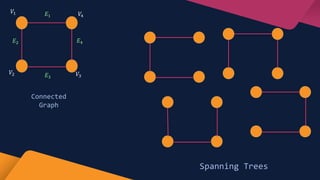
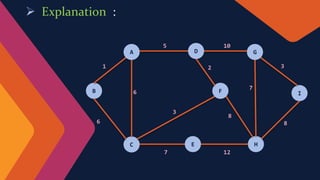
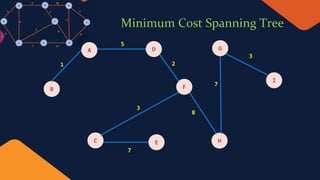
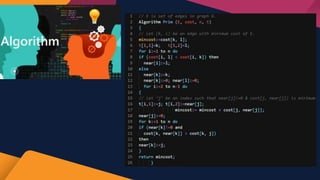
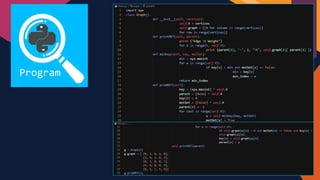
The document discusses Prim's algorithm, a greedy method for finding the minimum spanning tree of a connected, undirected, and weighted graph. It explains the characteristics of minimum spanning trees, how to calculate their costs, and includes an overview of time complexity considerations when implemented with a binary heap. Additionally, the document provides examples and a programmatic insight into the algorithm's efficiency.