The document summarizes several models of curriculum development:
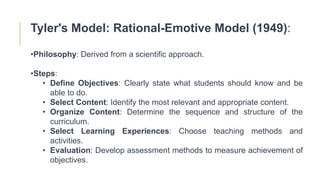
- Tyler's model from 1949 focuses on objectives-driven curriculum with five steps including defining objectives, selecting content, organizing content, selecting learning experiences, and evaluation.
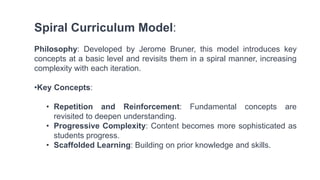
- Contemporary models discussed include Understanding by Design, Project-Based Learning, 21st Century Skills Framework, Integrated Curriculum model, Spiral Curriculum model, Competency-Based Education, and Culturally Relevant and Responsive Teaching.
- Each model has a different philosophical approach and set of key concepts for developing curriculum.