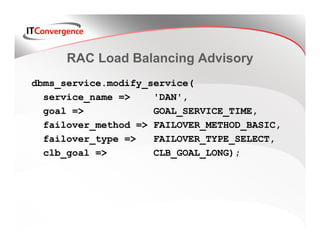
Oracle Real Application Clusters (RAC) provides load balancing and failover options through services like Fast Application Notification (FAN), Fast Connection Failover (FCF), and Transparent Application Failover (TAF). RAC monitors workload activity for each service across cluster instances and publishes load balancing advisories to recommend how to distribute workloads. Runtime connection load balancing in RAC 10g integrates with these advisories to adjust how existing connections distribute work based on backend node capacities over time.




















![Fast Connection Failover
Best Practices
Applications must catch SQLException and retry
connection requests
Fast Connection Failover relies on the Oracle Net
Services for connection creation and placement
In 10.1, listener’s config should contain
PREFER_LEAST_LOADED_NODE_[<listener_name>]=OFF
In 10.2 and above, Service CLB_GOAL must be set
Use Oracle RAC VIP in connect strings for all client
connections](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/loadbalancingandfailoveroptions-110818111555-phpapp01/85/Load-balancing-and-failover-options-22-320.jpg)