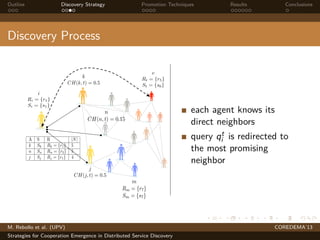
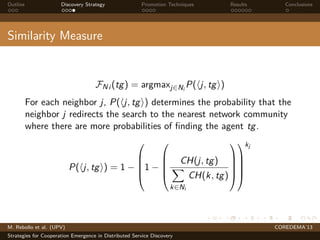
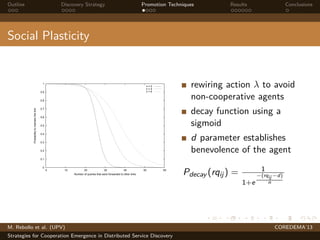
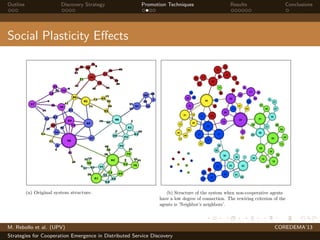
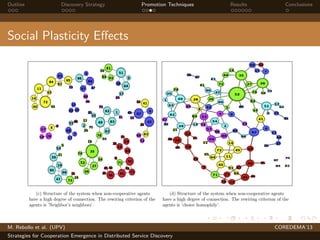
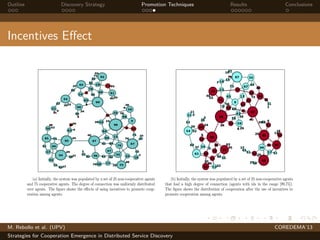
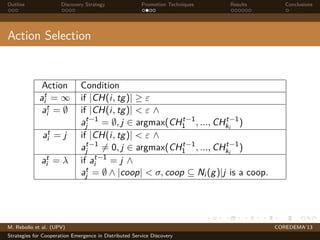
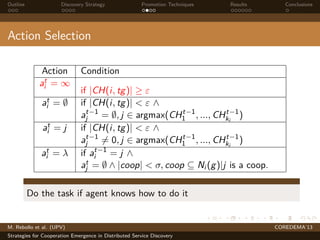
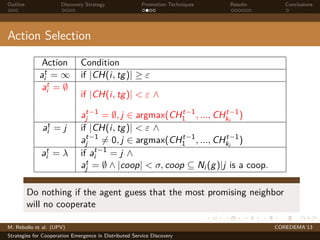
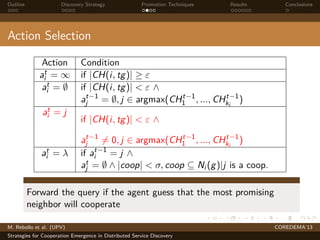
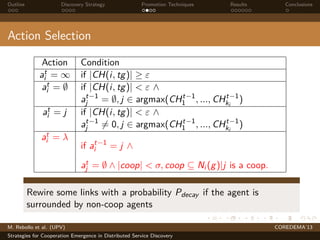
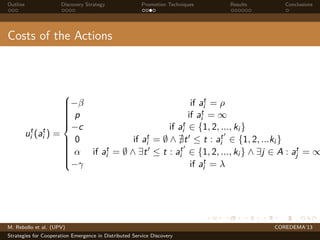
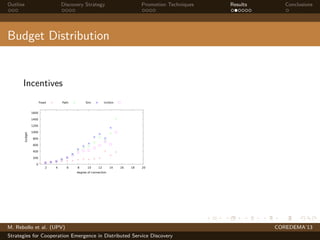
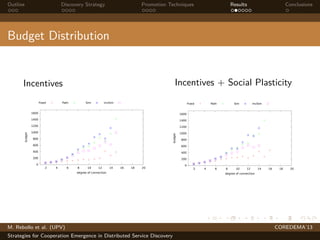
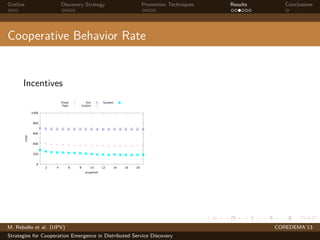
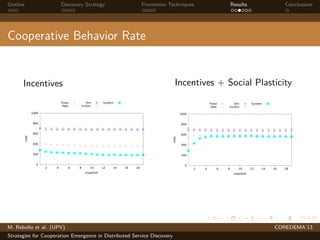
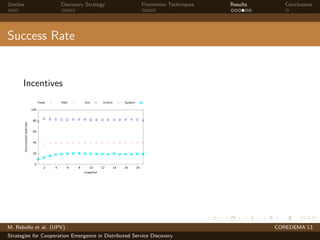
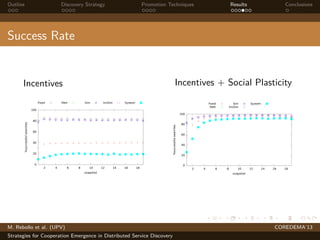
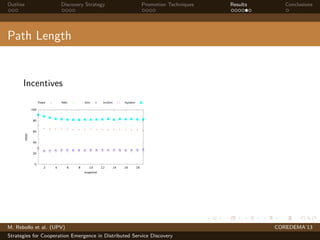
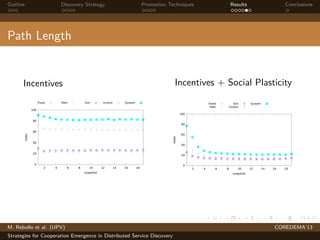
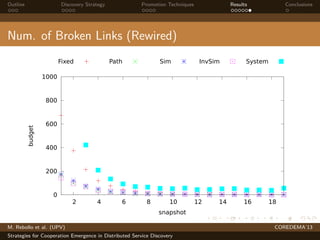
The document presents strategies to promote cooperative behavior in distributed service discovery networks. It proposes using social plasticity techniques like link rewiring and variable incentives. Simulation results show that combining social plasticity with different incentive policies like rewarding shorter paths or more similar services leads to higher cooperative behavior rates, search success rates and lower path lengths, even when cooperators are initially the minority.





![Outline Discovery Strategy Promotion Techniques Results Conclusions
Service Discovery
Purpose
Locate in the network a similar enough service offer by a concrete
role
qt
i = {stg , rtg , TTL, ε, {}}
stg required semantic service description
rtg organizational role the target agent should play
TTL: time to live
ε similarity threshold in [0, 1]
{} participant list (initially empty)
M. Rebollo et al. (UPV) COREDEMA’13
Strategies for Cooperation Emergence in Distributed Service Discovery](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mrebollocooperationslidescoredema13-130522183935-phpapp02/85/Strategies-for-Cooperation-Emergence-in-Distributed-Service-Discovery-6-320.jpg)