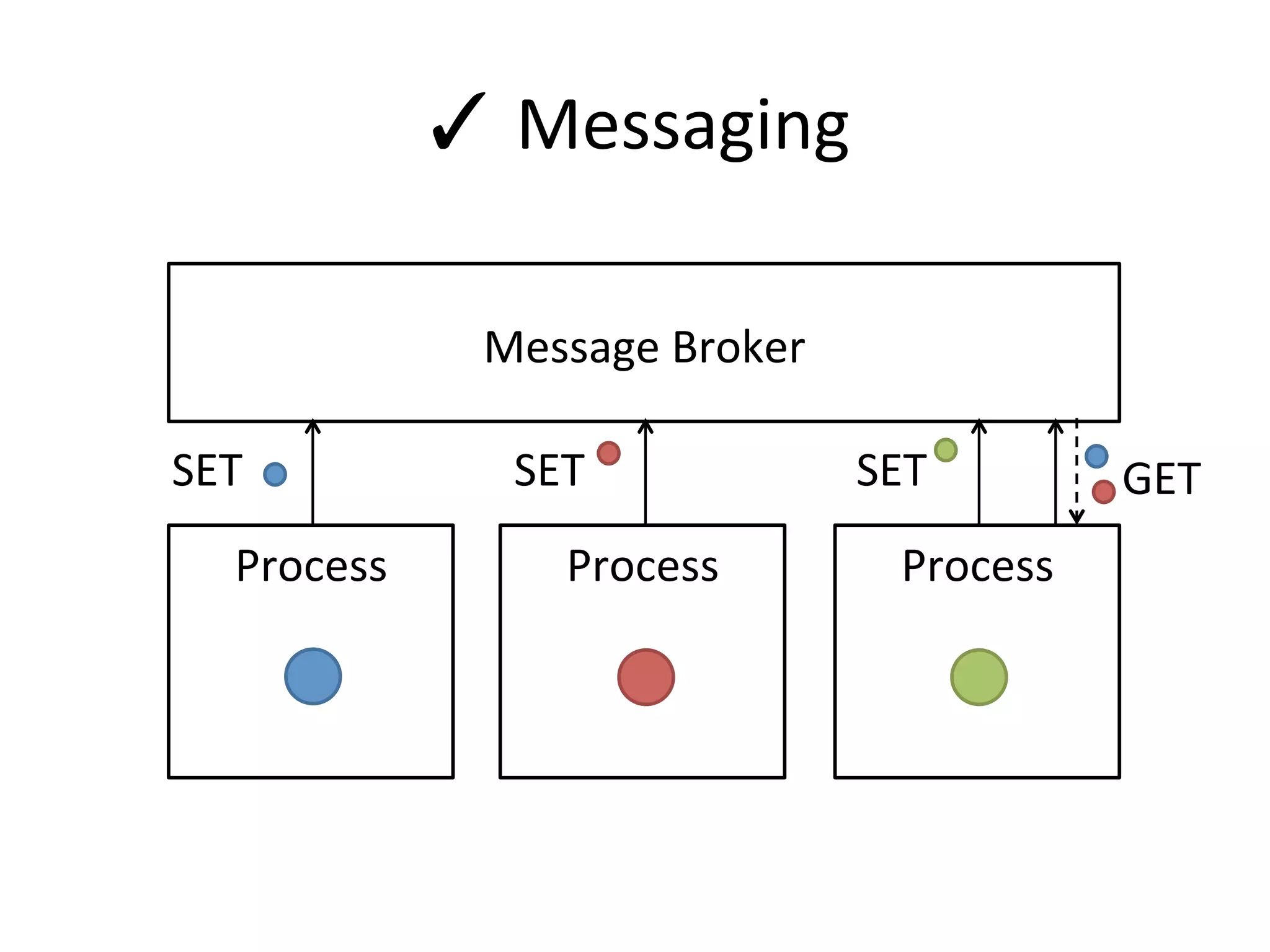
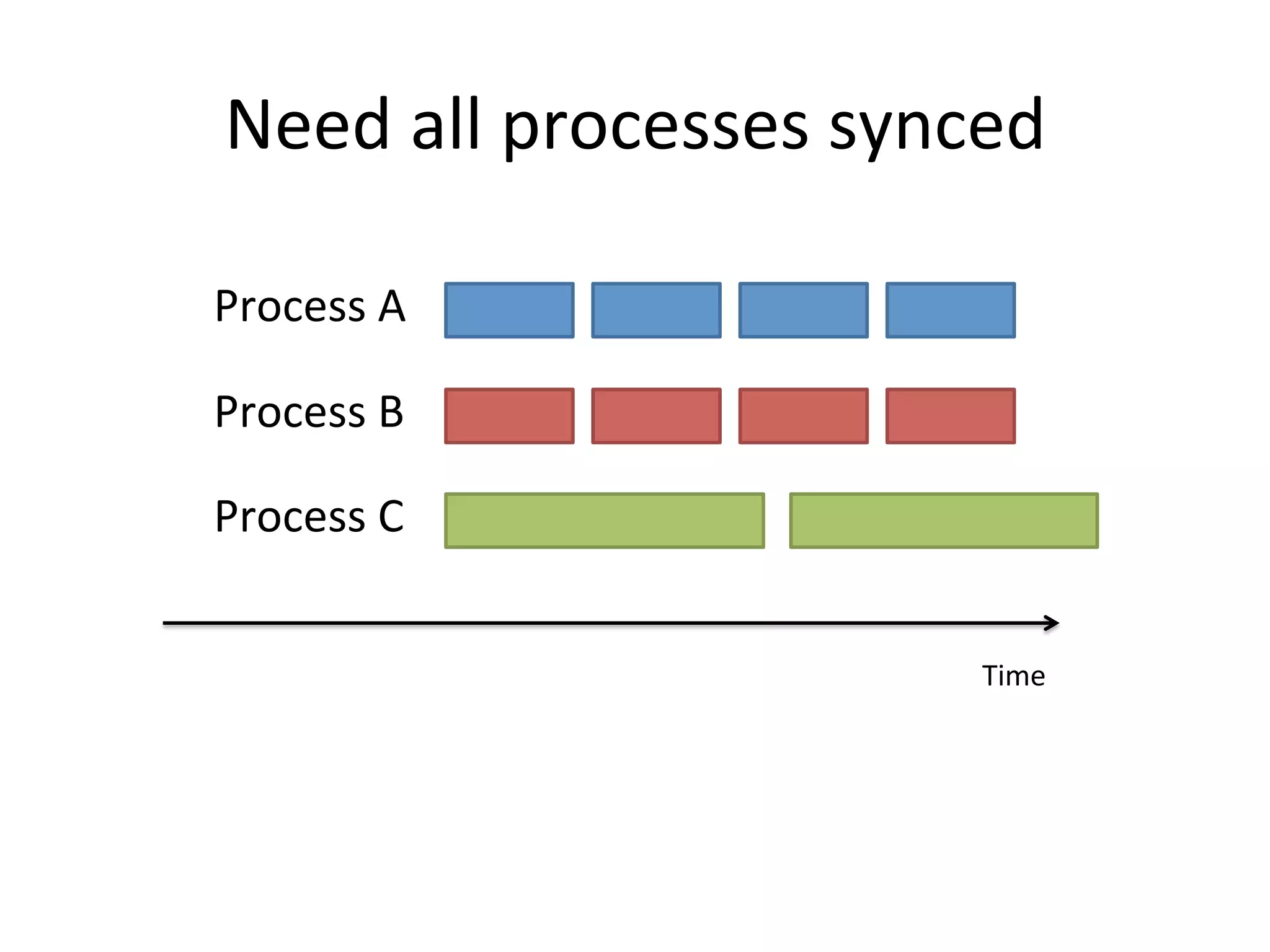
The document discusses using Go to run simulation apps in parallel while keeping them synchronized. It describes using shared memory and message passing between processes to delegate simulation work to DLLs and coordinate their execution. Key points include spawning goroutines to handle requests concurrently, suspending tasks if not ready, and flushing suspended tasks when conditions are ready to proceed in parallel while staying synchronized. The goal is to leverage Go's concurrency features to efficiently run multiple simulation objects in parallel instead of serially while maintaining sync between processes.










![Flush tasks when ready
func main() {
...
if readyToFlush(...) {
for _, t := range tasks {
t()
}
tasks := make([]task, 0)
}
...
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/syncapp-170325020650/75/My-client-wanted-their-apps-synced-and-I-made-it-with-Go-21-2048.jpg)