The document proposes a mobile voting system using iris recognition and cryptography. Voters would register through a website providing identification details. On voting day, authenticated voters would receive an encrypted SMS with candidate lists. Voters would select a candidate and the vote would be encrypted before transmission. The system aims to increase voter participation and security while reducing costs compared to traditional voting methods. However, mobile voting systems also face challenges regarding security, reliability, and preventing multiple votes.

![2
voter and double voting this latest technology
can’t be allowed.
An efficient and reliable system is
essential for the trustworthy and successful
implementation of this technology. The
proposed system uses mobile phone device
having: small in size, low power, low-price as
compared to computers and Direct Recording
Electronic voting System, Electronic Voting
Machine’s, provide mobility feature and
security. Proposed system uses Global System
for Mobile Communication technology which
is a secure and globally used mobile
technology in the current situation. Mobile
phone also uses Subscriber Identity Module
technology which provides user identity
privacy, user identity verification and
subscriber data secrecy providing more
security to the proposed system.
The key features of our proposed
Mobile Phone Voting System is:
1. Eligibility: only authorized voter can
cast their vote.
2. Uniqueness: Each user can cast their only
one vote.
3. Integrity: Valid vote should not be modified
or deleted.
4. Fairness: The election result should not be
accessible before the official time ended.
5. Secrecy: No one should be able to find how
voter cast their vote.
2.LITERATURE REVIEW:
Voting through the mobile phone it is
the new and advanced area of research. We
take the review of some IEEE papers which
presented in past.
[1] Proposes mobile phone voting system
developed on modular square root and blind
signature system uses confidentiality of voter,
secrecy of ballot, voter anonymity and no
computation cost and communication
overhead. CA (certificate authority) involves
as third party that is distribution of certificates
to voters is the responsibility of CA for
authentication purposes, delayed occurred
which make the process slow.
[2] Proposed GSM based mobile phone voting
system is used to cast vote without registering
for voting in advance and going to polling
booths. System prevents repetition voting but
It has big disadvantage to security, proposes
system does not used any cryptographic
algorithm.
[3] Proposed mobile phone voting system
based on public key encryption algorithm
RSA. It contains three parts: access control;
voting and election administrator server. First
part holds validation and identification for the
voters.
Voting part done by ciphering voter data using
RSA algorithm and last part is the election
administrator server classifies ending result
using decryption RSA private key for received](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/e7e8dc44-451e-4ebe-9f4e-7b28adcb8e4e-161029085855/75/mobile-iris-voting-system-1-2-2048.jpg)


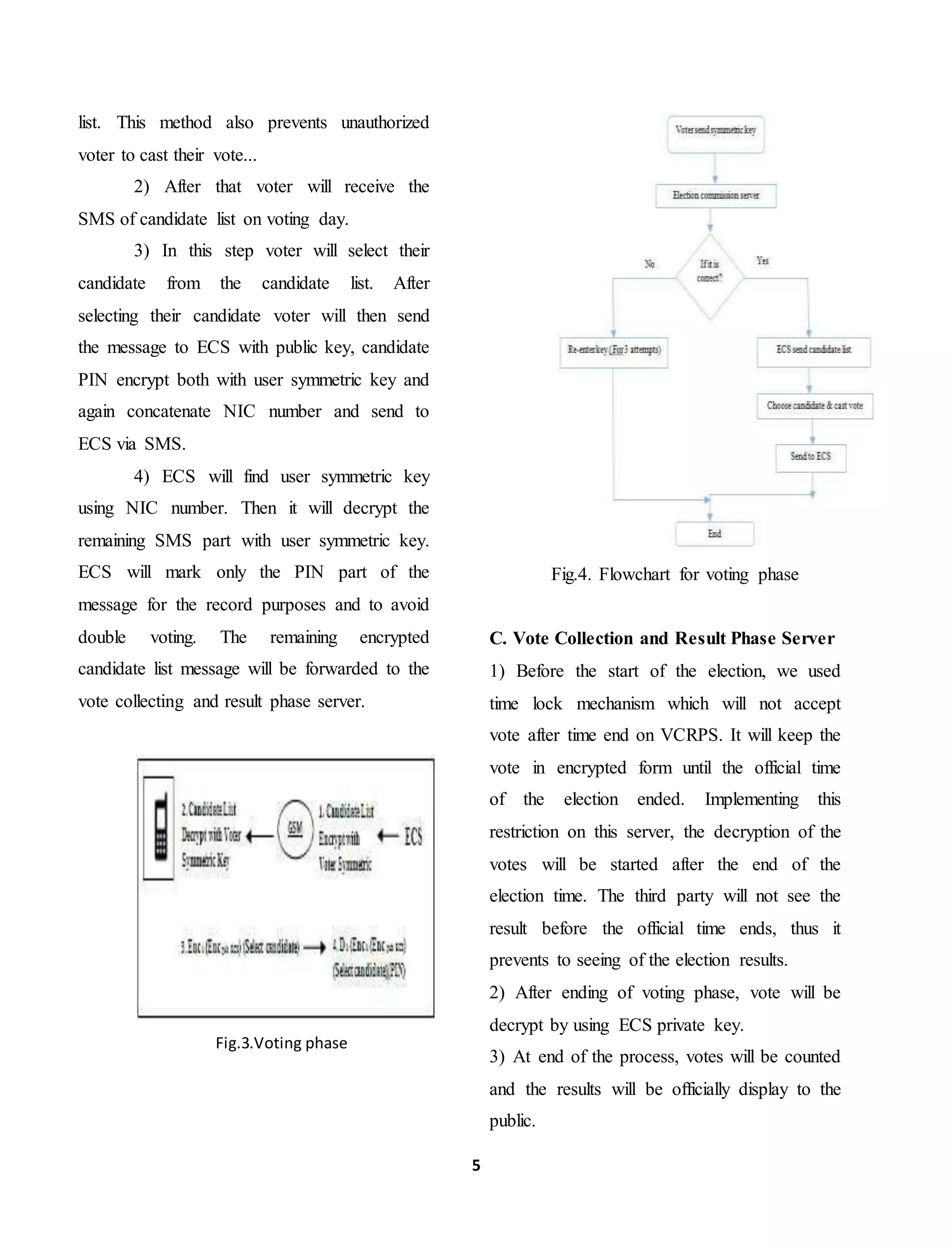
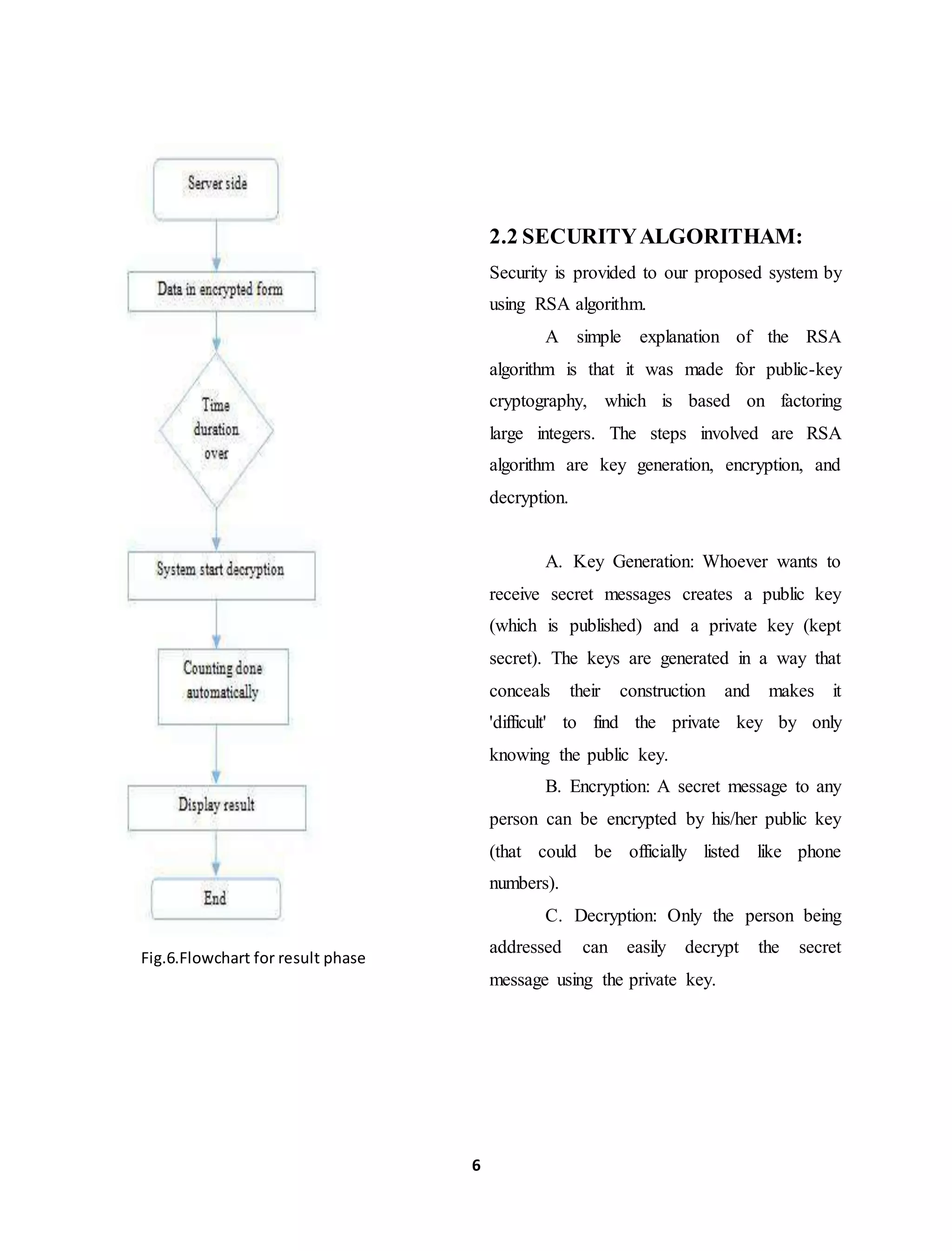


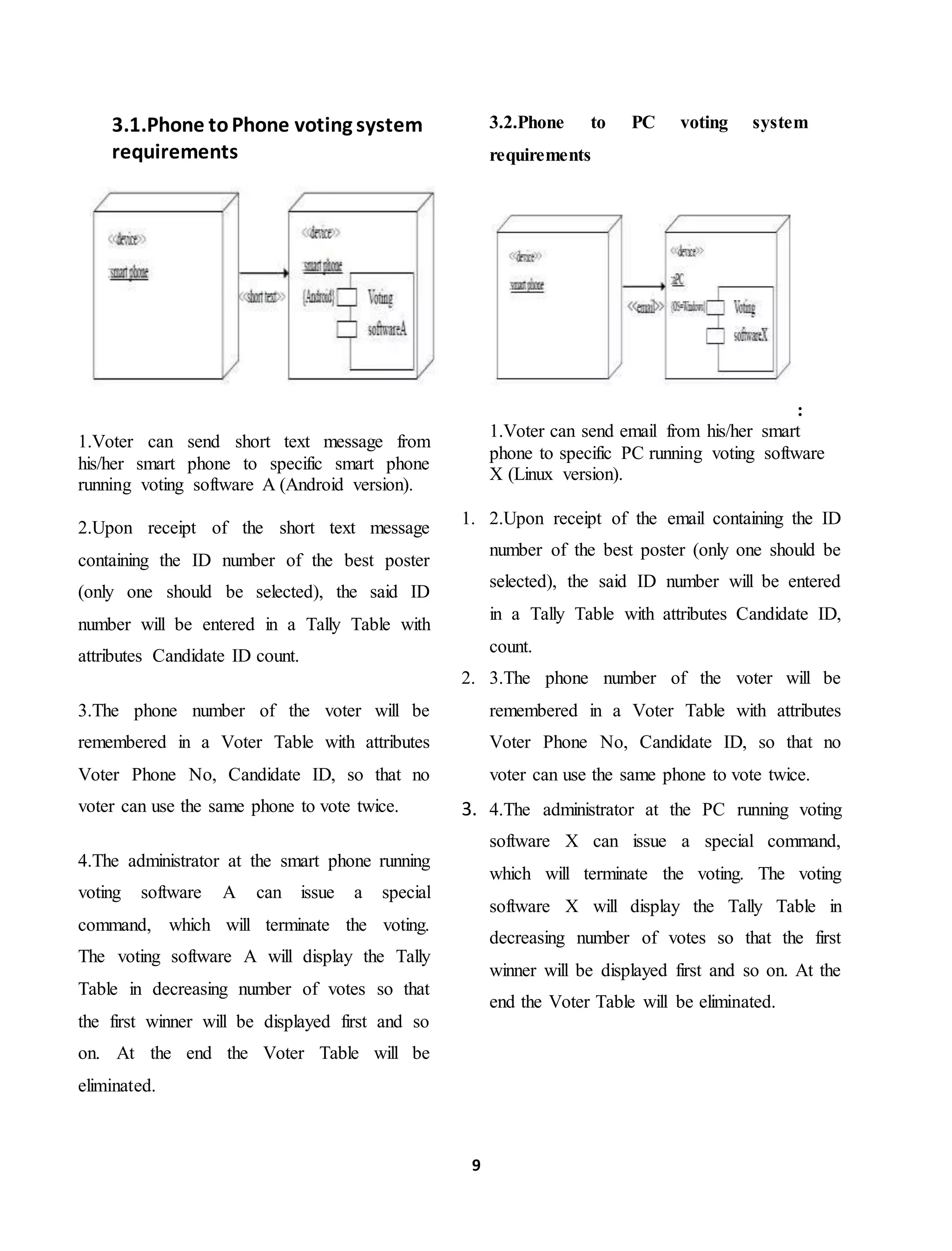
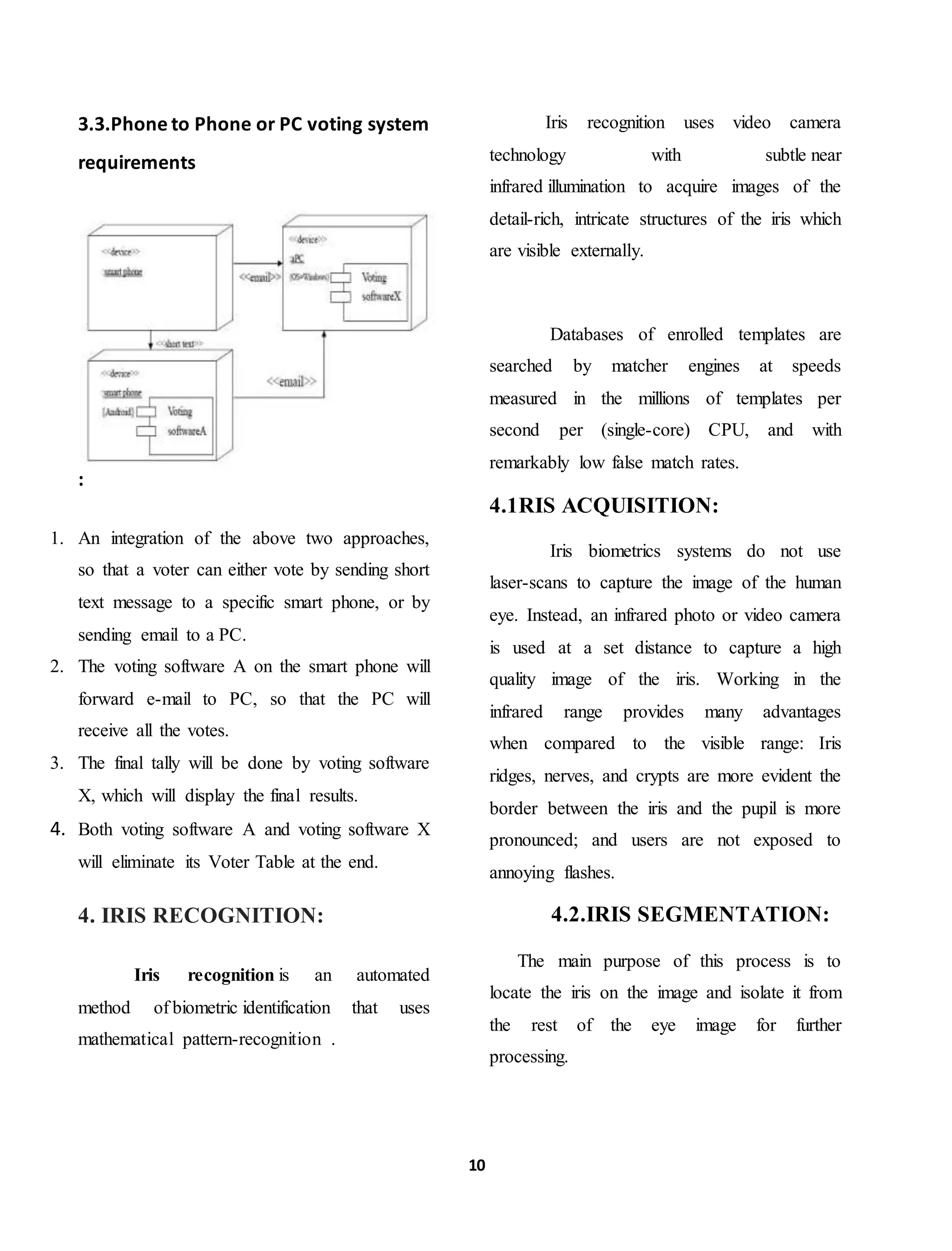

![12
Data confidentiality may be provided
by one of two categories of encryption
algorithm, namely symmetric cryptography
and asymmetric cryptography. Symmetric, or
conventional, cryptography requires that the
sender and receiver share a key, which is an
item of secret information used to encrypt and
decrypt data. The process by which two peers
agree upon a key over an insecure medium can
be problematic as, until the key is agreed, the
peers have no way to communicate in secret.
Asymmetric, or Public Key, cryptography
solves the key exchange problem by using two
keys, either of which may be used to encrypt a
message. The encrypted data may then only be
decrypted by means of the other key.
Messages may be received securely by
publishing one of the keys (for example, in the
footer of an e-mail message) as a Public Key
and keeping the second, the Private Key,
secret. Anyone wishing to send a secure
communication may then encrypt the message
with the recipient’s Public Key and, providing
the Private Key has not been disclosed, only
the intended recipient will be able to decrypt
the encrypted text and recover the original
message.
Cryptography or cryptology;
From Greek, "hidden, secret"; and "writing",
or "study", respectively is the practice and
study of techniques for secure
communication in the presence of third parties
called adversaries.]These adversaries are often
referred to as Eve in cryptography, while the
sender and recipient of messages are called
Alice and Bob respectively. Cryptography is
about constructing and
analyzing protocols that prevent third parties
or the public from reading private messages.
Various aspects in information security such
as data confidentiality, data
integrity, authentication, and non-
repudiation[5] are central to modern
cryptography. Modern cryptography exists at
the intersection of the disciplines
of mathematics, computer science,
and electrical engineering. Applications of
cryptography include ATM cards, computer
passwords, and electronic commerce.
The originator of an encrypted
message (Alice) shared the decoding technique
needed to recover the original information
only with intended recipients (Bob), thereby
precluding unwanted persons (Eve) from
doing the same.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/e7e8dc44-451e-4ebe-9f4e-7b28adcb8e4e-161029085855/75/mobile-iris-voting-system-1-12-2048.jpg)
