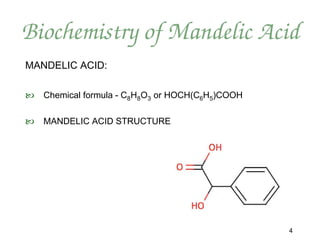
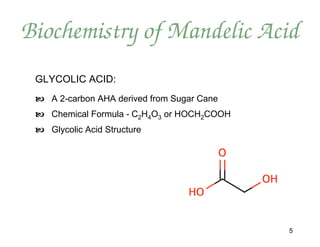
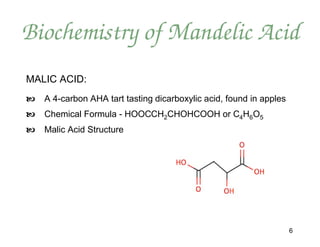
Mandelic acid is an alpha hydroxy acid derived from bitter almonds. It has several advantages over other AHAs like glycolic acid for skin treatments. Due to its larger molecular size, mandelic acid penetrates the skin more slowly and evenly, making it less irritating. It also does not disrupt melanin production or cause hyperpigmentation. Mandelic acid peels and products improve skin conditions like acne, hyperpigmentation, and signs of aging by exfoliating and stimulating collagen production. The document outlines protocols for 30-45% mandelic acid peels and a skin conditioning system to maximize their benefits.