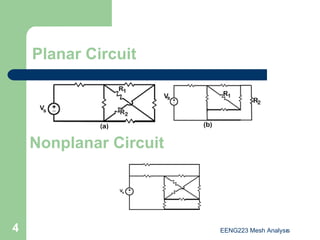
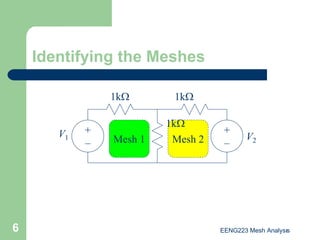
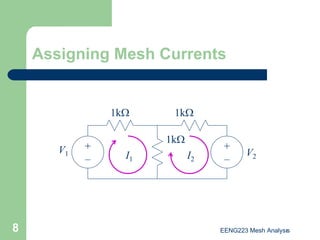
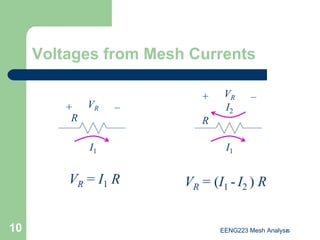
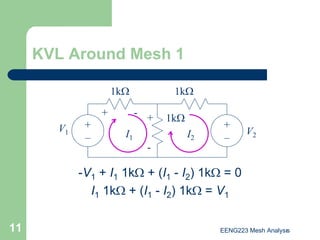
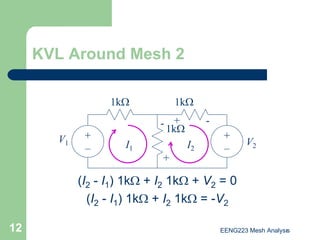
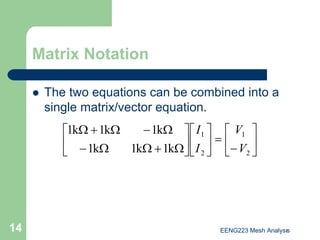
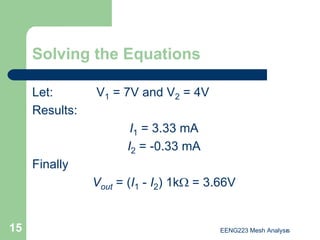
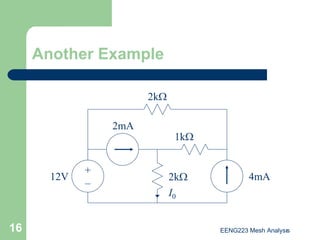
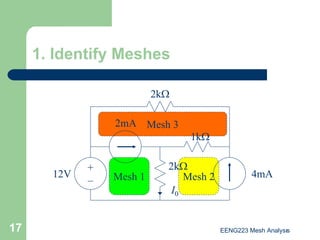
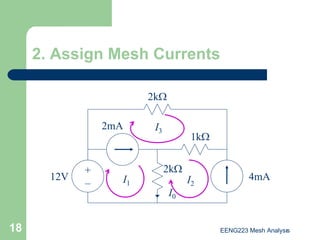
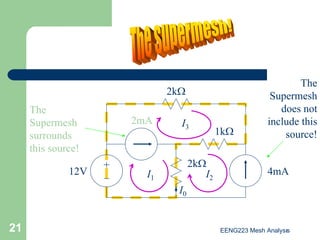
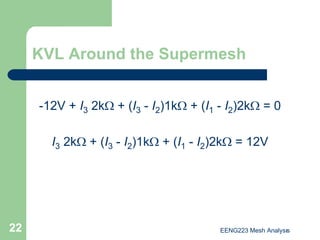
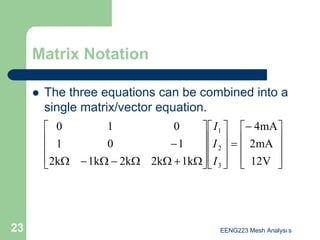
The document discusses the technique of mesh analysis for solving circuits. It begins by defining mesh analysis as applying Kirchhoff's voltage law around loops in a circuit to obtain equations relating loop currents. It then outlines the steps of mesh analysis as: 1) identifying meshes, 2) assigning currents to meshes, 3) applying KVL to obtain equations, 4) solving the resulting system of equations. Examples are provided to demonstrate identifying meshes, assigning currents, writing KVL equations, and setting up the matrix equations to solve.









![EENG223 Mesh Analysıs
24
Solve Using MATLAB
>> A = [0 1 0; 1 0 -1;
2e3 -1e3-2e3 2e3+1e3];
>> v = [-4e-3; 2e-3; 12];
>> i = inv(A)*v
i = 0.0012
-0.0040
-0.0008](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meshanalysis-220913124112-95861e83/85/Mesh-Analysis-pdf-24-320.jpg)

