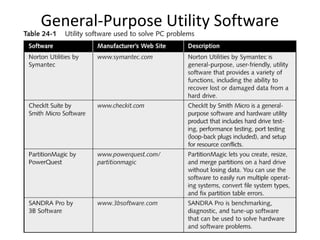
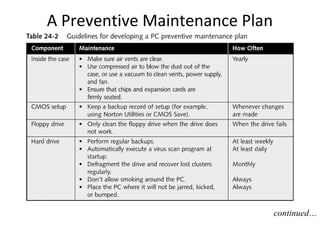
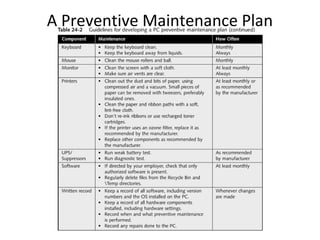
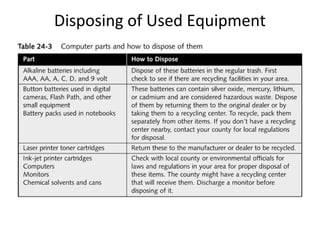
This document discusses troubleshooting and maintenance fundamentals for PC technicians. It covers tools for troubleshooting, diagnostic cards and software, fundamental rules for troubleshooting like isolating problems and gathering information from users. It also discusses developing a preventive maintenance plan to reduce failures and downtime, including organizing hard drives, creating rescue disks, and safety procedures like fire extinguishers and moving equipment.