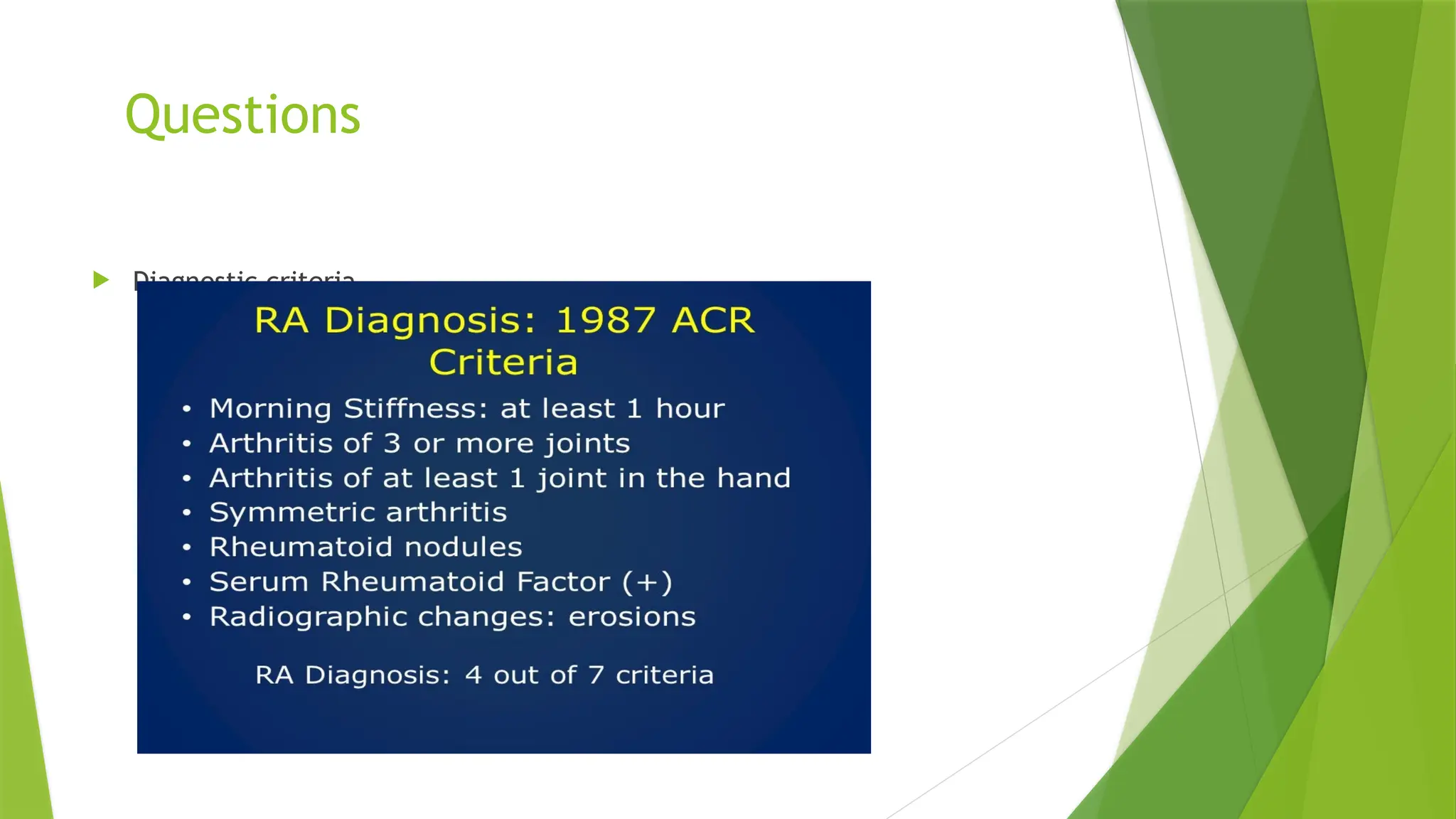
This document is a comprehensive tutorial on conducting musculoskeletal examinations by Dr. Sumreen Sarfaraz, covering hand examinations and diagnostic criteria for conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, and gout. It includes detailed steps for the examination process, patient interactions, findings to look for, and management options. The tutorial emphasizes the importance of patient consent, thorough assessments, and suggests further investigations as necessary.