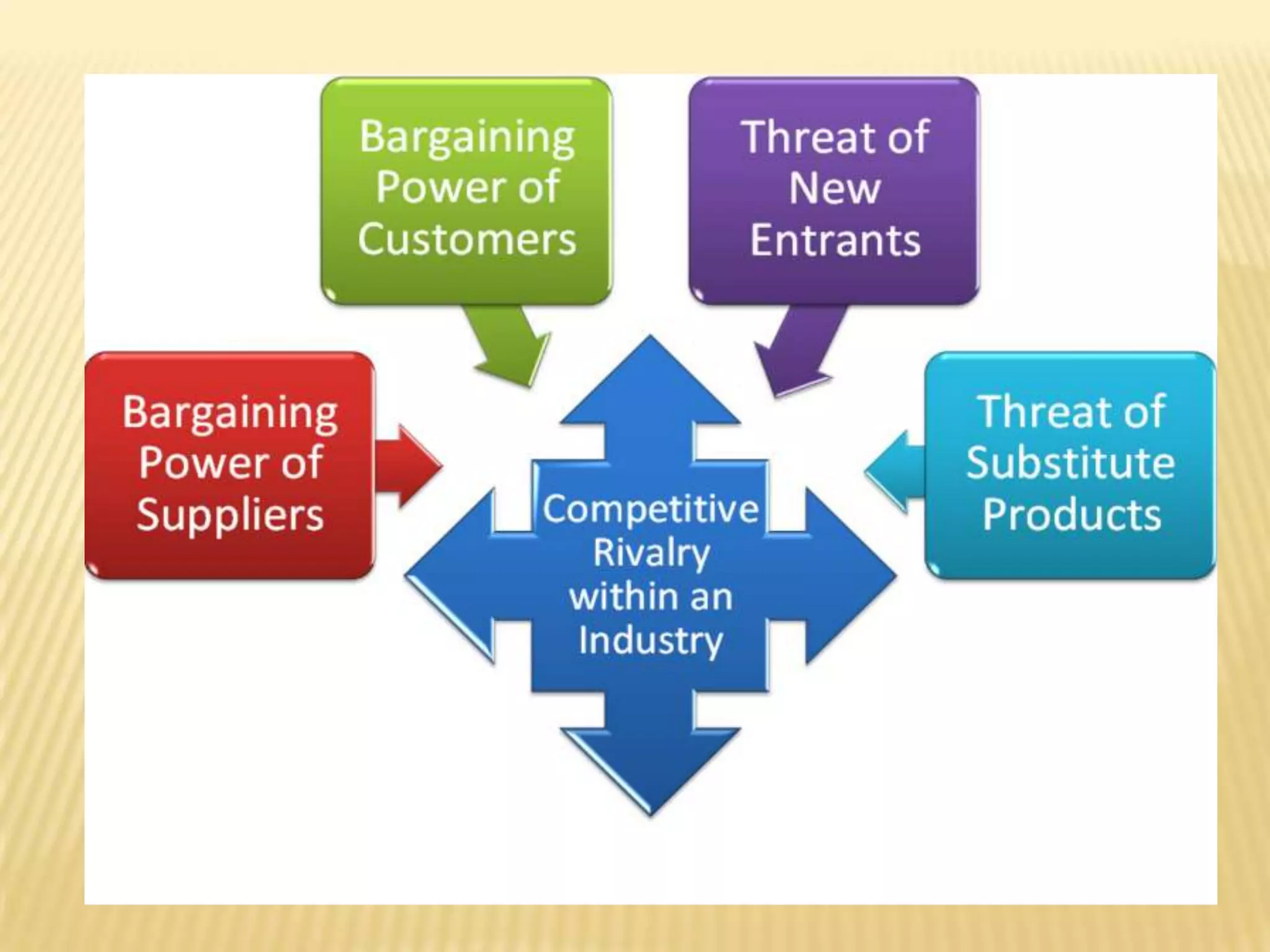
This document discusses barriers to entry, bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, and competitive rivalry in the Indian automobile industry. It notes that high startup costs and access to distribution channels pose barriers to entry. Buyer bargaining power is moderately high due to many options and financing schemes available, while supplier bargaining power is reduced by high switching costs. Competitive rivalry in the industry is extremely high due to competition from global brands.