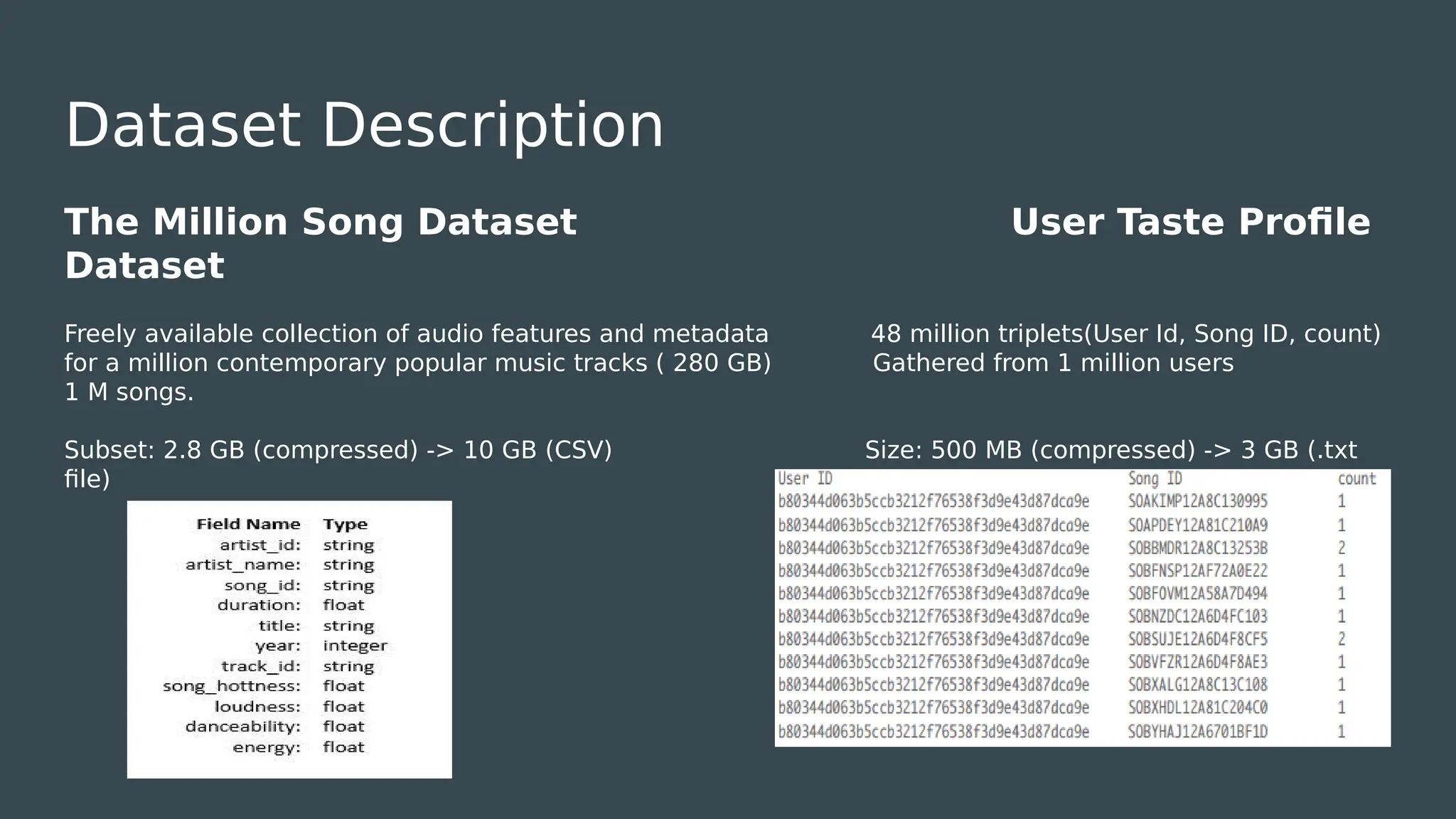
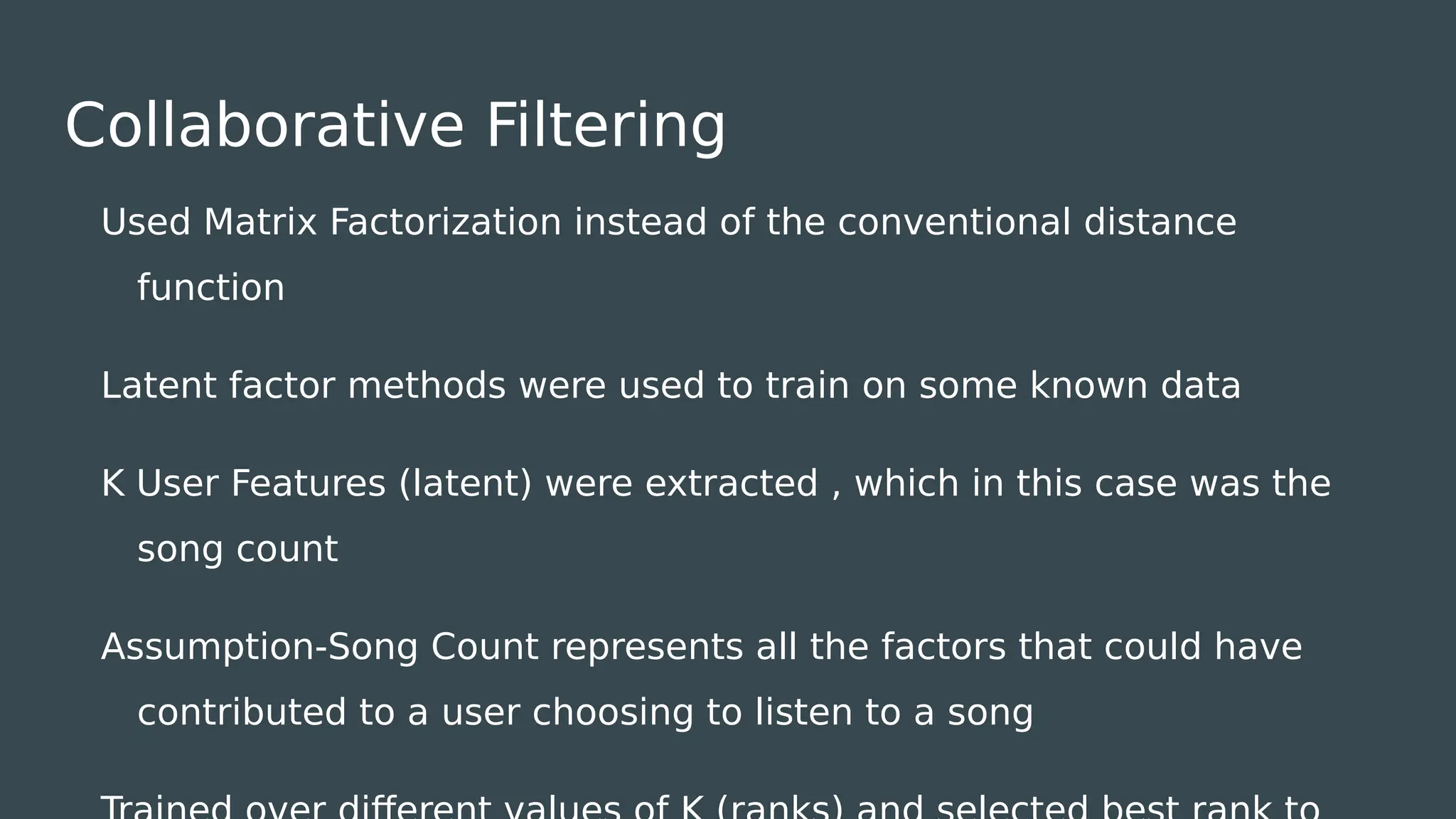
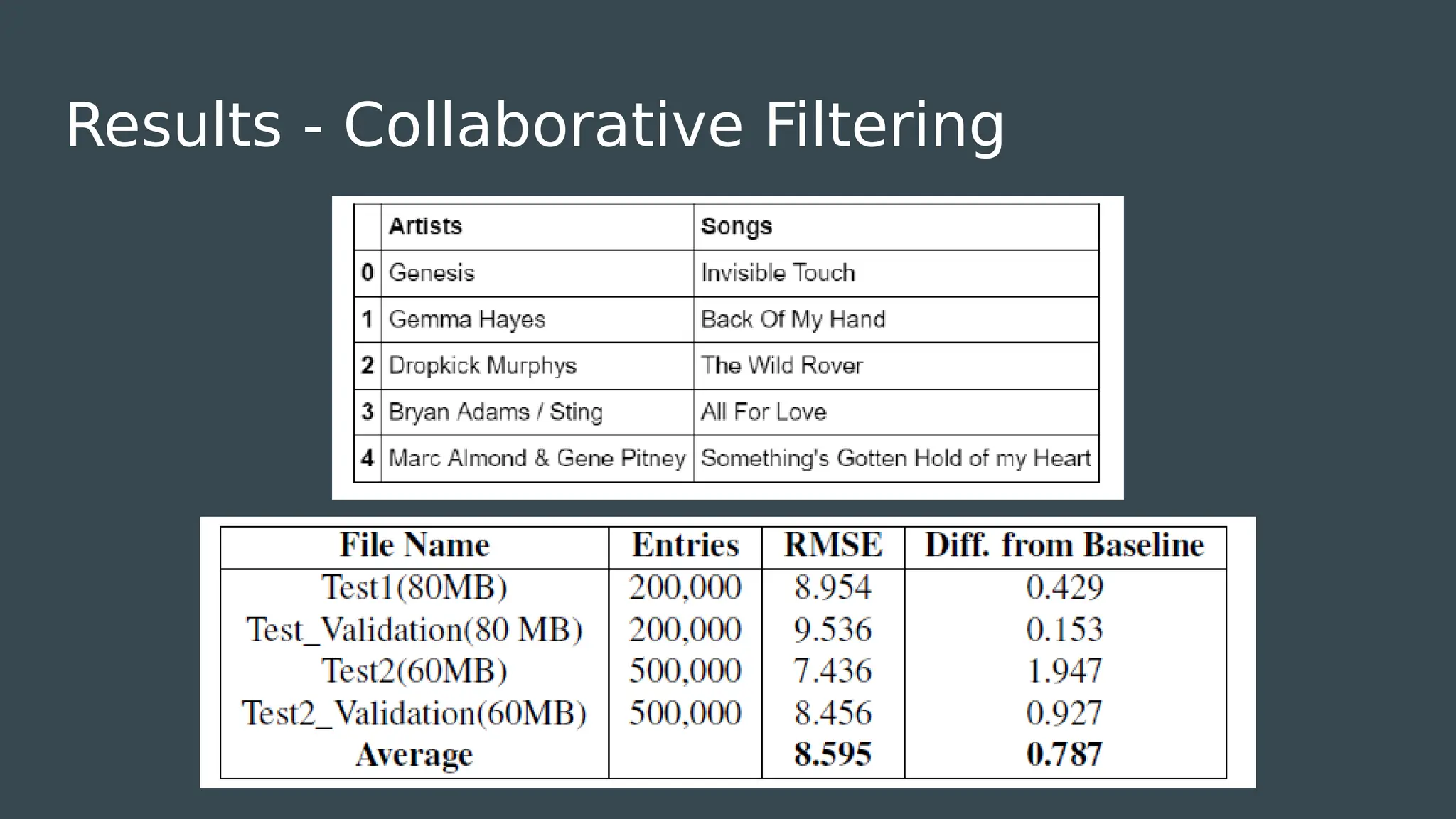
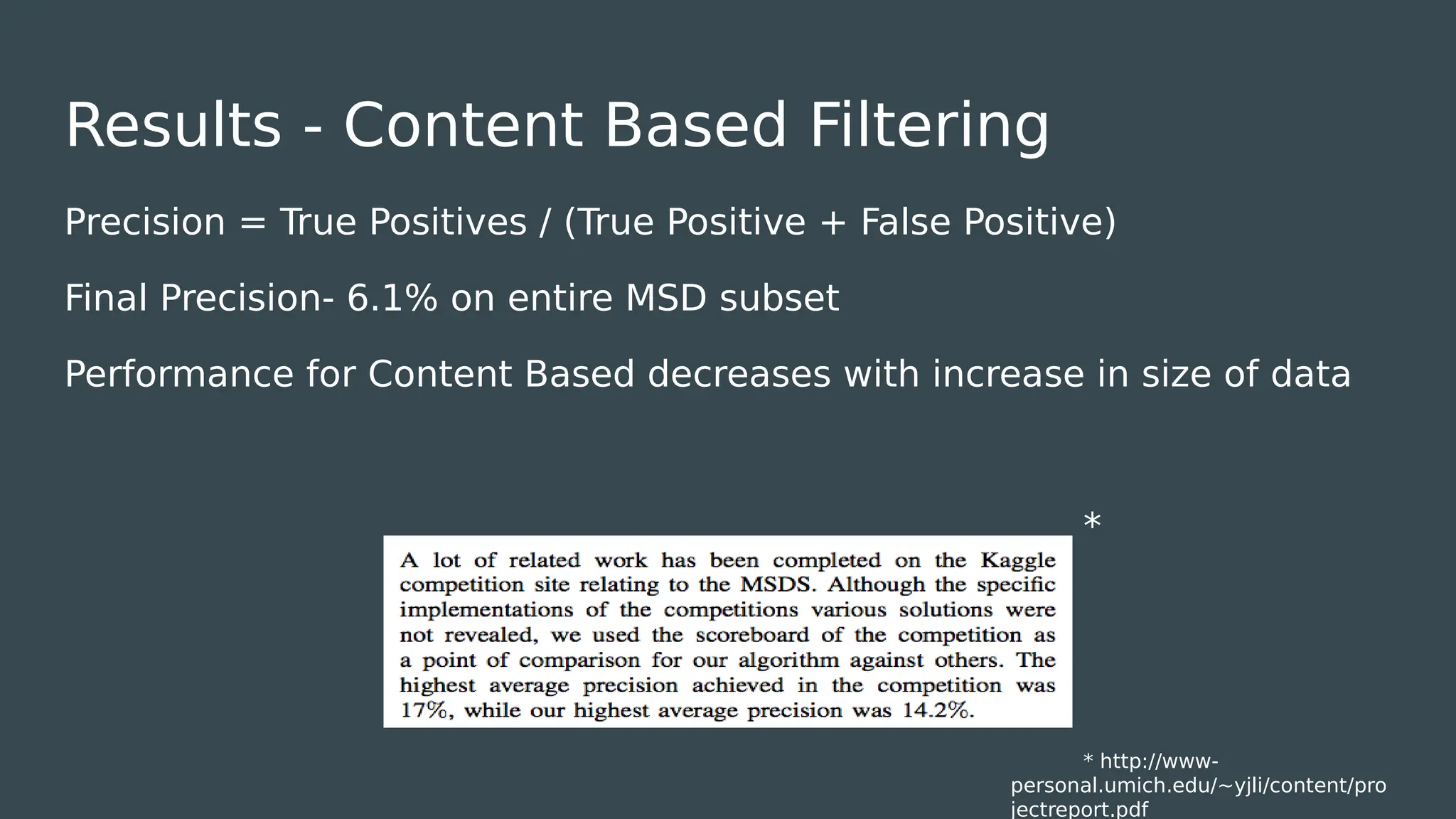
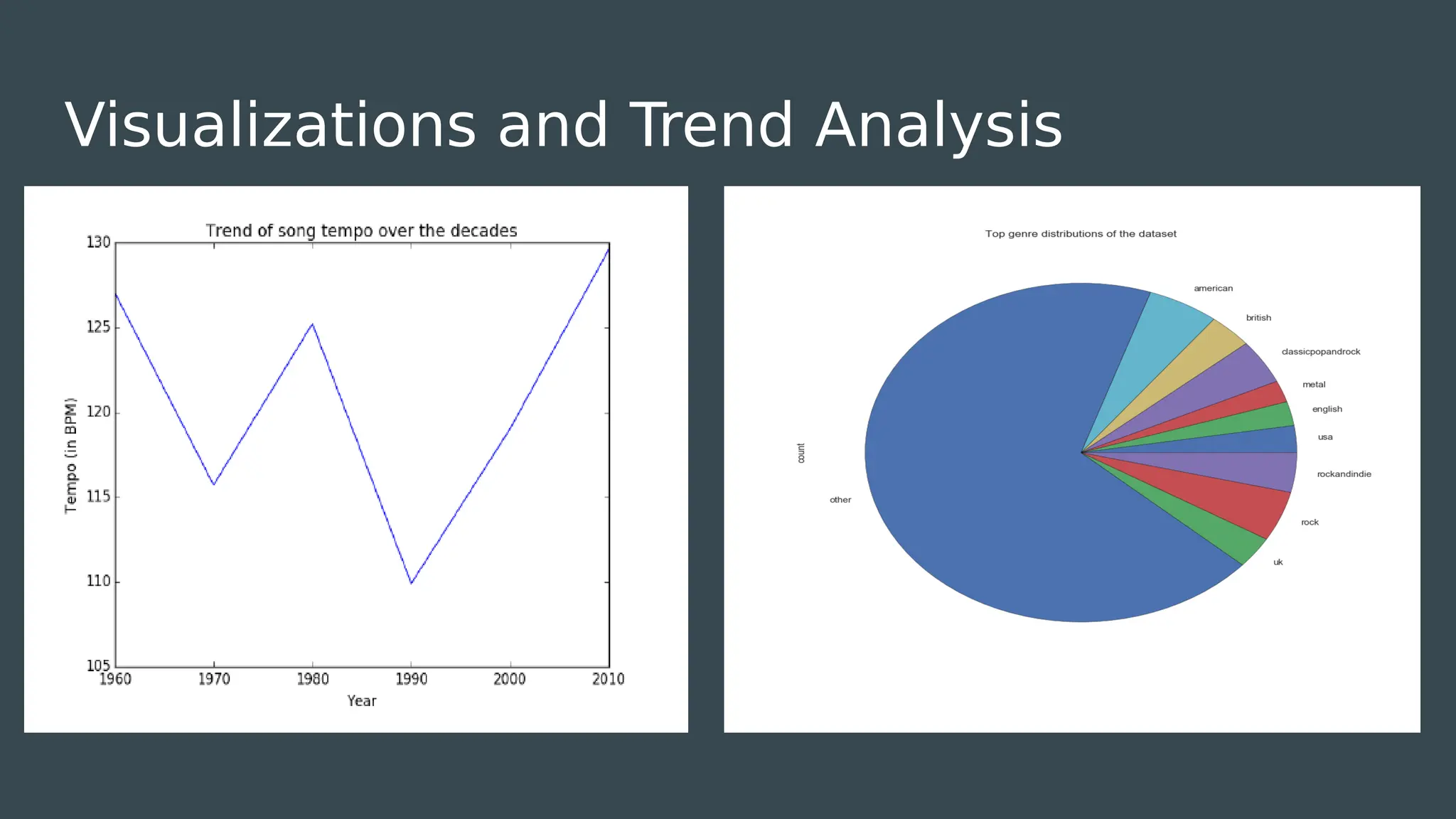
The document discusses the development of a music recommendation system using the Million Song Dataset, addressing the growing demand for music streaming services. It details methodologies including collaborative filtering and content-based recommendation, highlighting challenges, data cleaning processes, and evaluation metrics, with a reported precision of 6.1%. The project involved team collaboration to analyze data trends and visualize results, ultimately gaining insights into the complexities of big data in music recommendations.