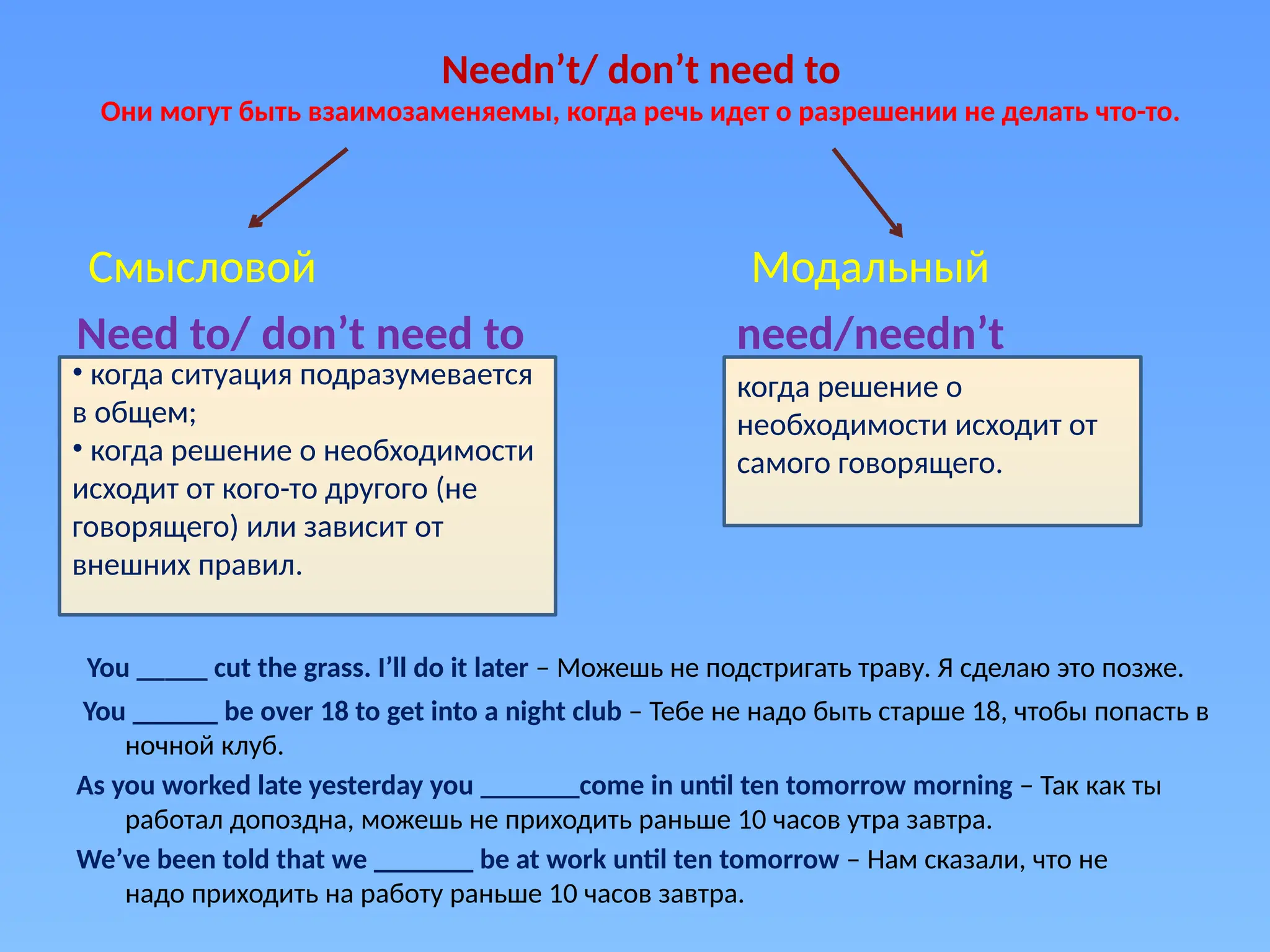
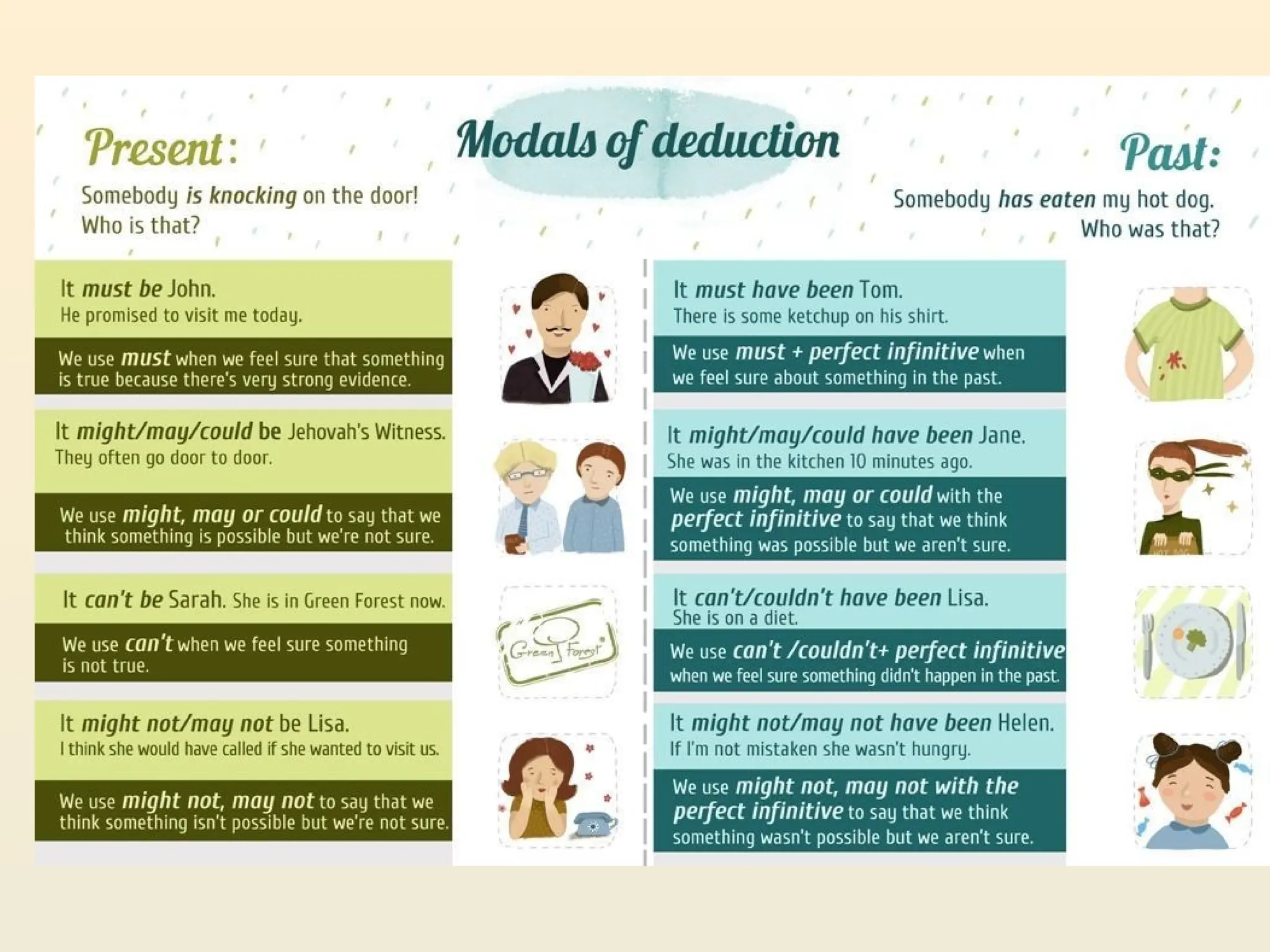
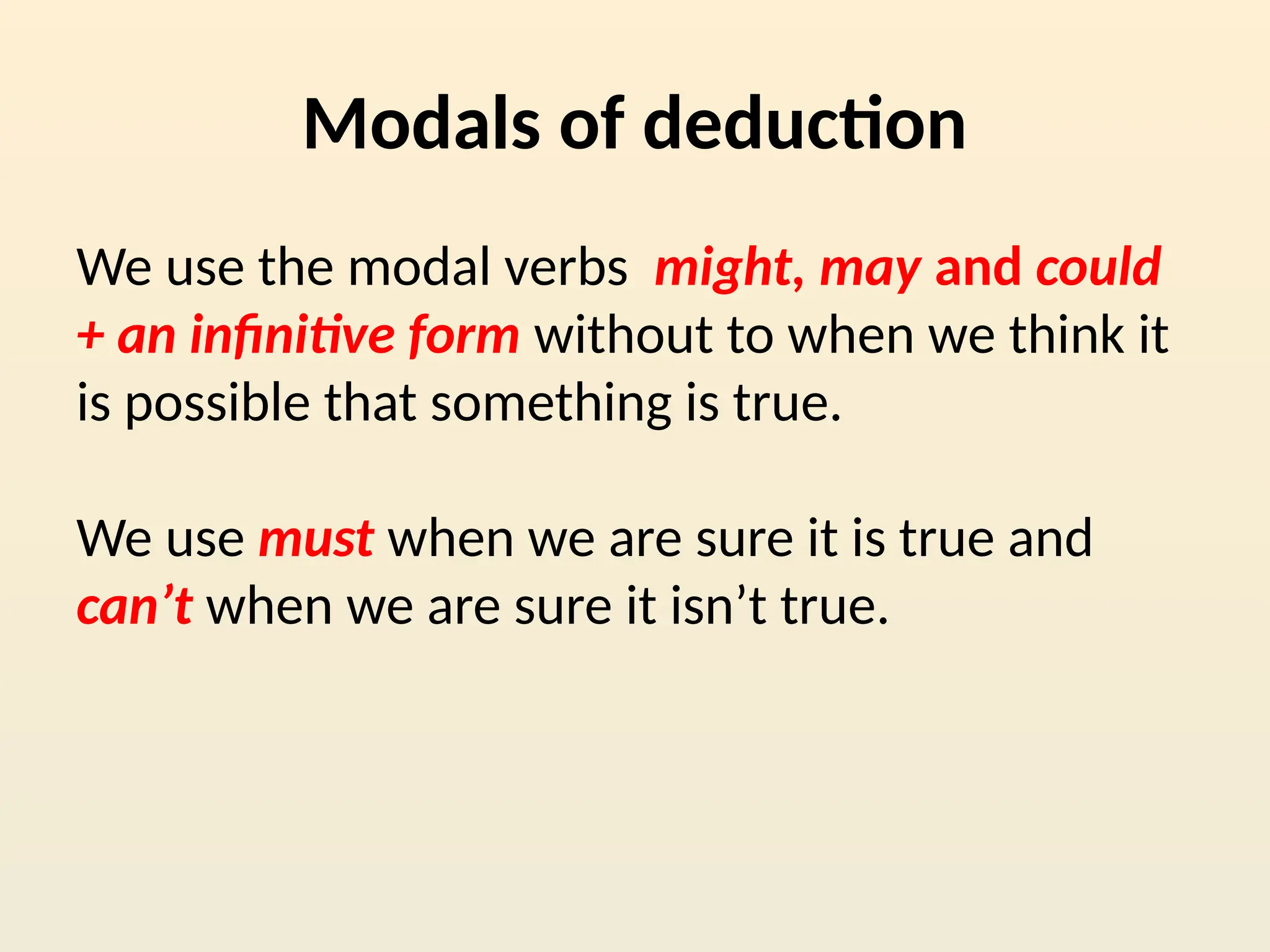
The document provides an overview of modal verbs in English, discussing their uses for expressing obligation, necessity, possibility, and advice. It includes examples and explanations for modals like must, should, have to, and others in various contexts including present, future, and past. Additionally, it details how to form sentences with modals and the nuances of their meanings in different situations.