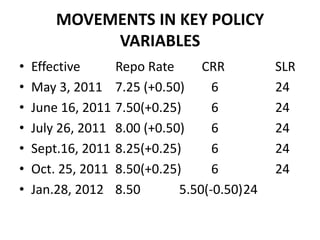
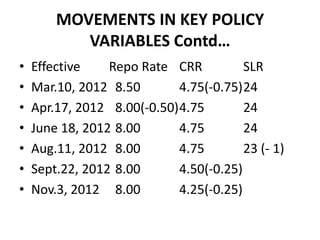
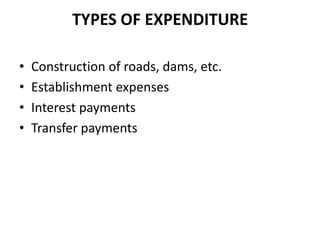
The document discusses monetary policy, fiscal policy, and India's transition to a more liberalized, privatized, and globalized economy through the LPG model since the 1990s. It outlines the objectives, instruments, and limitations of monetary and fiscal policy. It also discusses the economic reforms of liberalization, privatization, and globalization that opened India's economy and led to higher growth rates and integration with the global economy.