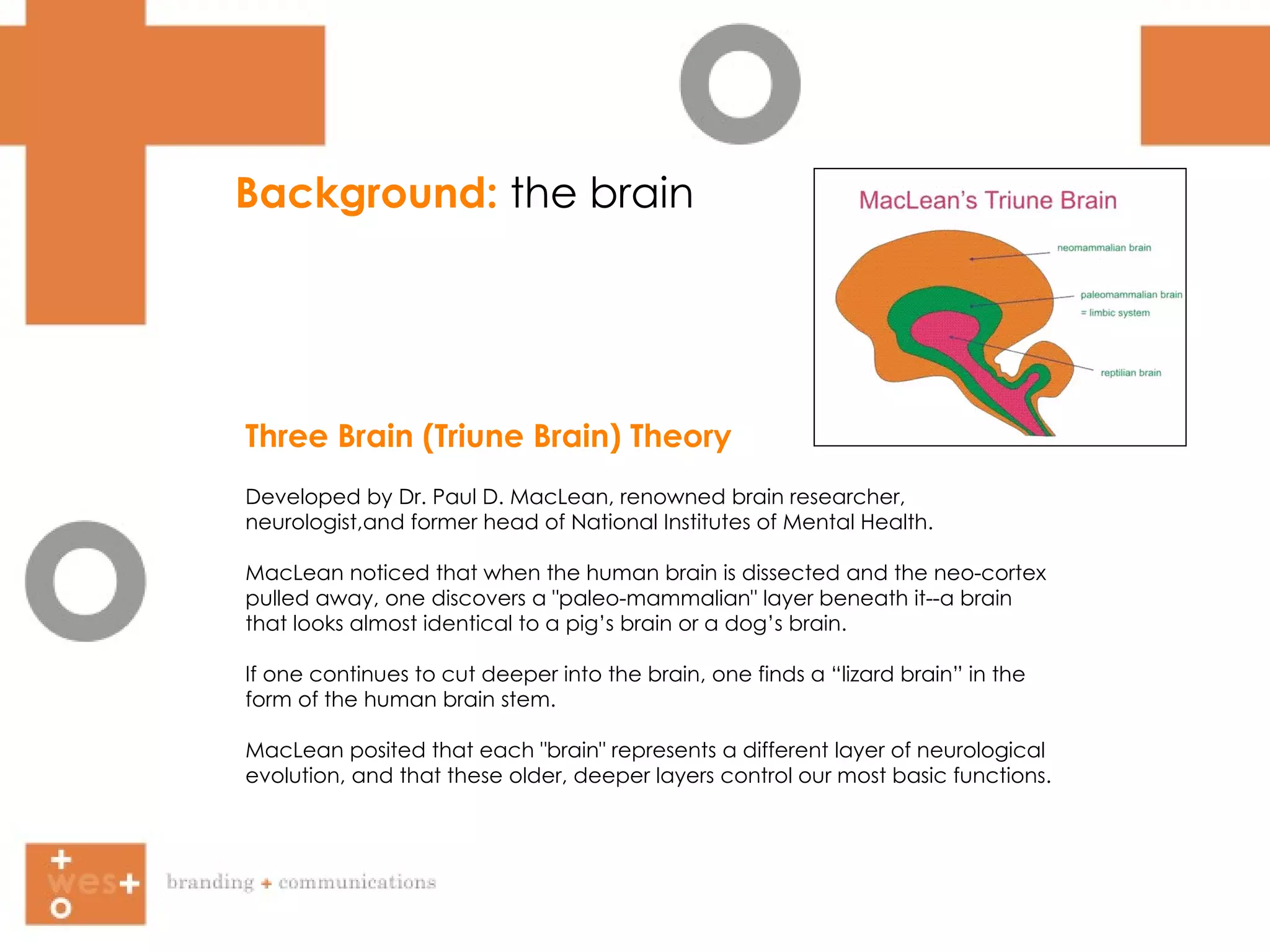
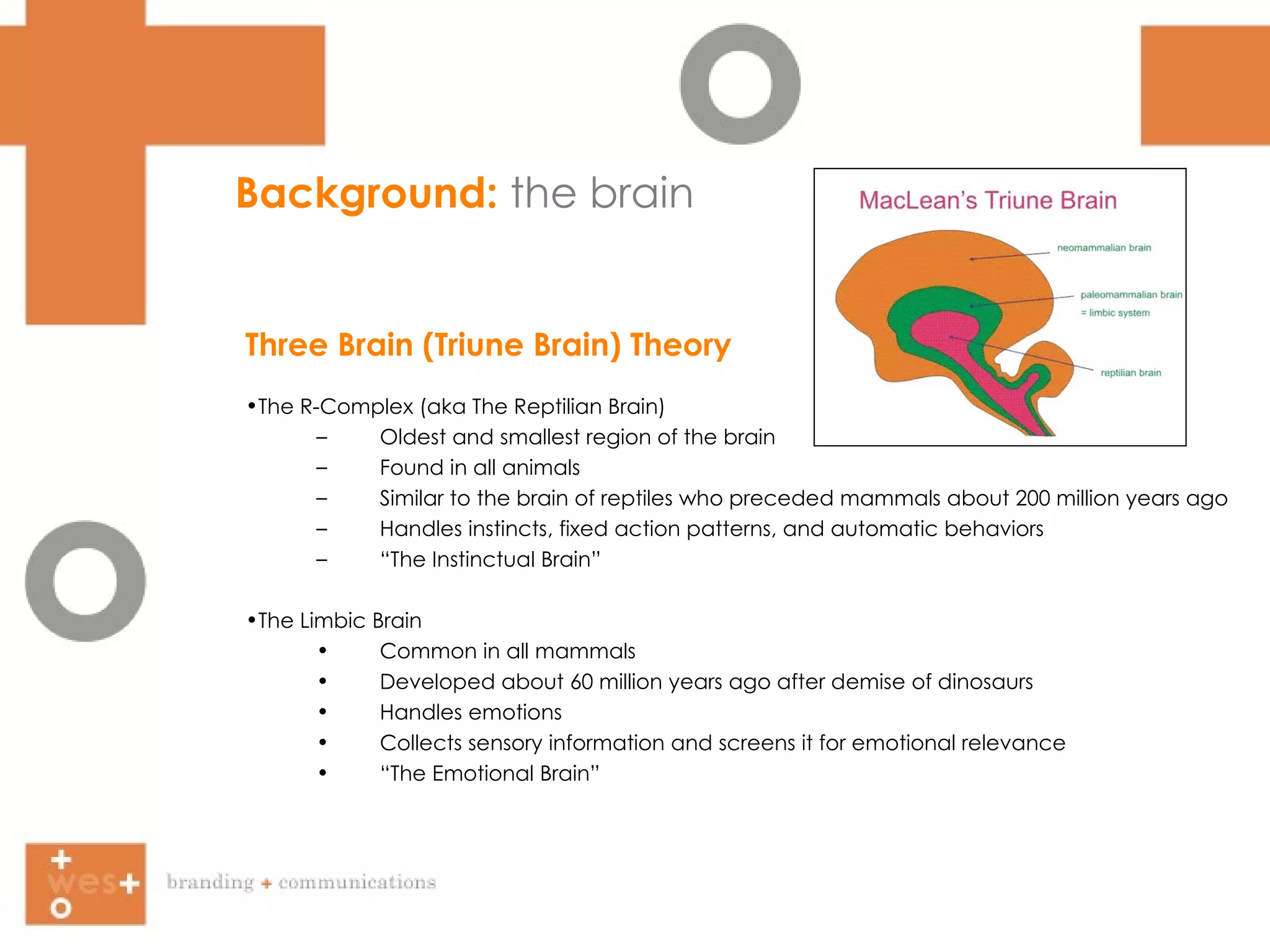
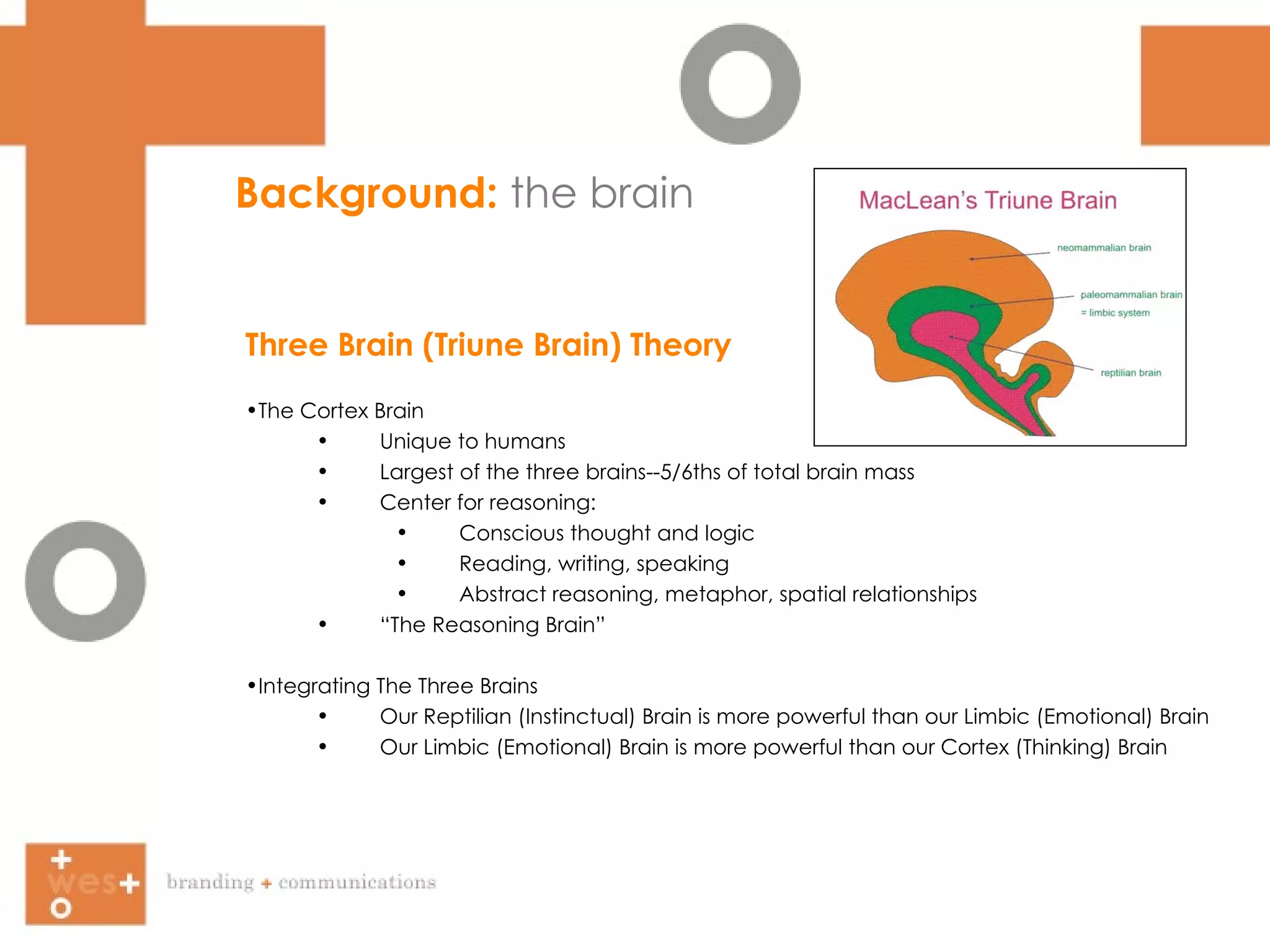
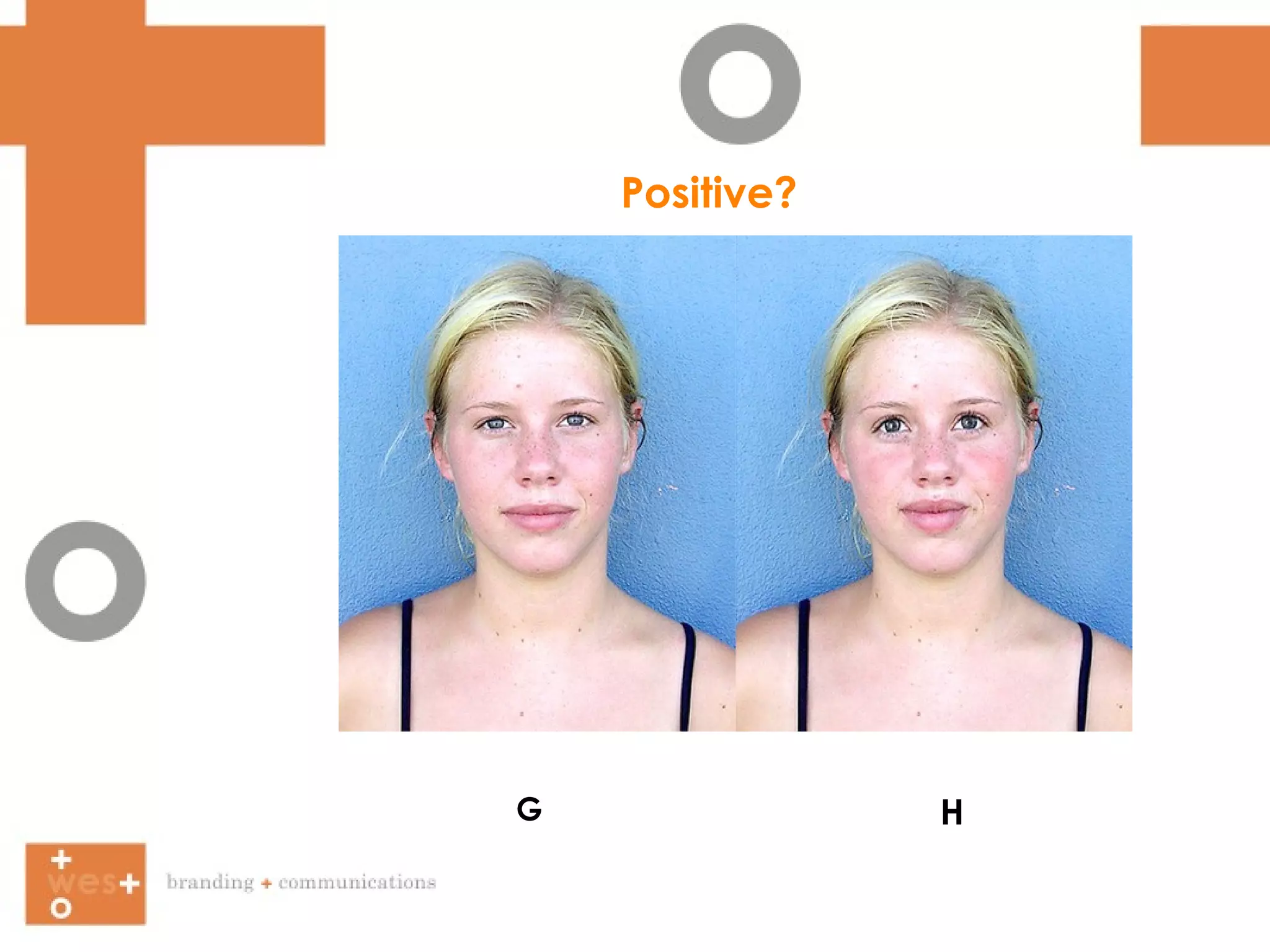
The document summarizes Paul MacLean's Three Brain Theory, which proposes that the human brain is composed of three evolutionarily distinct structures - the reptilian brain, limbic brain, and cortex brain. It then discusses how facial expressions, body language, eye contact, and facial symmetry influence communication and perception of traits like trustworthiness. Marketing approaches that target both the conscious and subconscious minds are suggested.