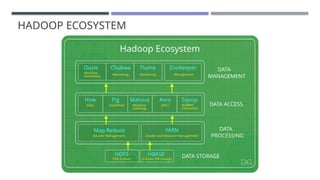
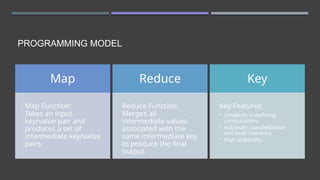
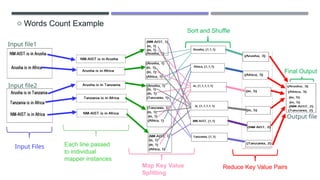
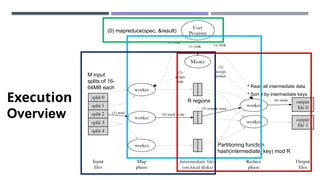
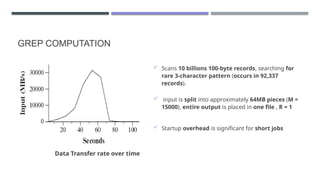
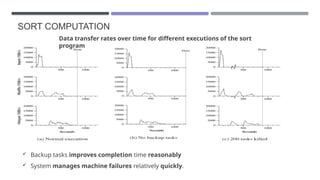
The document discusses MapReduce, a programming model developed by Jeffrey Dean and Sanjay Ghemawat to simplify data processing on large clusters, enabling automatic parallelization, fault tolerance, and data distribution. It introduces Hadoop as an open-source framework utilizing MapReduce for distributed processing and highlights its architecture, advantages, and ecosystem components like HDFS and YARN. The document also covers the execution flow, performance optimization, and use cases for MapReduce in large-scale data tasks.