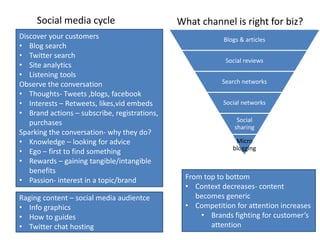
The document provides an overview of marketing concepts including needs, wants, demands, segmentation, targeting, positioning, and the marketing mix (4Ps).
It begins by defining needs, wants, and demands, using examples to illustrate how marketers can turn needs into demands by directing them at specific products. It then discusses segmentation, targeting, positioning, and the 4Ps framework as the core components of a "Go To Market" marketing strategy. Specific examples are provided for each concept. Finally, it covers distribution channels and challenges, the sales hierarchy, and factors to consider for designing an effective distribution network and social media marketing campaign.