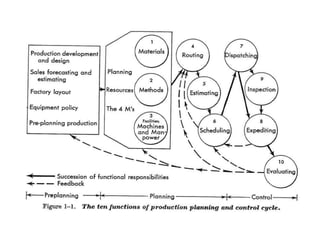
Production planning and control (PPC) coordinates manufacturing activities to achieve the highest production efficiency. PPC involves planning production targets, carrying out operations according to plans, and monitoring control to ensure targets are met efficiently. PPC aims to utilize resources optimally by coordinating material and component flows, defining operation times, and assigning jobs based on machine capabilities. PPC helps avoid delays, inefficiencies, and bottlenecks to maximize output.