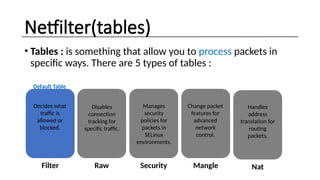
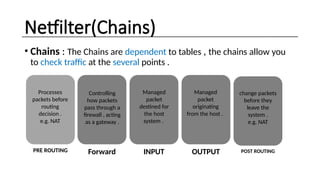
The document provides an overview of Linux firewalls, focusing on the netfilter framework and its key components: tables, chains, and targets, as well as various tools for configuration like iptables, nftables, and ufw. It discusses the advantages of using a Linux firewall, such as flexibility, scalability, and compatibility with other services. Additionally, it explains the roles of different tables in packet processing and provides example command usage for managing firewall rules.






![Iptable
• Iptable : is a command-line tool used in Linux to configure the
system’s firewall rules .
• Structure : Iptable [options] –[ACD] [Chain] [match condition ] –j [target/action ]
-[Options ] : for listing , for saving ….
-[ACD] : -A (append) , -C(check the rule in exists in the chain ) , -D(Delete a rule from chain )
-[chain] : input, output, forward …
-[match condition] : -p(protocol) , -s (source address) , -d (destination address), --dport
(destination port )
- j[target] : Accept , Drop , Reject …
- EXAMPALE : [ Iptable –A INPUT -p tcp –-dport 22 –j ACCEPT ]
• Itable :equivalent of ‘Iptable’ for IPV6 network .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linux-firewall-241125094314-2dee474f/85/Linux-Firewall-Netfilter-and-tools-pptx-9-320.jpg)

