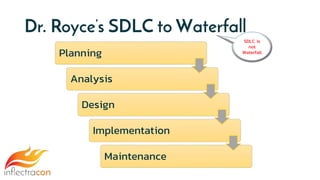
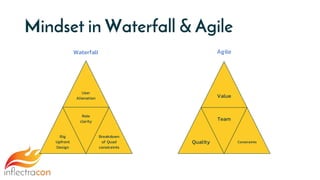
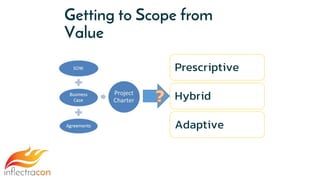
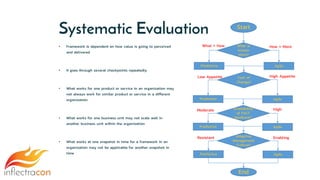
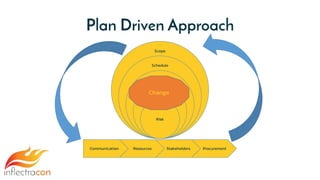
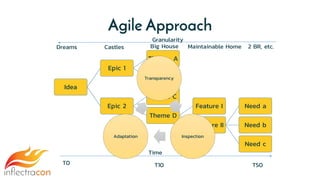
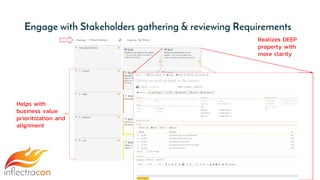
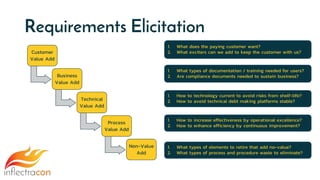
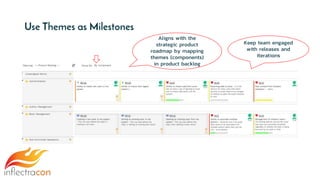
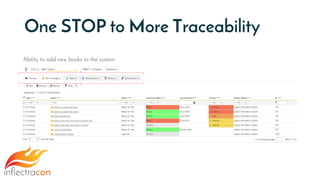
The document discusses the integration of Spira and its methodologies for managing waterfall and agile projects, emphasizing the importance of stakeholder engagement and requirements management to enhance project performance. It highlights the distinct phases of software development life cycle (SDLC), the necessity of adapting frameworks to specific organizational contexts, and the value of transparency and collaboration in project management. Additionally, it addresses common myths about SDLC and presents key considerations for effectively managing requirements and ensuring successful project outcomes.