The document discusses modems, including their functions, components, types, features, standards, and installation. Specifically:
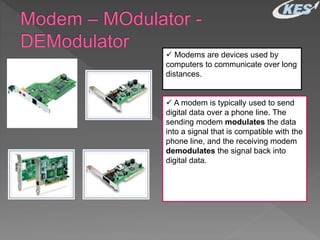
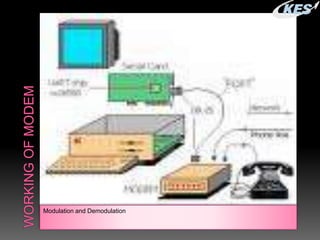
- Modems allow computers to transmit digital data over telephone lines by modulating digital signals for transmission and demodulating the signals upon receipt.
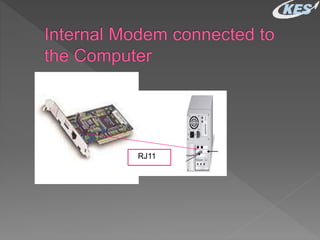
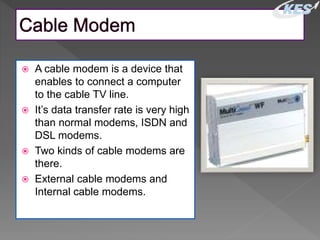
- There are two main types - internal modems installed inside computers and external modems connected via cable. Features, transmission speeds, and capabilities can vary between modems.
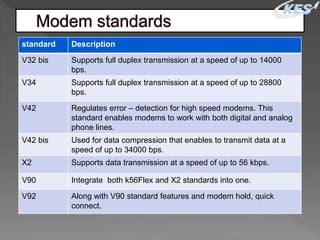
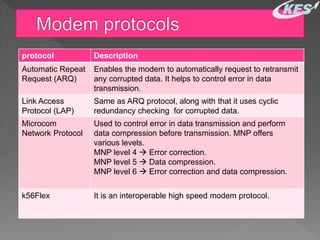
- Common standards that govern modem functions include V90, V92, X2, and protocols like ARQ that ensure error-free data transmission. Installation is typically straightforward after inserting an internal modem or connecting an external one.