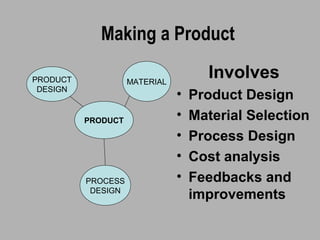
This document provides an overview of the ME3102 Manufacturing Science course, which covers casting processes, forming, and joining over four modules totaling 42 hours. The course requires a basic knowledge of materials science and practical workshop classes from the first year. Manufacturing is defined as making products from raw materials through organized processes and operations using machinery. The course will cover primary manufacturing processes like casting as well as forming and joining. Students will be evaluated through assignments, quizzes, and a final exam.




![Product- something that is produced.
[Manufacturing Engineering – in U.S.
Production Engineering – in Japan & Europe]
Manufacturing -,a complex activity.
Involves
MATERIALS, CAPITAL, ENERGY, PEOPLE
People, (of various disciplines and skills)
Variety of machinery, equipment
tooling with various levels of automation
(computers etc), Material handling](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/00me3102manufacturingscience-160807124224/85/manufacturing-science-NITC-5-320.jpg)