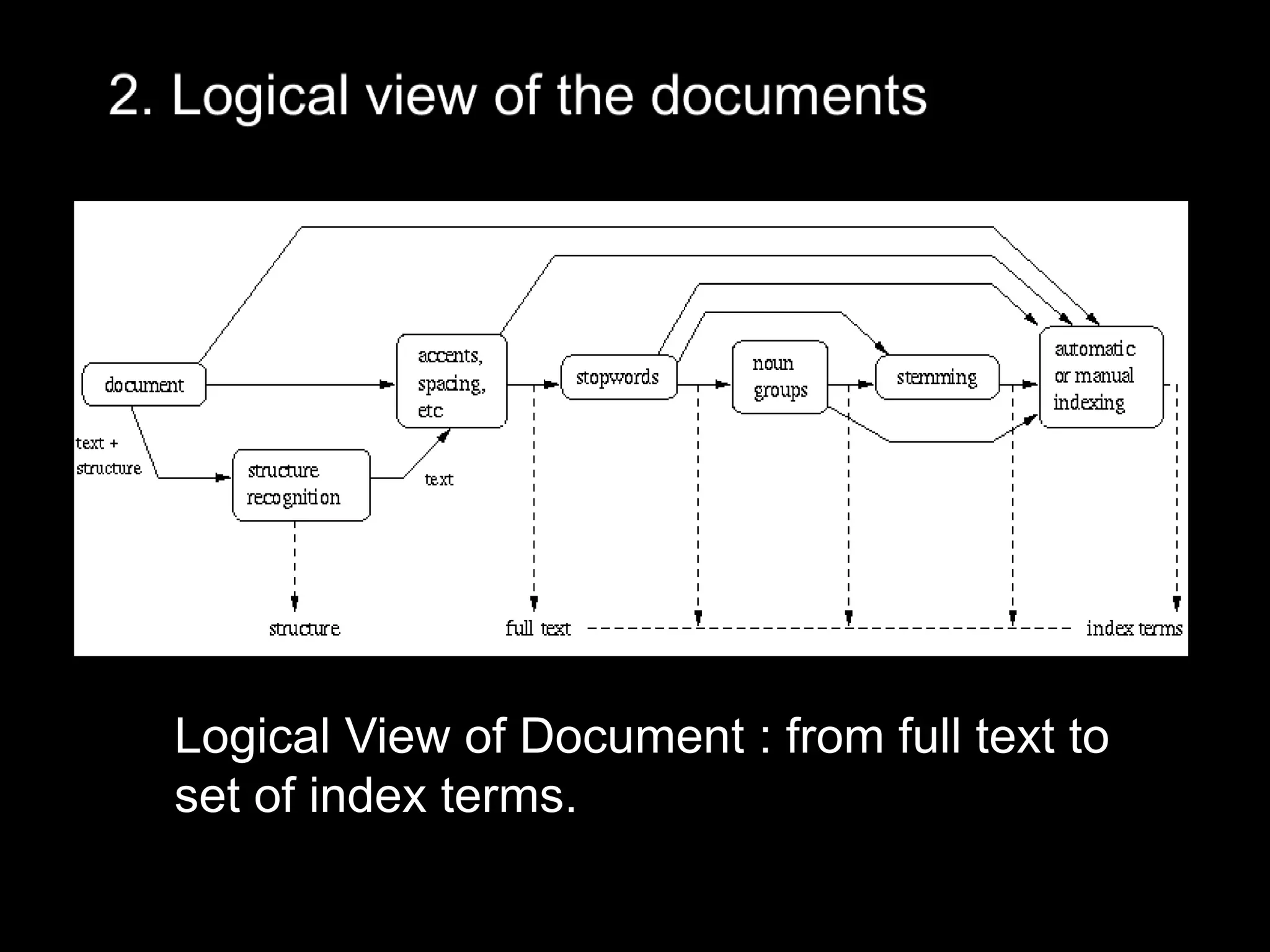
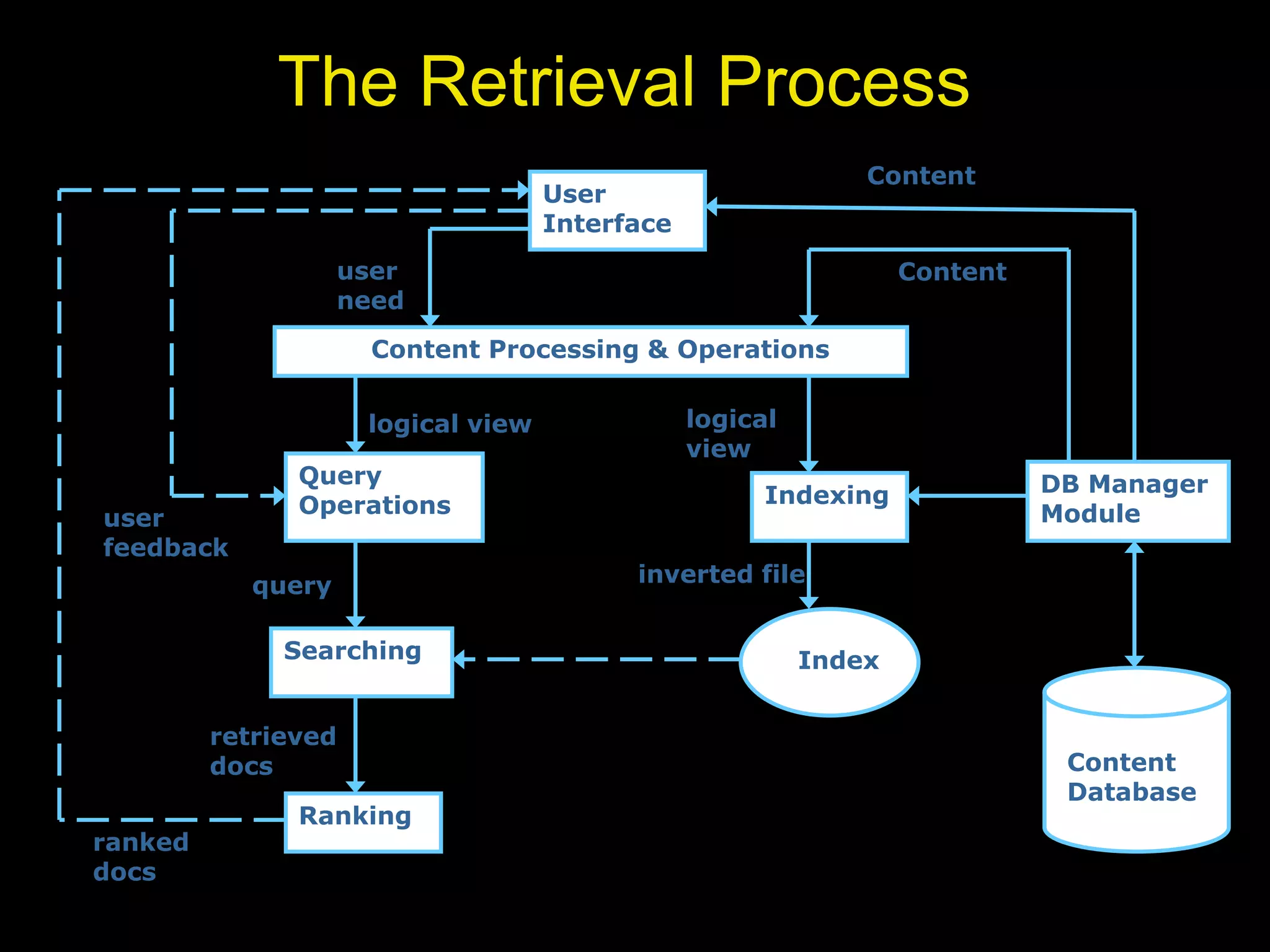
This document provides an introduction to information retrieval. It discusses how information retrieval is concerned with representing, storing, organizing, and accessing information items. The key aspects of information retrieval are focusing on the user's information need and emphasizing retrieval of information rather than data. Information retrieval systems interpret document contents, generate relevance rankings, and the notion of relevance is most important. A brief history of information retrieval discusses how it began with human indexing and searching of information collections and became a field of computer science. The advent of the web increased the universal repository of knowledge and changed the perception of information retrieval.