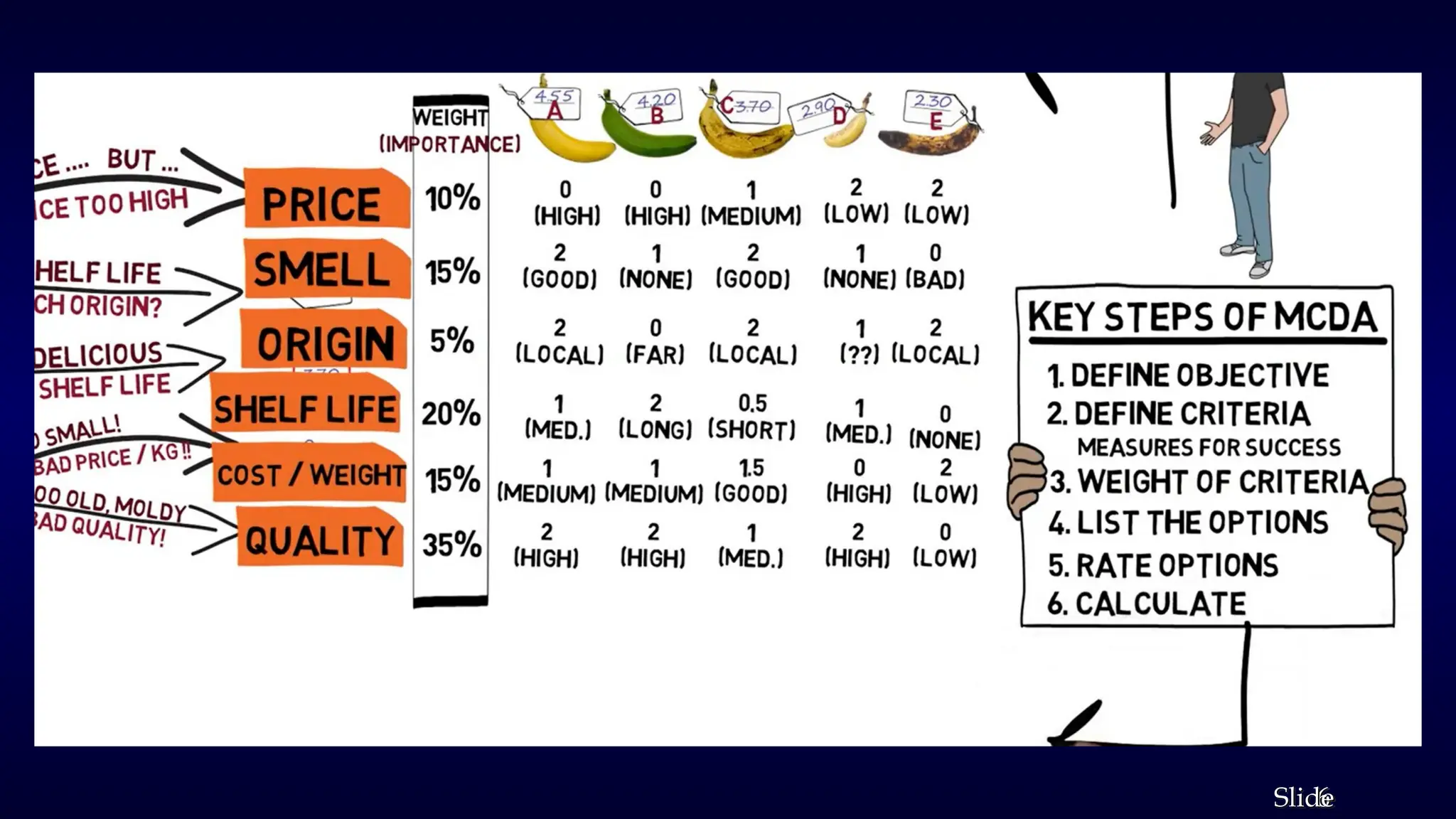
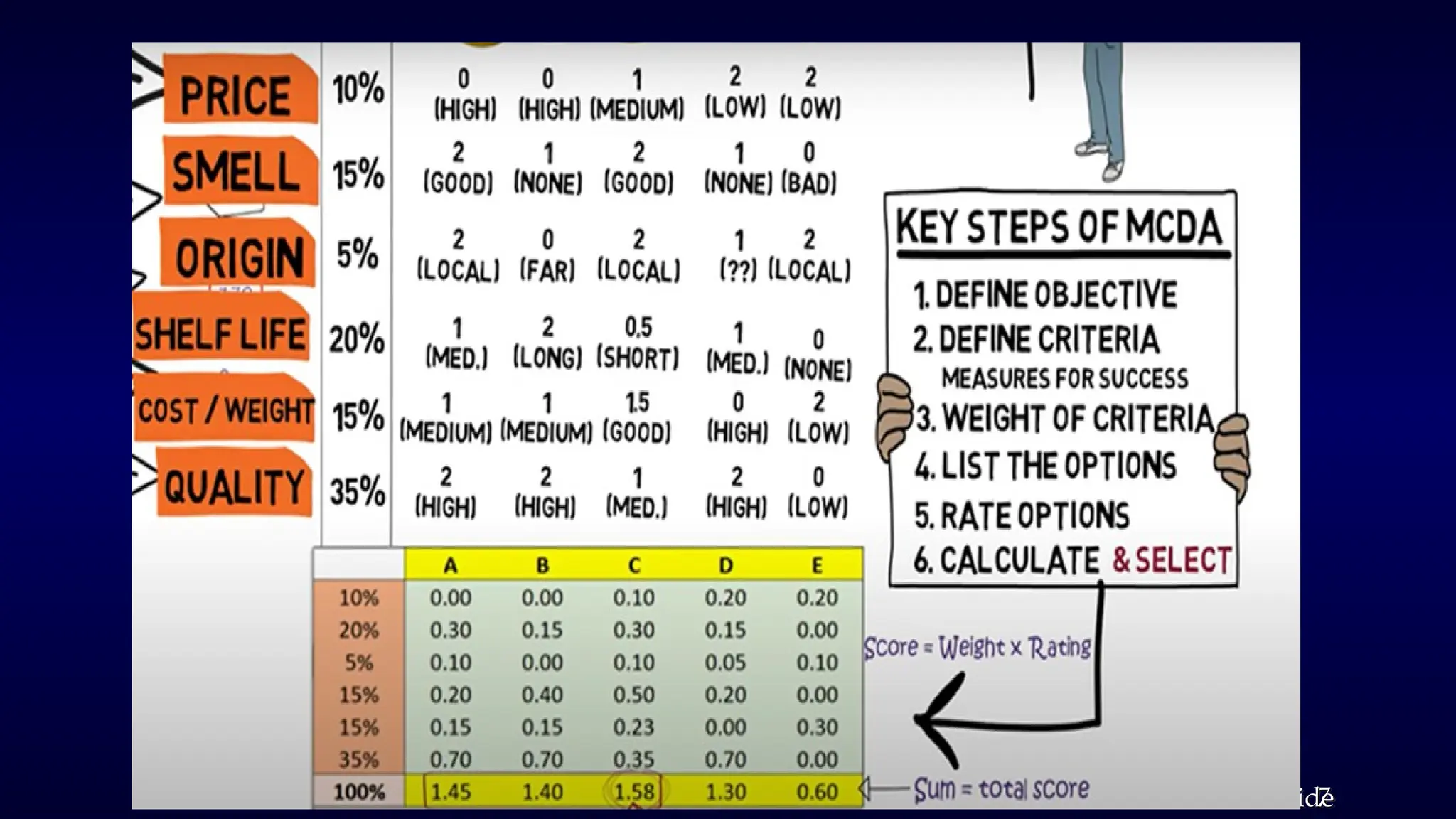
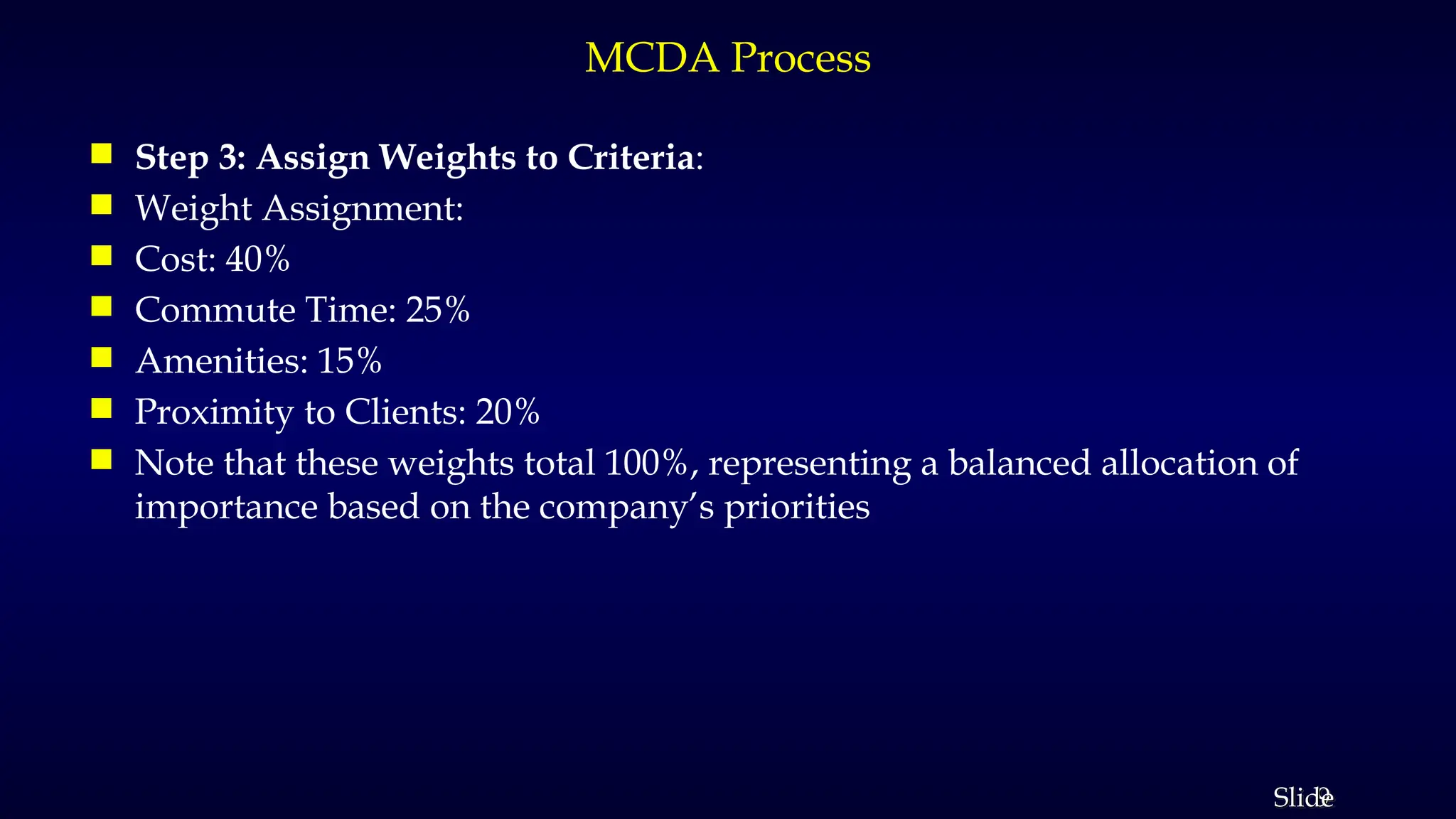
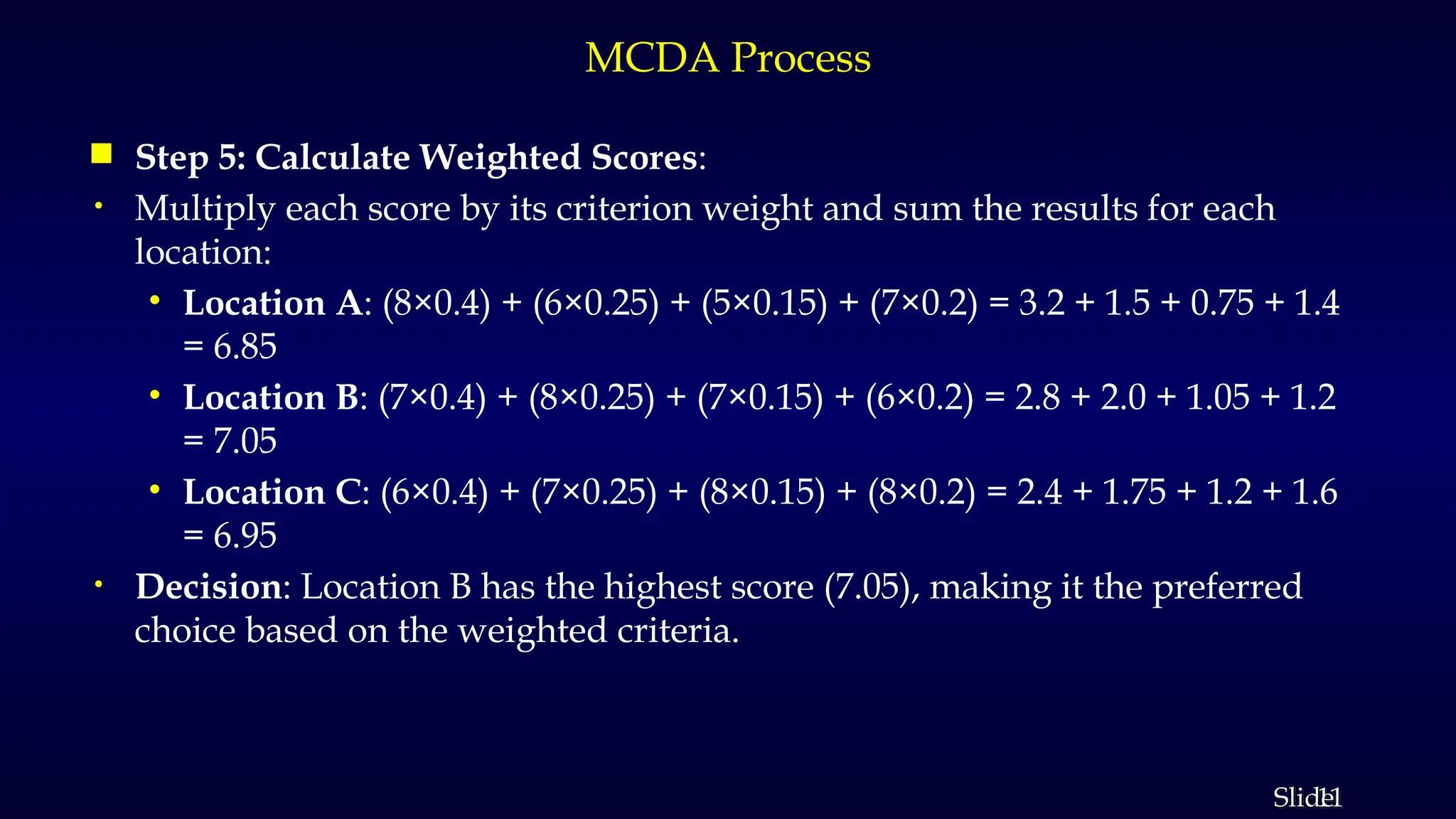
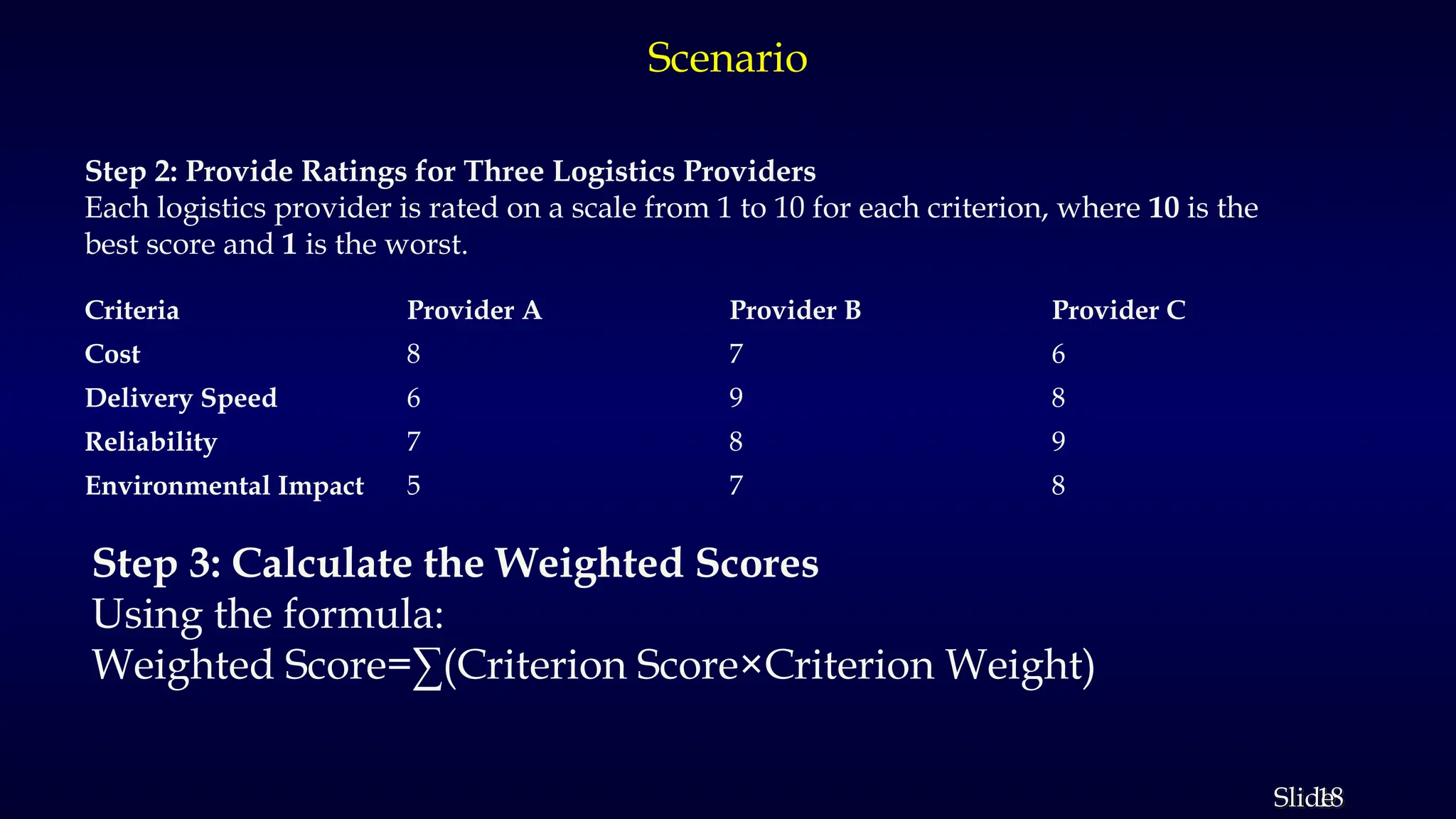
The document outlines Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis (MCDA), a framework for evaluating decisions involving multiple conflicting criteria, promoting data-driven choices. It details the MCDA process, including defining decision problems, identifying criteria, assigning weights, scoring alternatives, and calculating weighted scores, illustrated with examples and real-world applications in healthcare, environmental management, and corporate strategy. Various MCDA methods such as the Weighted Sum Model, Analytic Hierarchy Process, and TOPSIS are also explained, highlighting their relevance in complex decision-making scenarios.