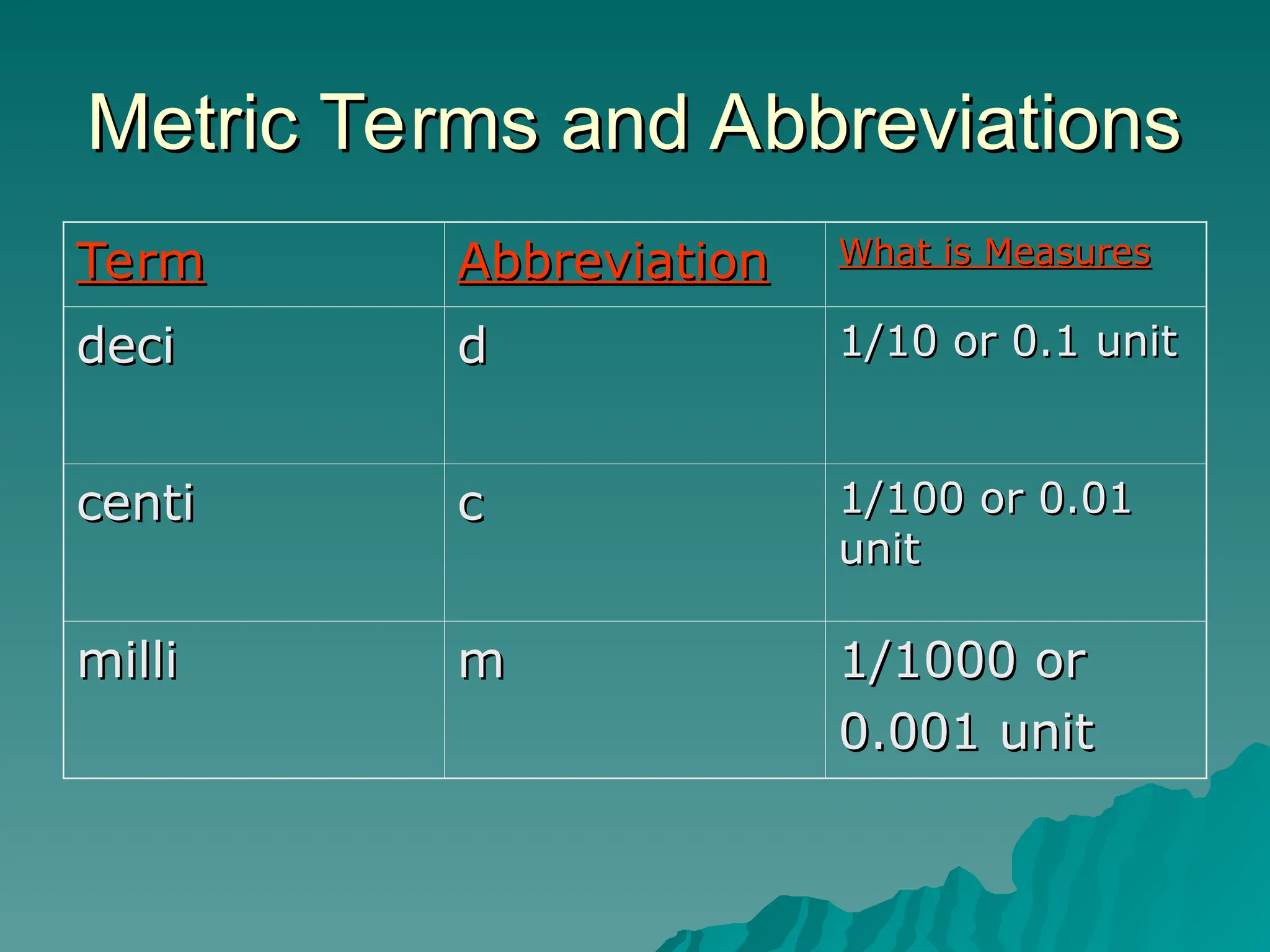
The document covers essential mathematical concepts needed for healthcare professionals, including basic arithmetic operations and the metric system. It explains the significance of understanding numbers, measurements, and the correct usage of metric abbreviations. Additionally, it details conversions between various units of measurement and the 24-hour military time system used in medical facilities.