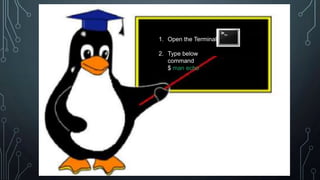
This document provides a summary of basic Linux commands including ls, date, pwd, cd, touch, mkdir, cat, head, tail, cp, mv, man, rm, who, w, df, du, uptime, hostname, echo, history, clear, su, and exit. It explains what each command is used for and provides examples of basic syntax.






![Command : mkdir
command is used to create a new directory
Syntax : mkdir directory_name
Example:
• mkdir new_dir
• mkdir –p dir/dir1 [creating along with parent directory]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linuxbasics-211109095832/85/Linux-basics-11-320.jpg)
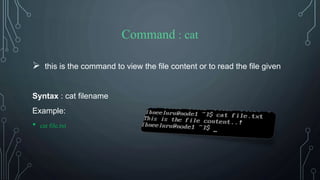

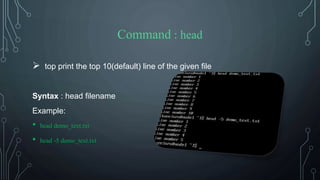
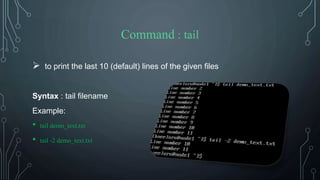
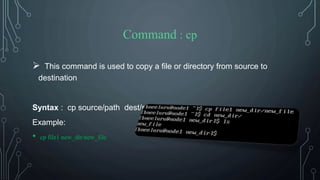
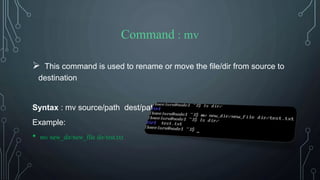

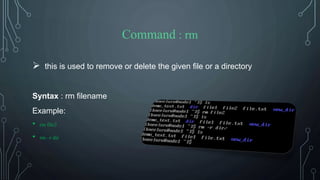
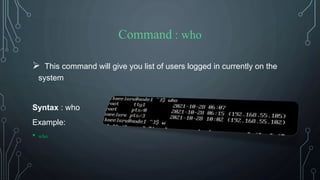
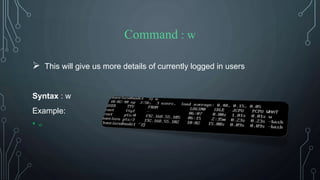
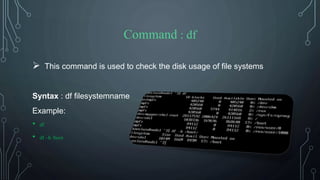
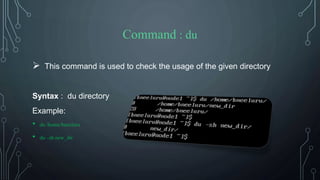
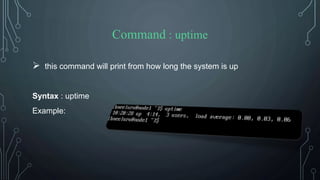

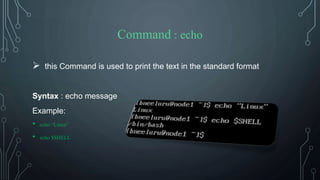

![Command : clear
this command is used to clear the screen
Syntax : clear
Example:
• clear
• Crtl+L [Shortcut key]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linuxbasics-211109095832/85/Linux-basics-28-320.jpg)
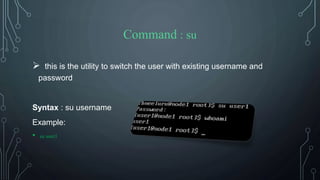
![Command : exit
this command is used to exit from the terminal and the exit as the current
user
Syntax : exit
Example:
• exit
• Ctrl+D [Shortcut key]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linuxbasics-211109095832/85/Linux-basics-30-320.jpg)
