The document discusses Ruby metaprogramming techniques such as class variables, class inheritance, singleton classes, blocks, evaluation, dynamic method definition, mixins, monkey patching, and hooks. It provides examples of how these techniques can be combined to add dynamic behavior to classes and modules in Ruby.





























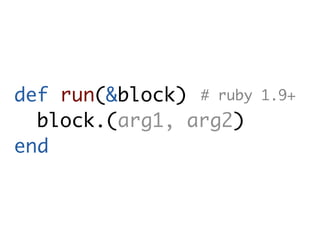
![def run(&block)
block[arg1, arg2]
end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/metaprogramming-100912125200-phpapp02/85/Ruby-Metaprogramming-30-320.jpg)































![class MyLib
NAMES = { :name => "mylib’s instance" }
def method_missing(method, *args)
if NAMES.key?(method.to_sym)
NAMES[method.to_sym]
else
super
end
end
end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/metaprogramming-100912125200-phpapp02/85/Ruby-Metaprogramming-64-320.jpg)








![class String
def to_permalink
self.downcase.gsub(/[^[a-z0-9]-]/, "-")
end
end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/metaprogramming-100912125200-phpapp02/85/Ruby-Metaprogramming-73-320.jpg)











