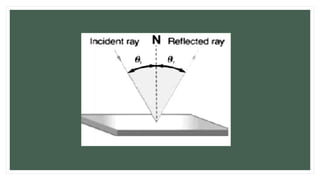
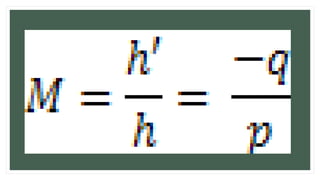The document explains the concept of mirrors and reflection, detailing the characteristics of plane and curved mirrors. It describes how to conduct an activity to observe image properties in a plane mirror, including aspects of size, orientation, and types of images (real vs. virtual). Additionally, it covers the concepts of incident and reflected rays, as well as the normal line associated with reflection.