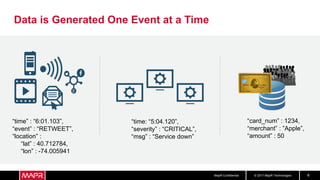
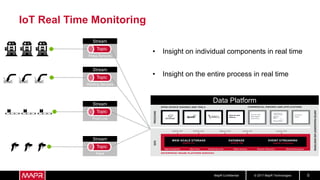
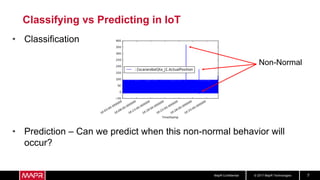
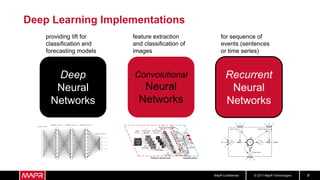
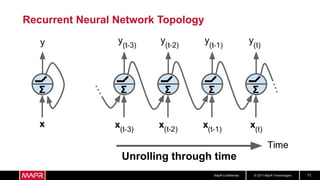
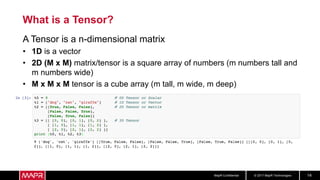
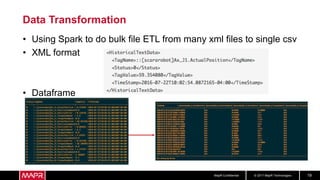
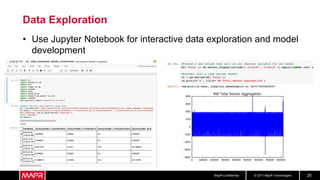
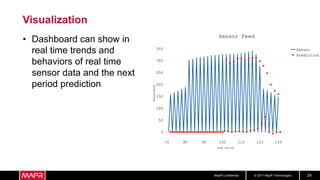
The document discusses using recurrent neural networks (RNNs) for predictive maintenance of industrial equipment using IoT sensor data. It describes how RNNs are well-suited for analyzing sequential sensor data to predict failures. The discussion includes importing sensor data from manufacturing devices into a Hadoop filesystem, transforming the data, exploring it with Jupyter notebooks, developing an RNN model for failure prediction, and deploying the trained model as new sensor data streams in to generate alerts before failures occur. Visualizing the real-time data and predictions on a dashboard is also proposed.