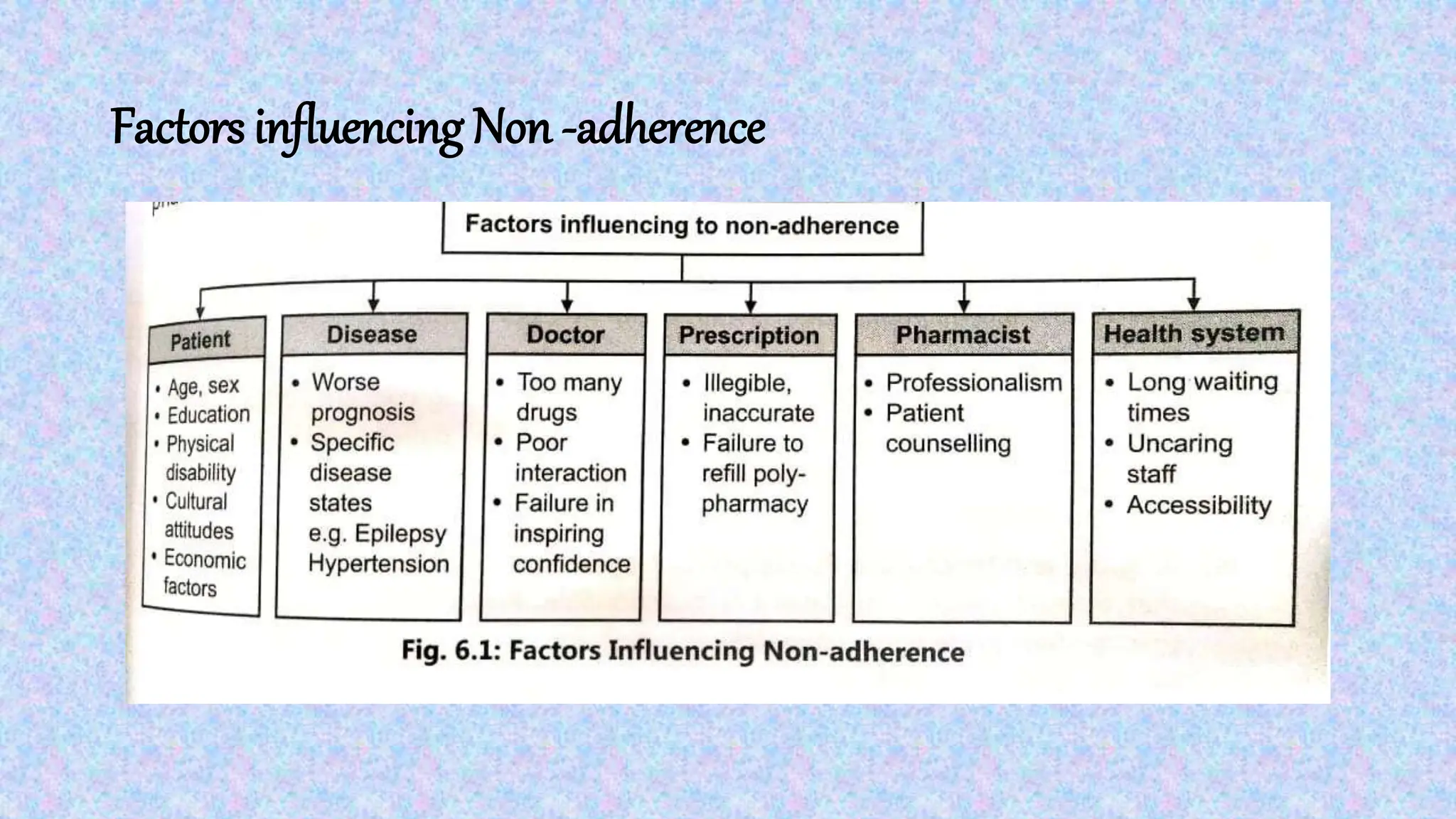
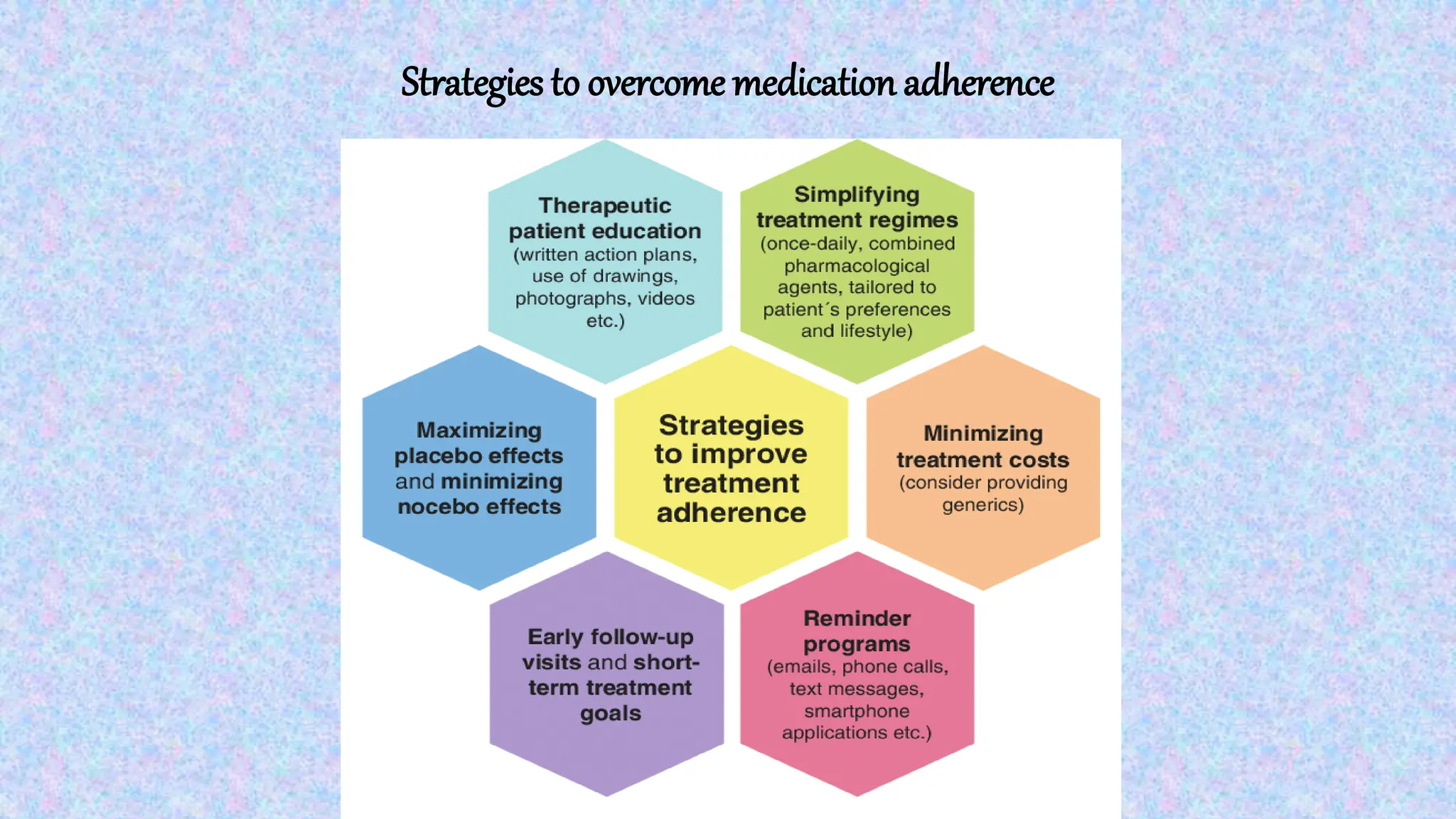
Medication adherence refers to the correct following of medical advice by patients, crucial for effective treatment. Factors influencing non-adherence include patient demographics, disease severity, doctor-patient interactions, and health system issues. Strategies to improve adherence encompass tailored education, involving family support, simplifying regimens, and ensuring clear communication regarding instructions and side effects.