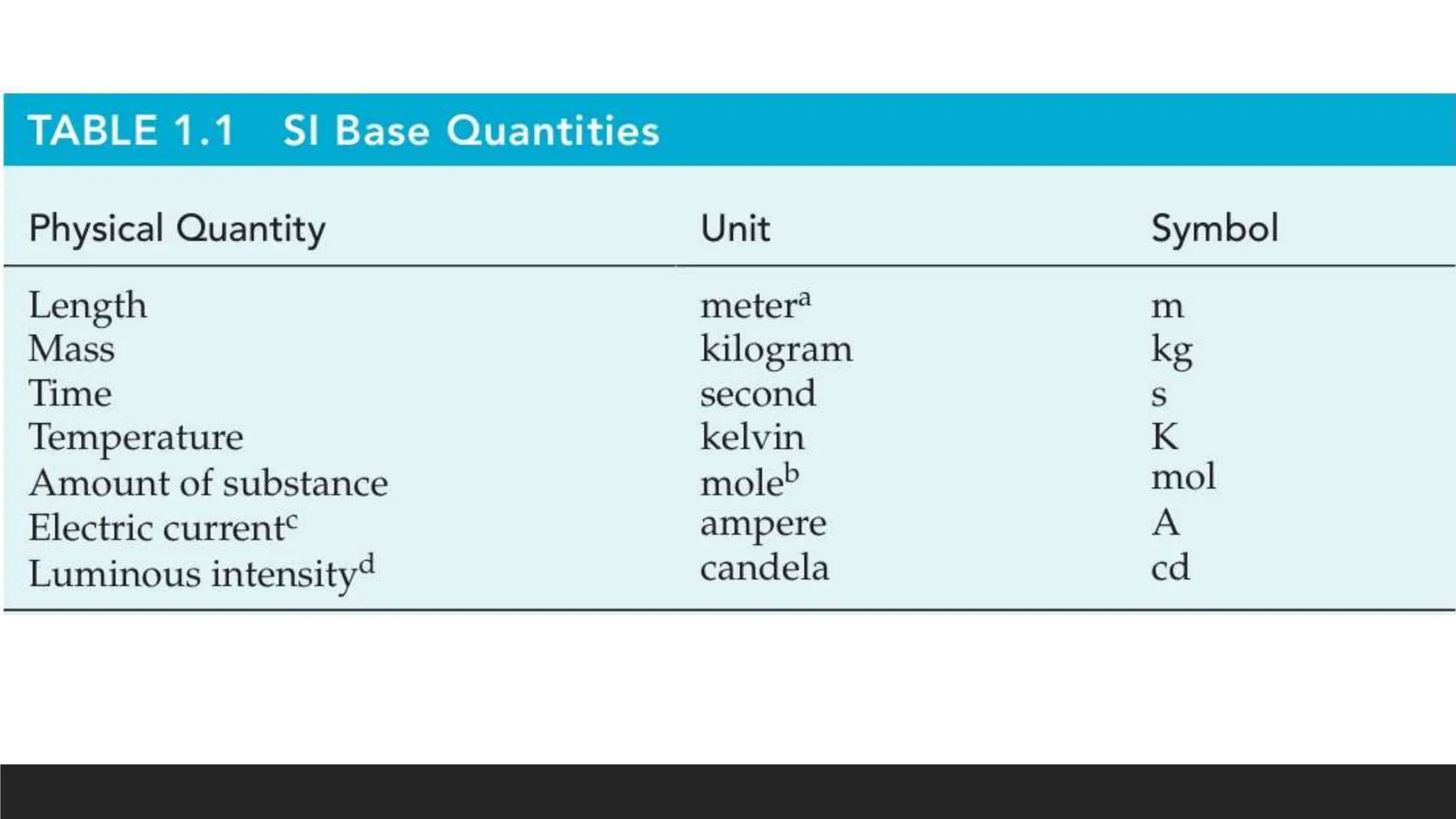
This document discusses measurement units in the International System of Units (SI), including units for volume, mass, weight, and temperature. It explains that the liter and milliliter are commonly used metric units for volume, with 1 liter being a cube 10 cm on each side and 1 milliliter being a cube 1 cm on each side. For mass, the standard unit is the kilogram, but the gram is more commonly used, and weight is directly proportional to mass. Finally, it describes the Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Kelvin temperature scales, noting zeros and conversion formulas between them.