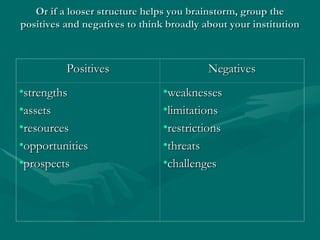
This document discusses the SWOT analysis method, which evaluates strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats to aid in strategic planning and decision-making. It emphasizes the importance of recognizing both internal and external factors and suggests inclusive, collaborative techniques for developing a SWOT analysis. Ultimately, the analysis serves as a vital tool for institutions to understand their current position and make informed choices moving forward.