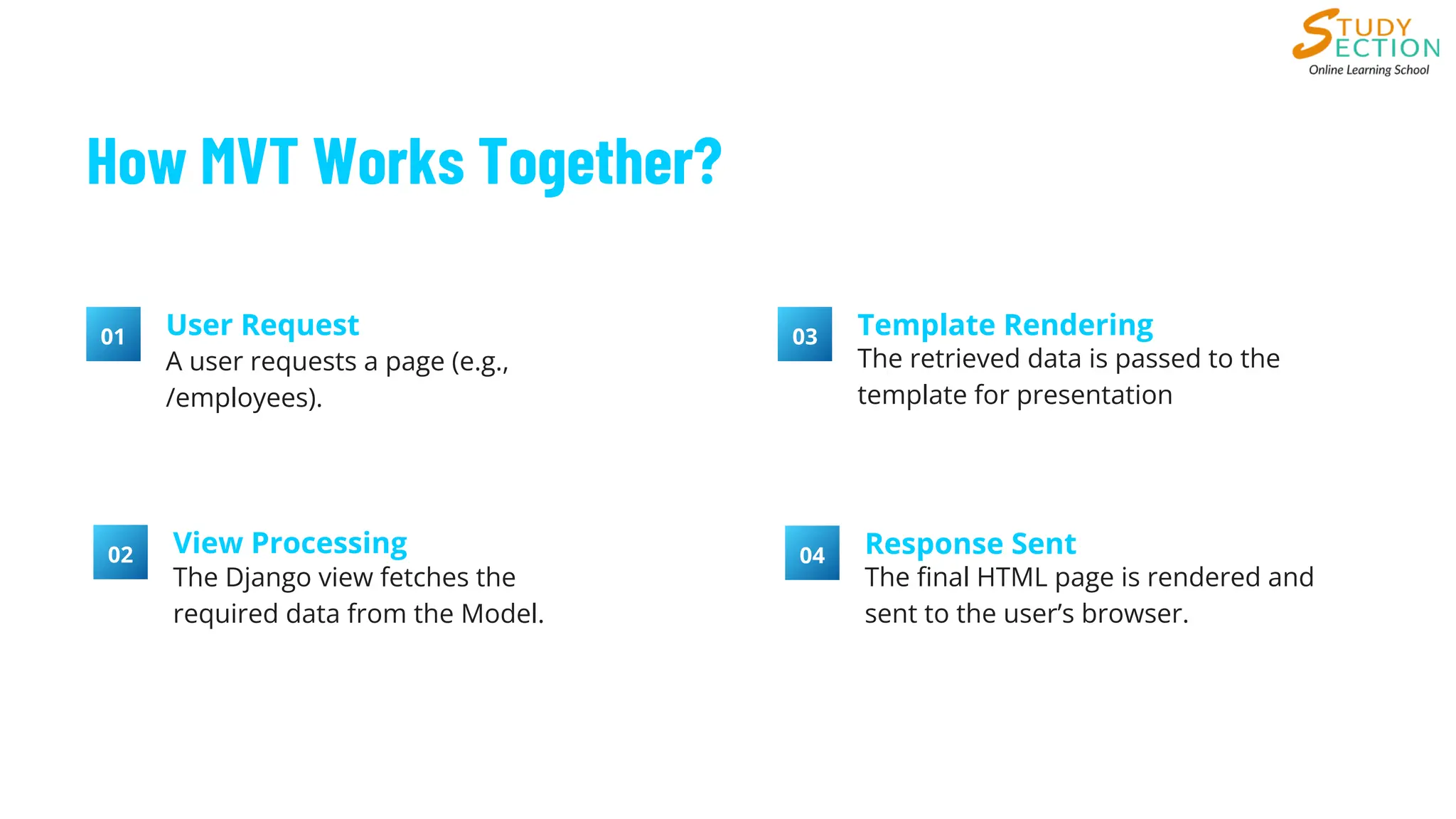
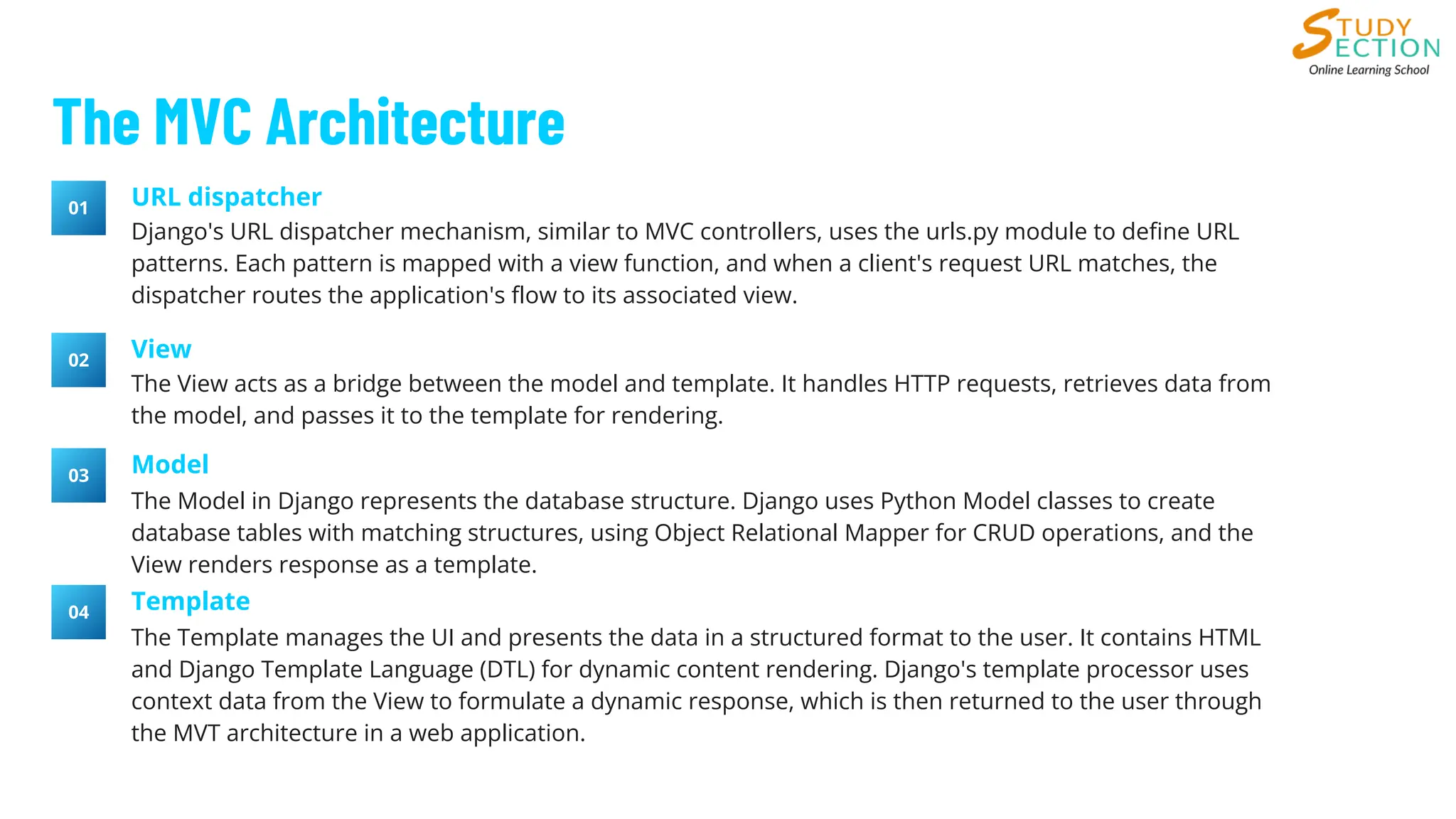
Understanding the Model-View-Template (MVT) architecture in Django is essential for efficient web development. This blog explains how Django’s URL dispatcher, Views, Models, and Templates work together to handle user requests, process data, and render dynamic web pages. Learn how Django simplifies web app development with reusable components, efficient session management, and seamless integration with templating tools. Read more on the StudySection blog!