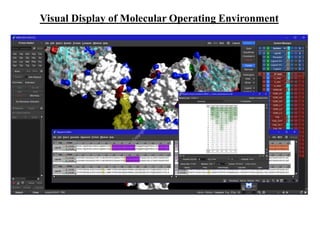
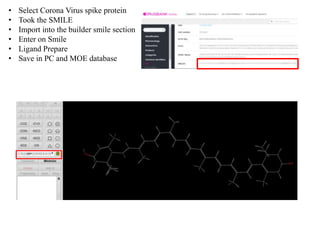
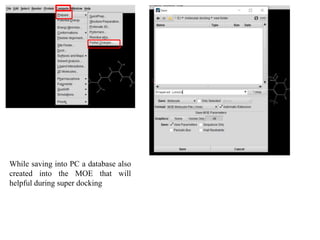
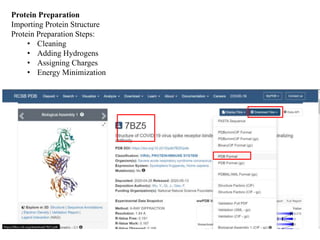
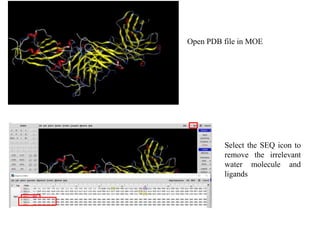
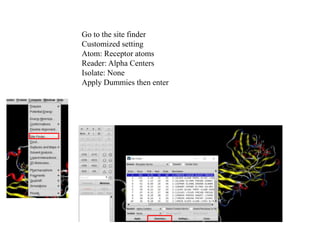
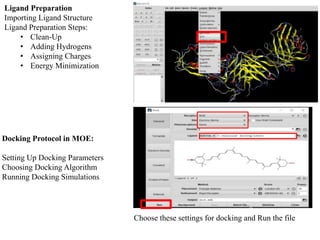
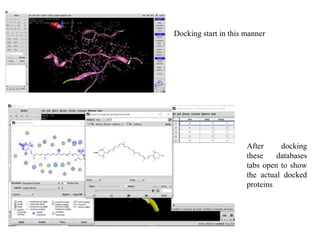
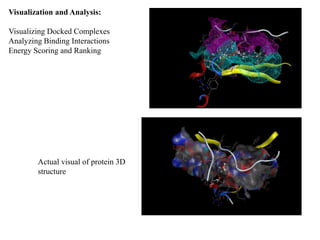
The document outlines the process of molecular docking, which is used to predict how small molecules bind to proteins, facilitating drug discovery. It discusses the importance of this computational method in understanding protein-ligand interactions and highlights the use of MOE software for molecular modeling and docking simulations. Additionally, it covers the specific case of the compound 7bz5 interacting with coronavirus spike proteins, presenting results and implications for future drug development.