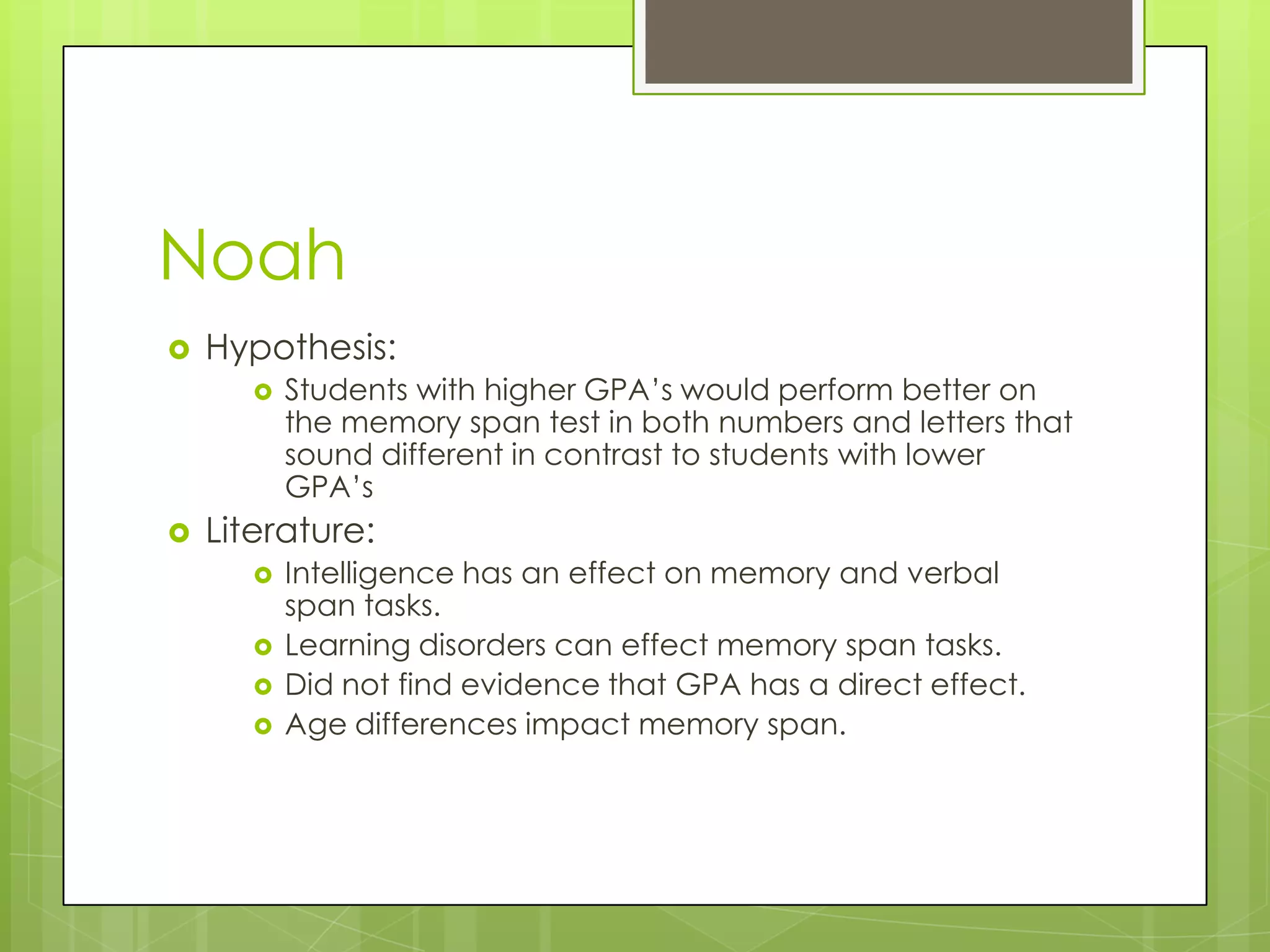
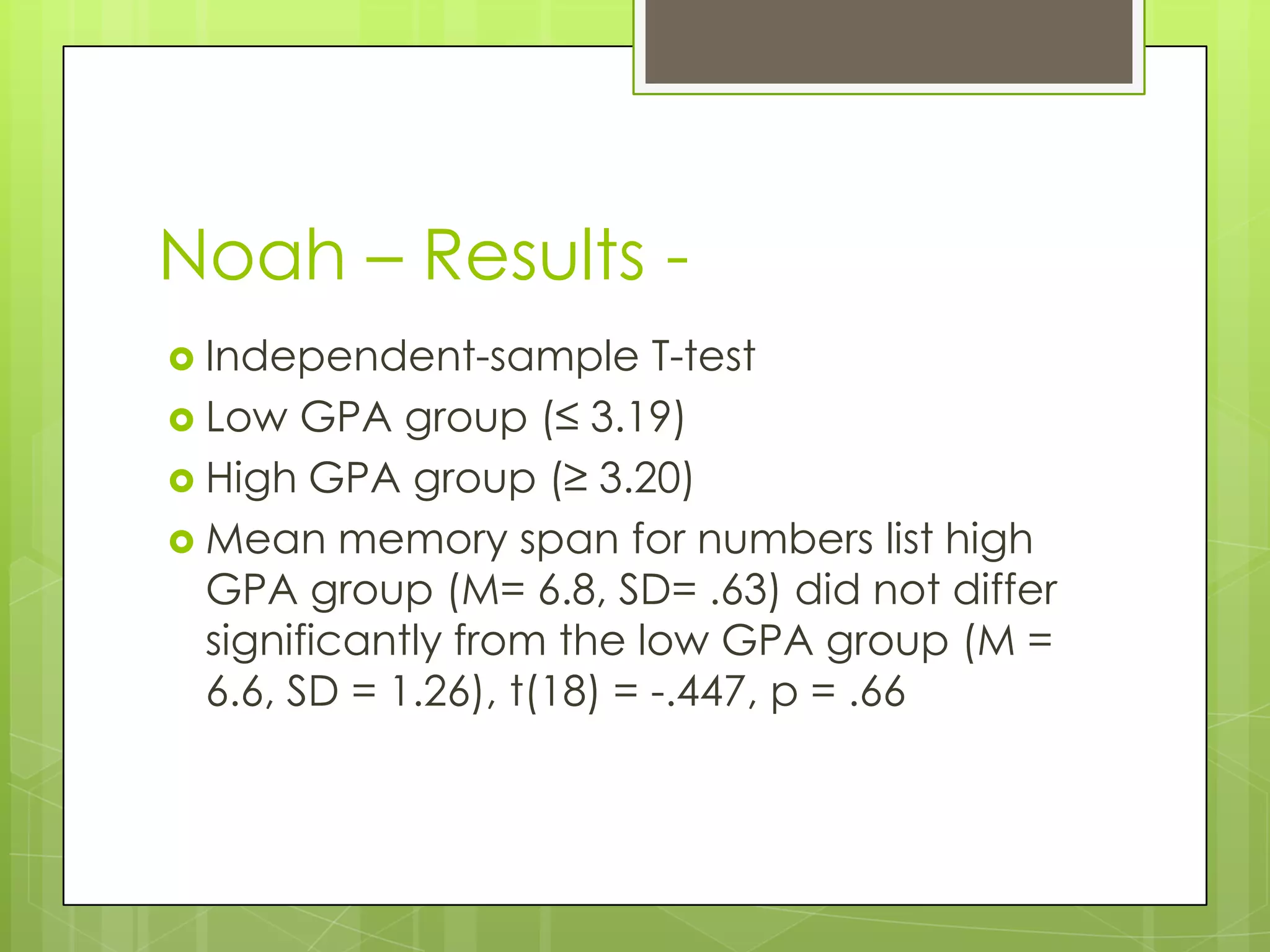
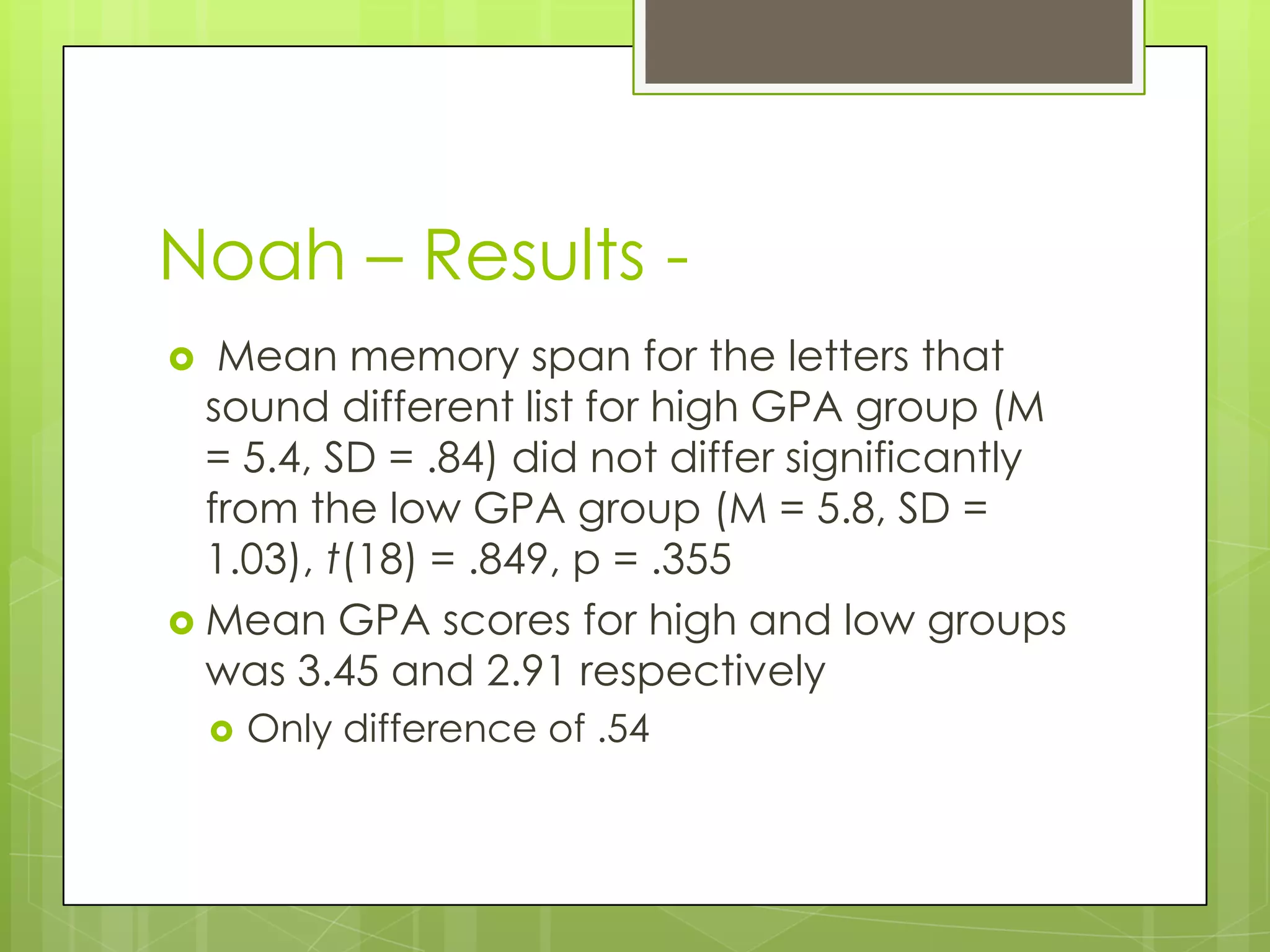
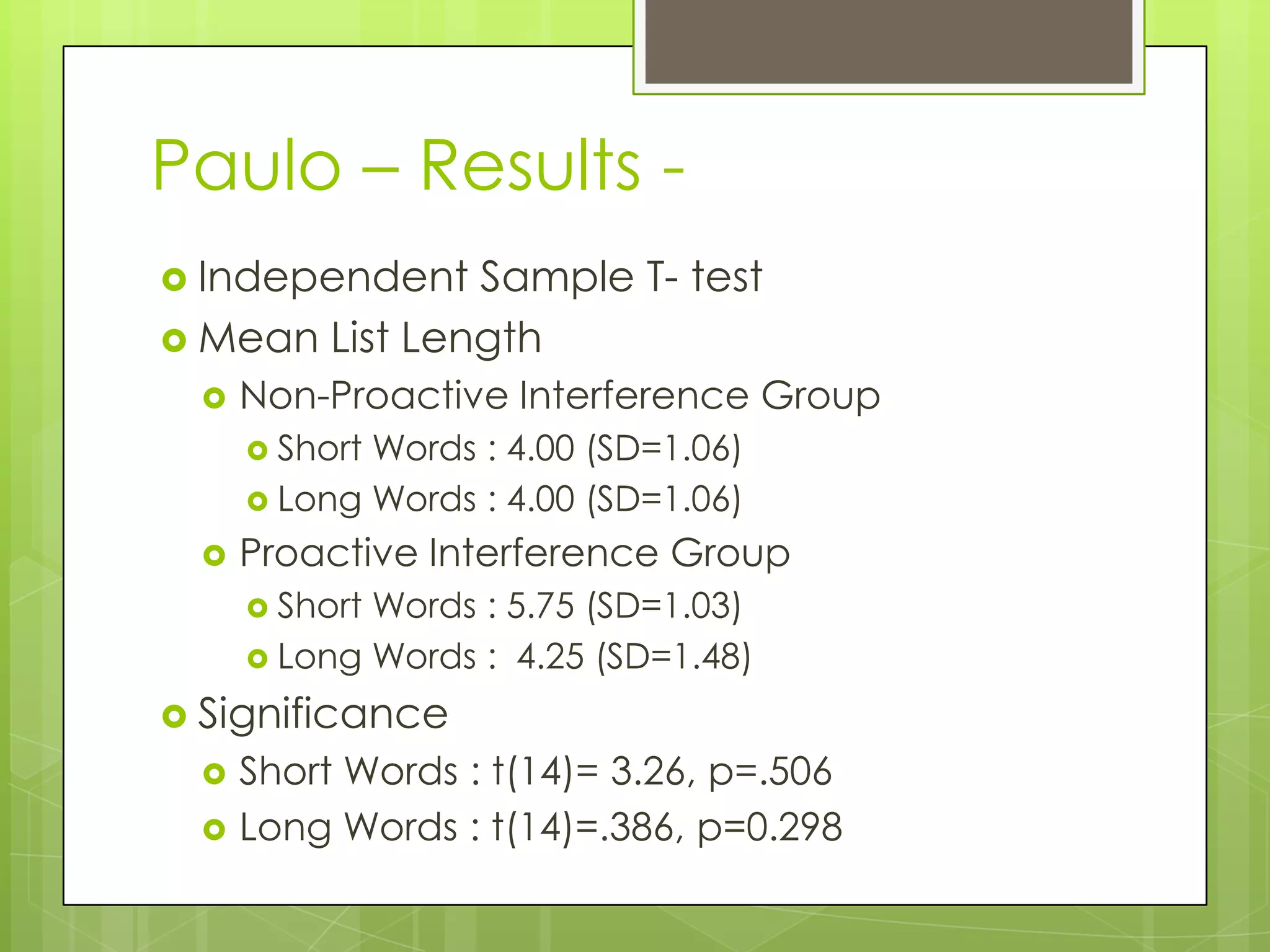
The document summarizes three memory span experiments conducted by Amanda, Noah, and Paulo. Amanda found a significant correlation between perceived stress and memory span. Noah found no significant difference in memory span between high and low GPA groups. Paulo found no significant impact of proactive interference on memory span. The conclusion discusses limitations and need for further research.