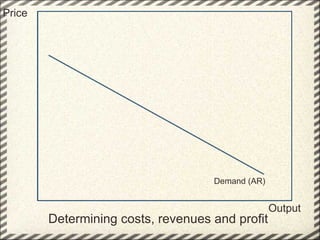
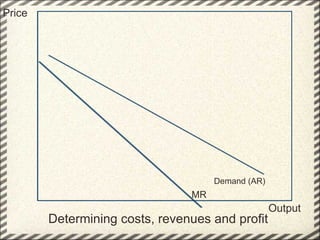
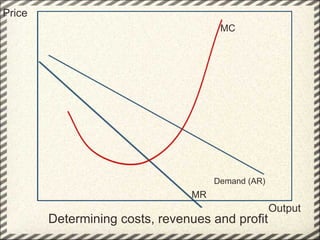
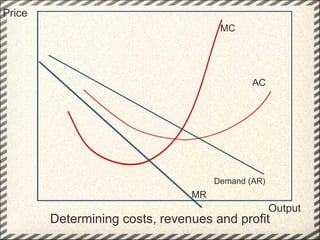
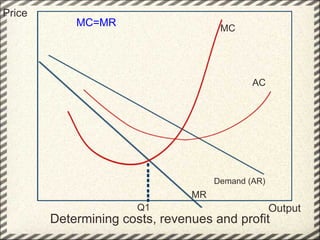
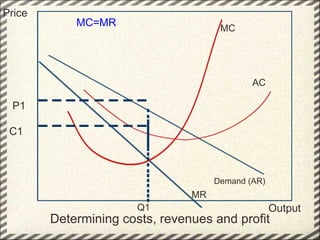
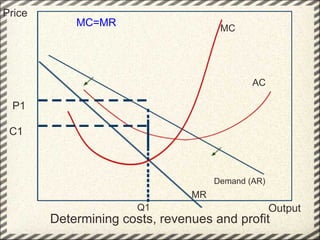
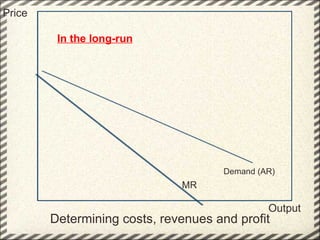
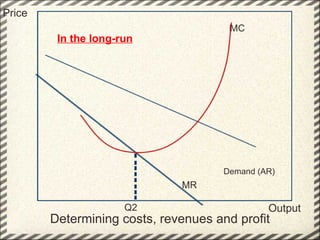
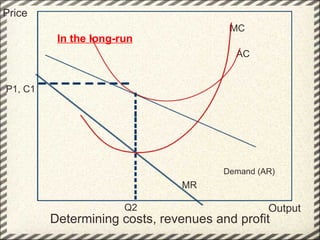
This document discusses monopolistic competition, including its key characteristics, assumptions, and how firms determine costs, revenues, and profits in the short and long run. Some key aspects of monopolistic competition are that firms have differentiated products, there are many firms but some are small, and there are relatively low barriers to entry. Firms set price at the point where marginal cost equals marginal revenue to maximize profits in the short run. In the long run, firms earn normal profits and the industry reaches equilibrium. Examples given include soft drink companies, sports shoe companies, and other branded consumer goods industries.