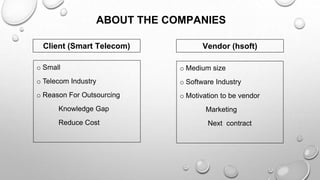
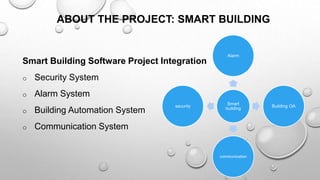
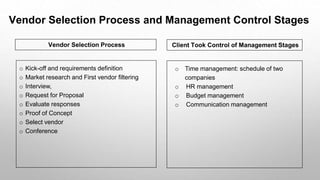
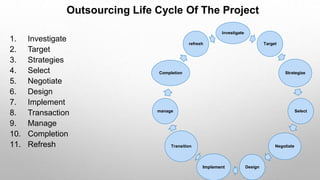
This document presents an autoethnographic study of the outsourcing lifecycle between a small client, Smart Telecom, and a medium-sized vendor, Hsoft, focusing on a smart building software project. It explores the client-vendor relationship, the significance of knowledge gaps, cost reduction motivations, and the detailed processes involved in vendor selection and project management. The methodology emphasizes personal reflection and self-observation throughout the outsourcing stages, from investigation to project completion.