Early and accurate identification of lung abnormalities such as pneumonia, tuberculosis, and lung
cancer is critical for timely medical intervention and improved patient outcomes. This paper proposes a fast
and efficient framework that leverages Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) to analyze chest CT scans
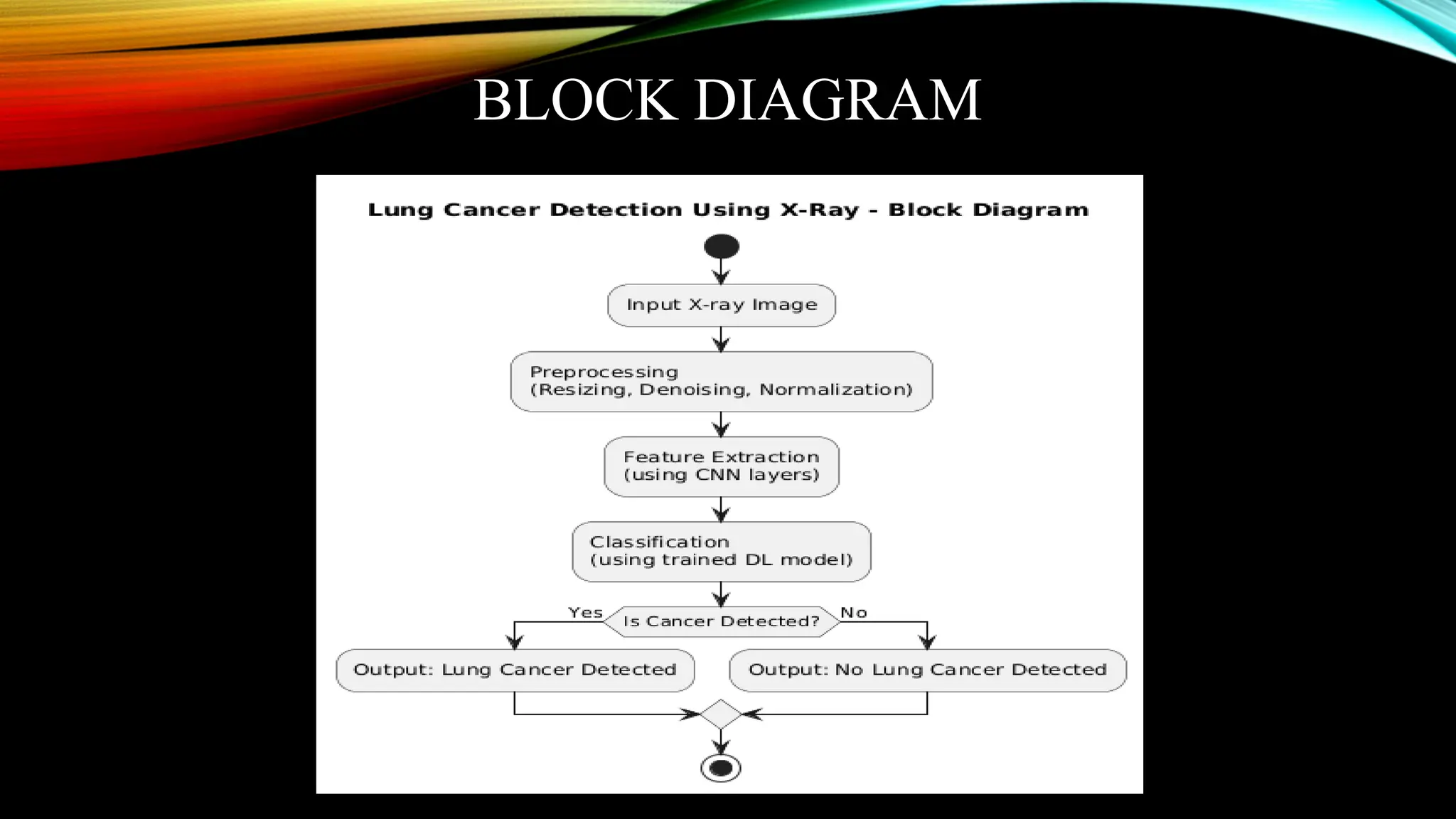
and X-ray images for automated lung abnormality detection. The framework integrates state-of-the-art deep
learning models with explainability techniques like Grad-CAM and LIME to ensure diagnostic transparency
and clinician trust. Emphasis is placed on computational efficiency to enable real-time or near-real-time
diagnostics, making the system suitable for deployment in both advanced and resource-limited healthcare
settings. Extensive experimentation on publicly available datasets demonstrates the proposed system’s high
accuracy, sensitivity, and interpretability in identifying a wide range of lung conditions.
![RAJEEV INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
HASSAN
DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND
ENGINEERING
PROJECT ON
UNDER THE GUIDENCE OF,
Mr. CHIRANJEEVI M R
ASSISTANT PROFESSOR,
DEPT OF CSE,
RIT HASSAN.
SUBMITTED BY,
SHAIK MOHAMMED AYAN [4RA21CS077]
SURAJ B [4RA22CS413]
KIRAN KUMAR C V [4RA22CS405]
GAGAN B G [4RA22CS403]
“Lung Abnormality Identification
With Explainable AI”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lungfinal-1-250513011023-8f9098cc/75/Lung-abnormalities-indentification-with-explainable-AI-1-2048.jpg)