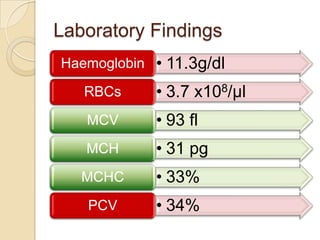
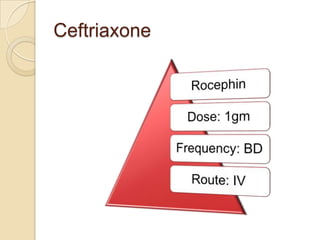
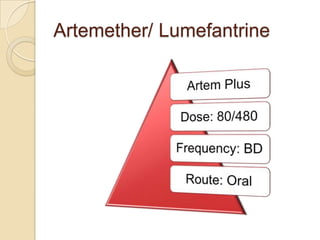
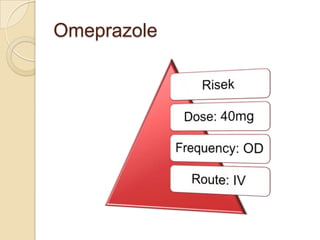
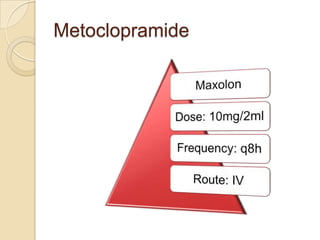
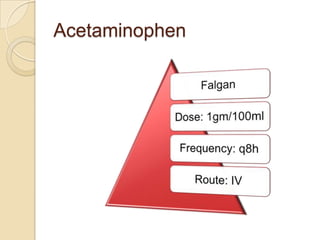
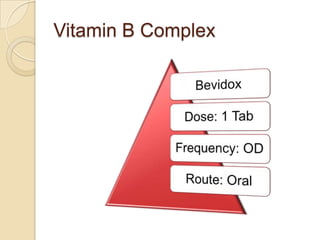
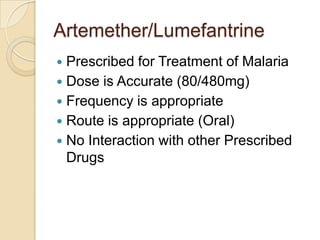
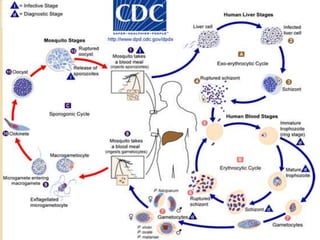
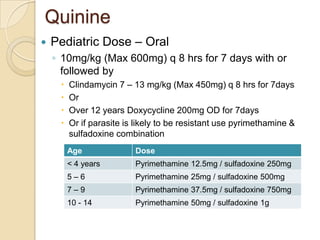
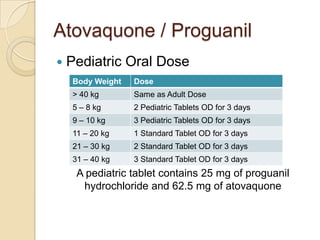
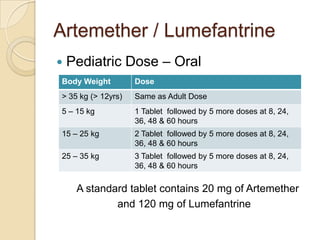
This case study describes a 21-year-old male patient presenting with fever, chills, vomiting, and epigastric pain for several days. Laboratory tests found malaria parasites and anemia. The patient was diagnosed with malaria and prescribed Ceftriaxone, Artemether/Lumefantrine, Omeprazole, Metoclopramide, Acetaminophen, and Vitamin B Complex to treat the infection, symptoms, and anemia. Malaria is caused by Plasmodium parasites transmitted by mosquitoes and has both benign and malignant forms treatable with drugs like chloroquine, quinine, and artemisinin combinations.