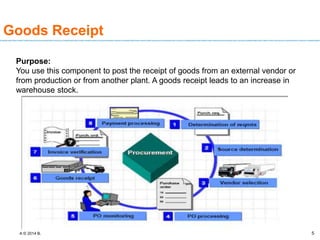
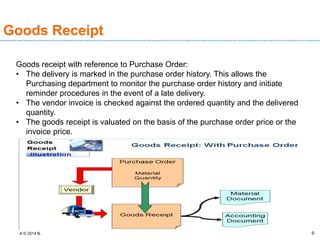
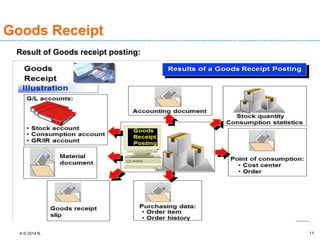
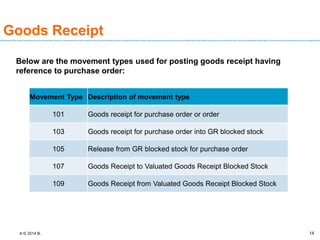
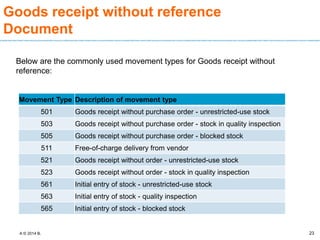
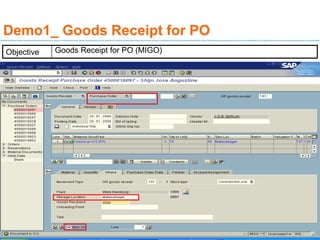
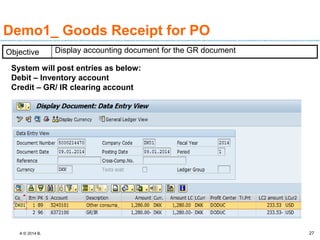
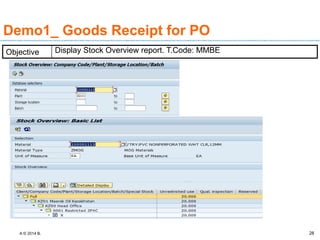
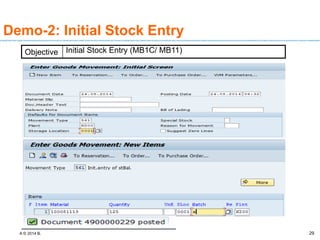
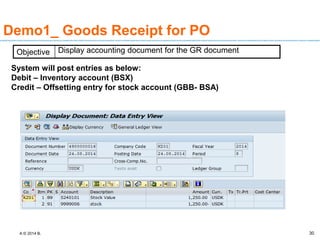
The document discusses goods receipt processes in SAP. It defines goods receipt as increasing warehouse stock by receiving goods from a vendor or production. It outlines different types of goods receipts like planned vs unplanned and with vs without reference to a purchase order. It also describes the accounting entries and impact on materials and stock for different goods receipt scenarios.