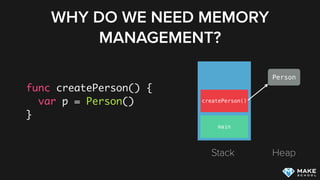
The document discusses Swift memory management and ARC. It explains that Swift uses reference counting, where objects remain in memory as long as their retain count is above zero. With ARC, memory management calls like retain and release are inserted by the compiler based on strong, weak and unowned references. While reference counting works automatically with ARC, some issues like retain cycles cannot be detected as they can with tracing garbage collectors used in other languages.








![MANUAL REFERENCE COUNTING
- (void)createPerson {
Person *person = [[[Person alloc] init] autorelease];
return person;
}
+1 -1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/memorymanagement-151103000811-lva1-app6891/85/Memory-Management-on-iOS-10-320.jpg)
![MANUAL REFERENCE COUNTING
@interface Business : NSObject
@property (nonatomic, strong) Person *name;
@end
+1 -1- (void)createOwner {
self.owner = [[[Person alloc] init] autorelease];
}
+1
- (void)freeOwner {
self.owner = nil;
}
-1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/memorymanagement-151103000811-lva1-app6891/85/Memory-Management-on-iOS-11-320.jpg)








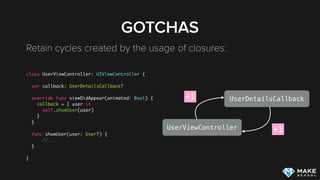
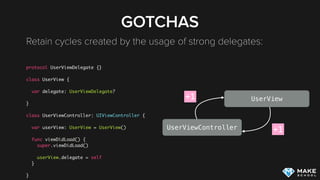
![GOTCHAS
Fix retain cycles using weak/unowned:
class UserViewController: UIViewController {
var callback: UserDetailsCallback?
override func viewDidAppear(animated: Bool) {
callback = { [unowned self] user in
self.showUser(user)
}
}
func showUser(user: User?) {
//...
}
}
UserViewController
UserDetailsCallback+1
+0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/memorymanagement-151103000811-lva1-app6891/85/Memory-Management-on-iOS-21-320.jpg)