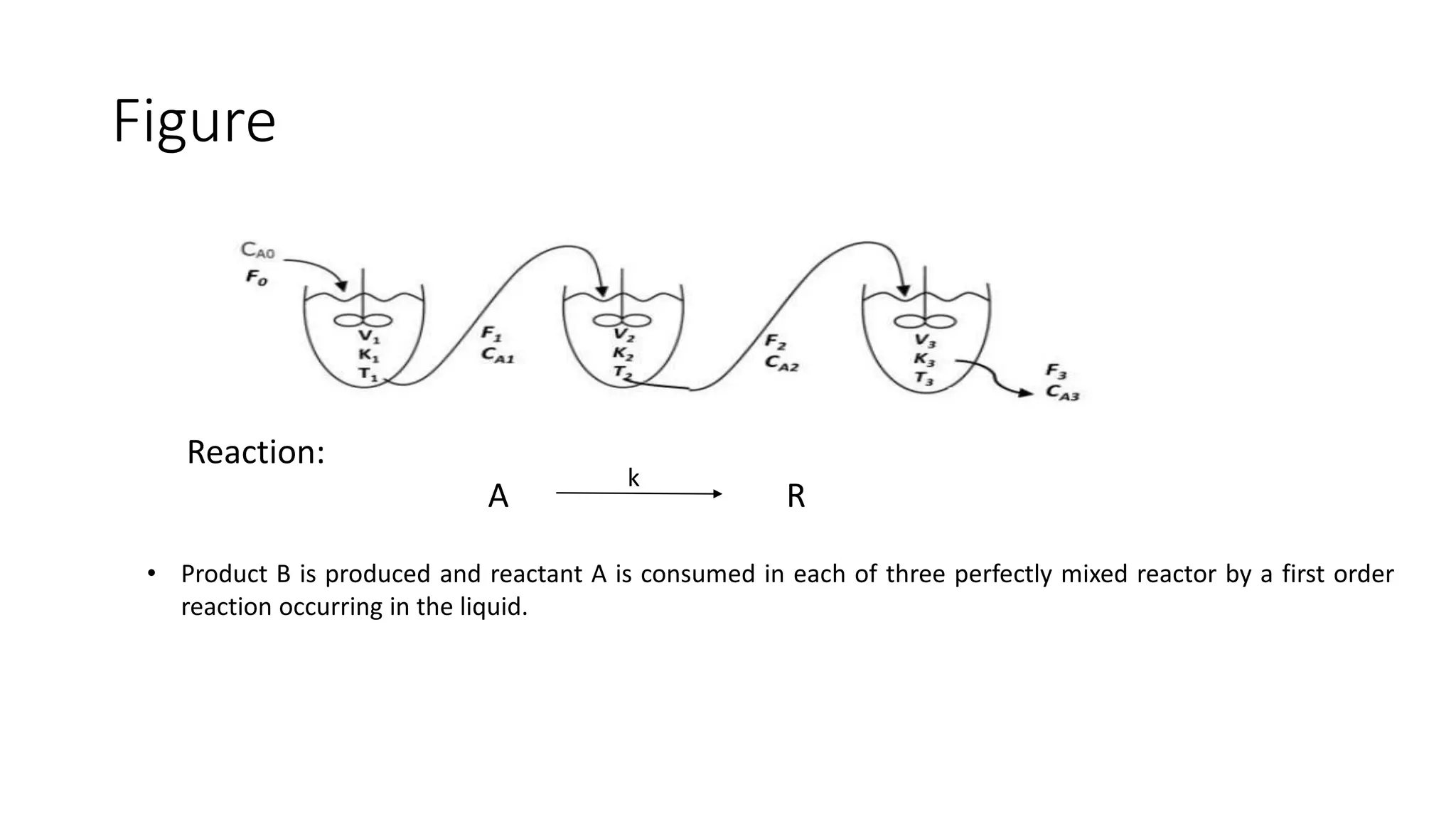
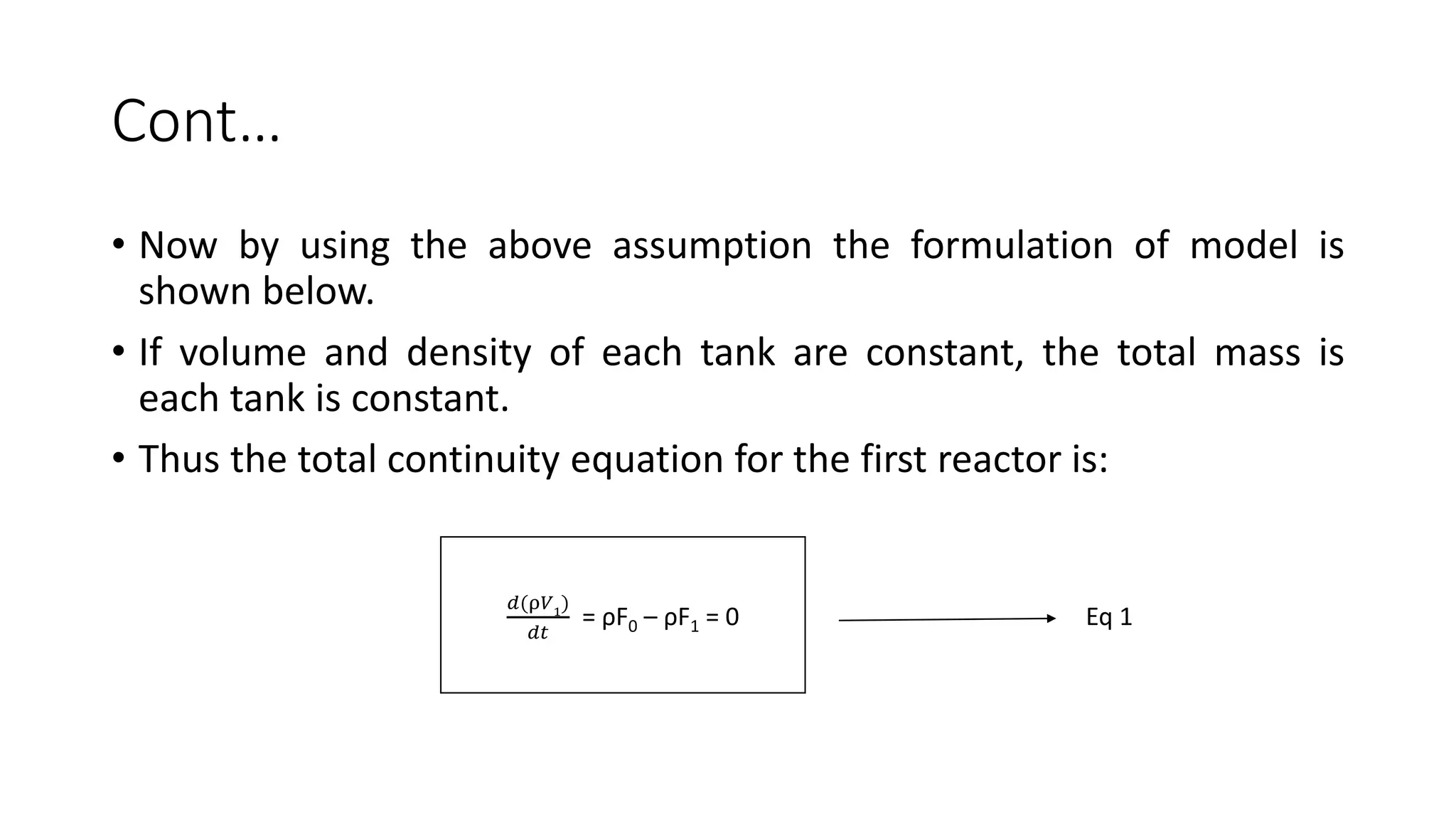
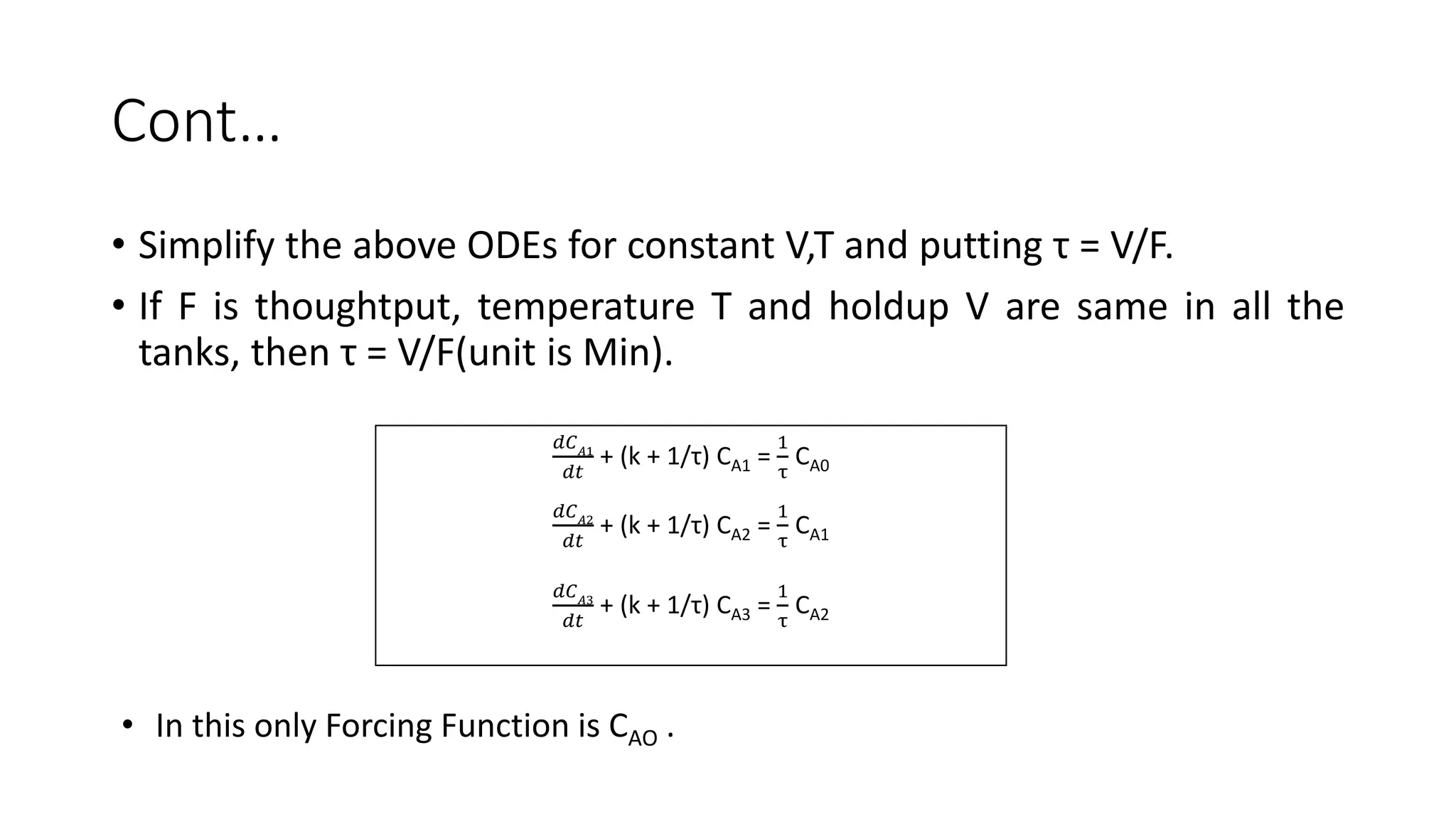
This document presents a mathematical model for a system of three continuously stirred tank reactors (CSTRs) in series where reactant A is converted to product B through a first-order reaction. It describes the assumptions made, including constant temperature, volume, and density in each reactor. Component continuity equations are developed for reactant A in each reactor to model how the concentration of A changes over time based on the inlet and outlet flows and the rate of the reaction. The specific reaction rates are defined using the Arrheusius equation. The model results in a set of three non-linear first-order ordinary differential equations that describe the dynamics of the system.