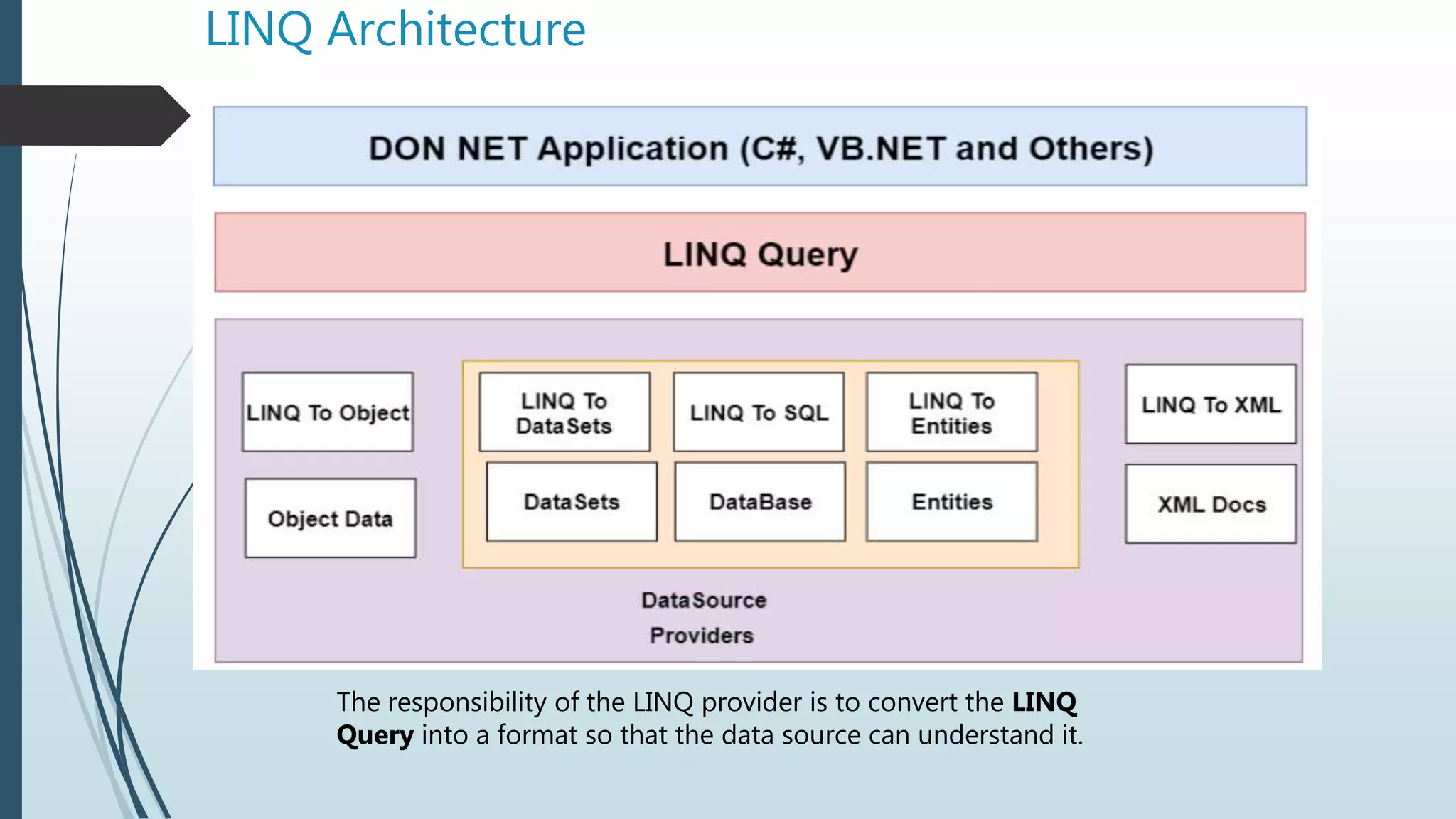
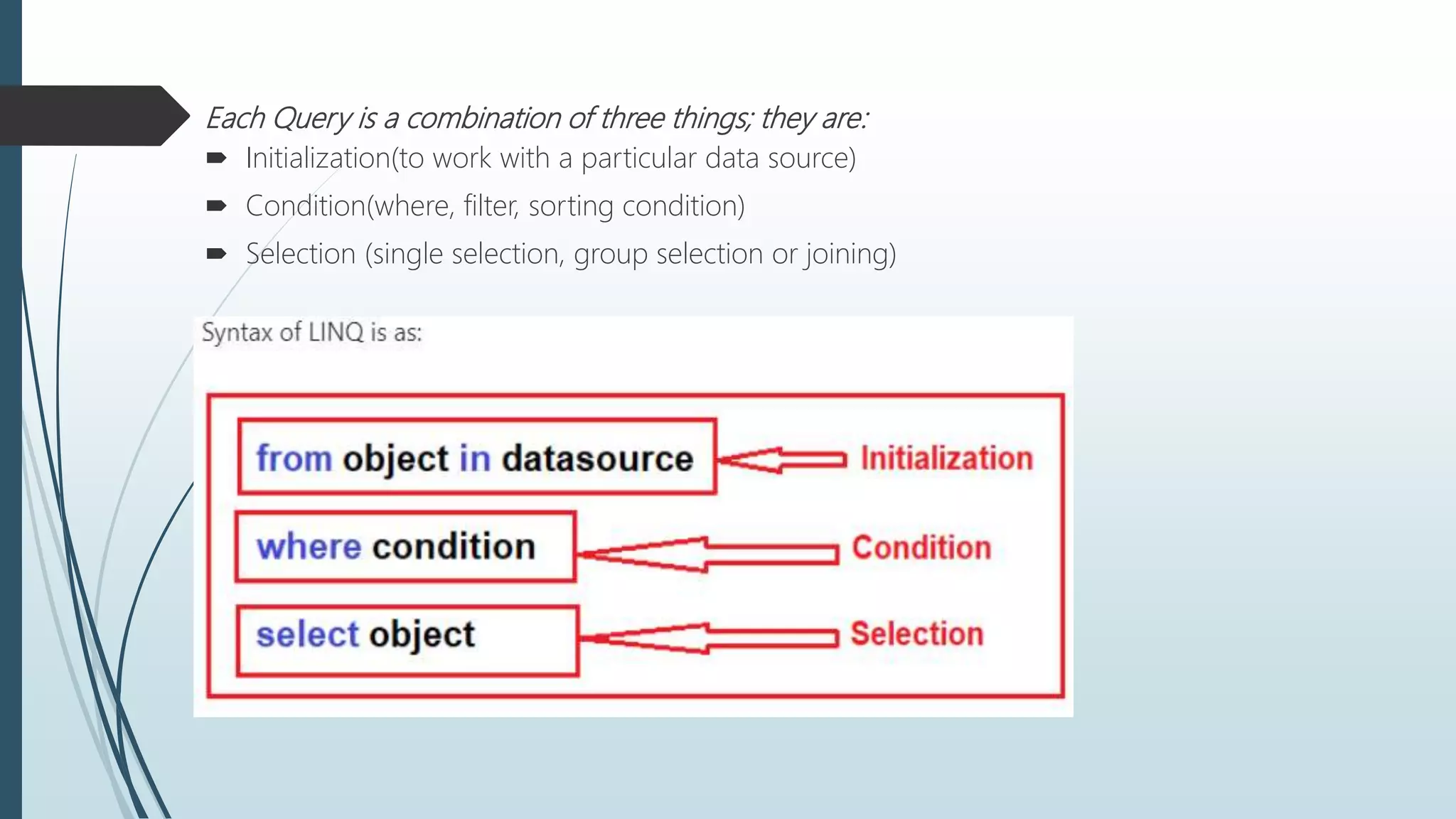
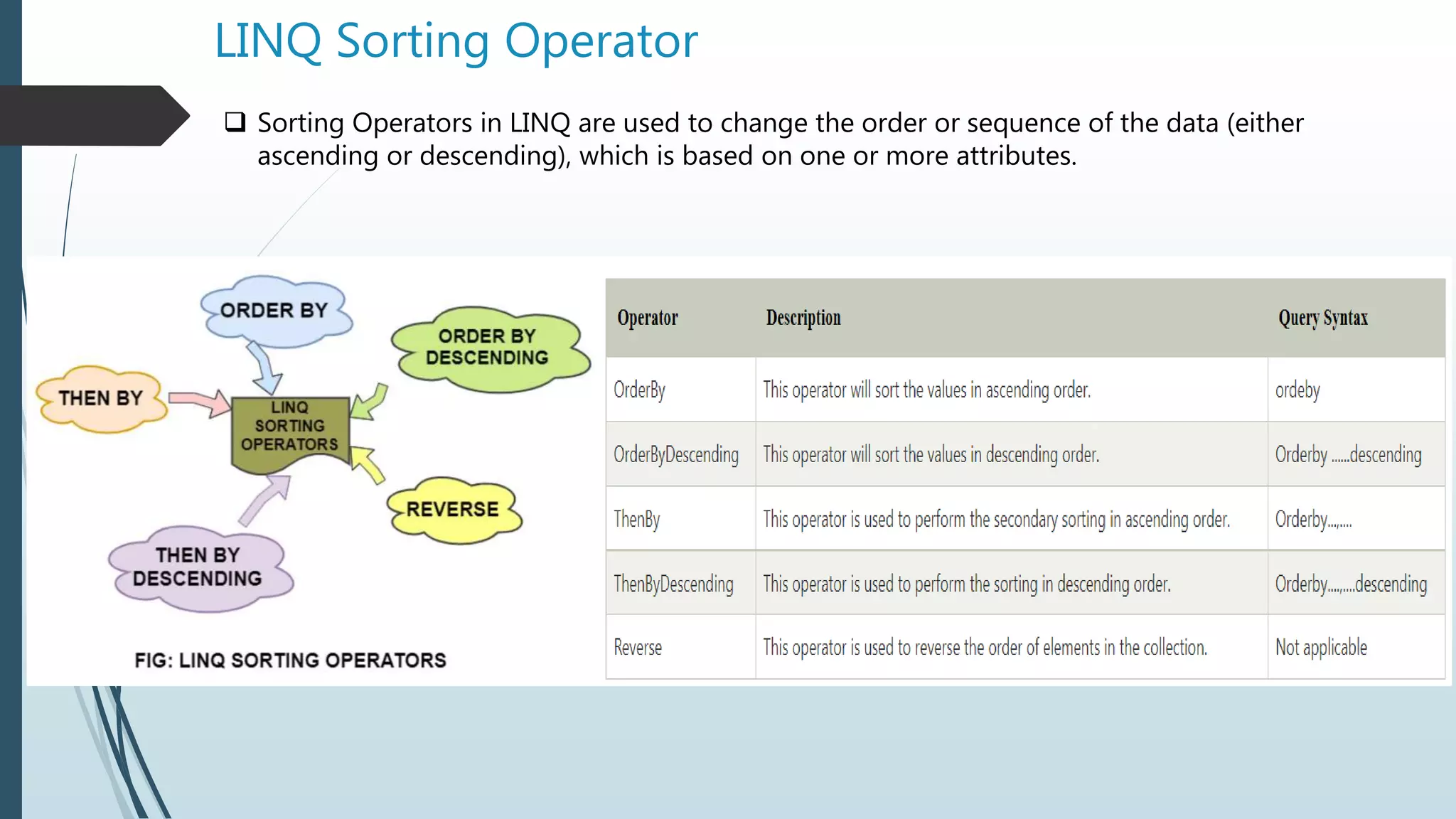
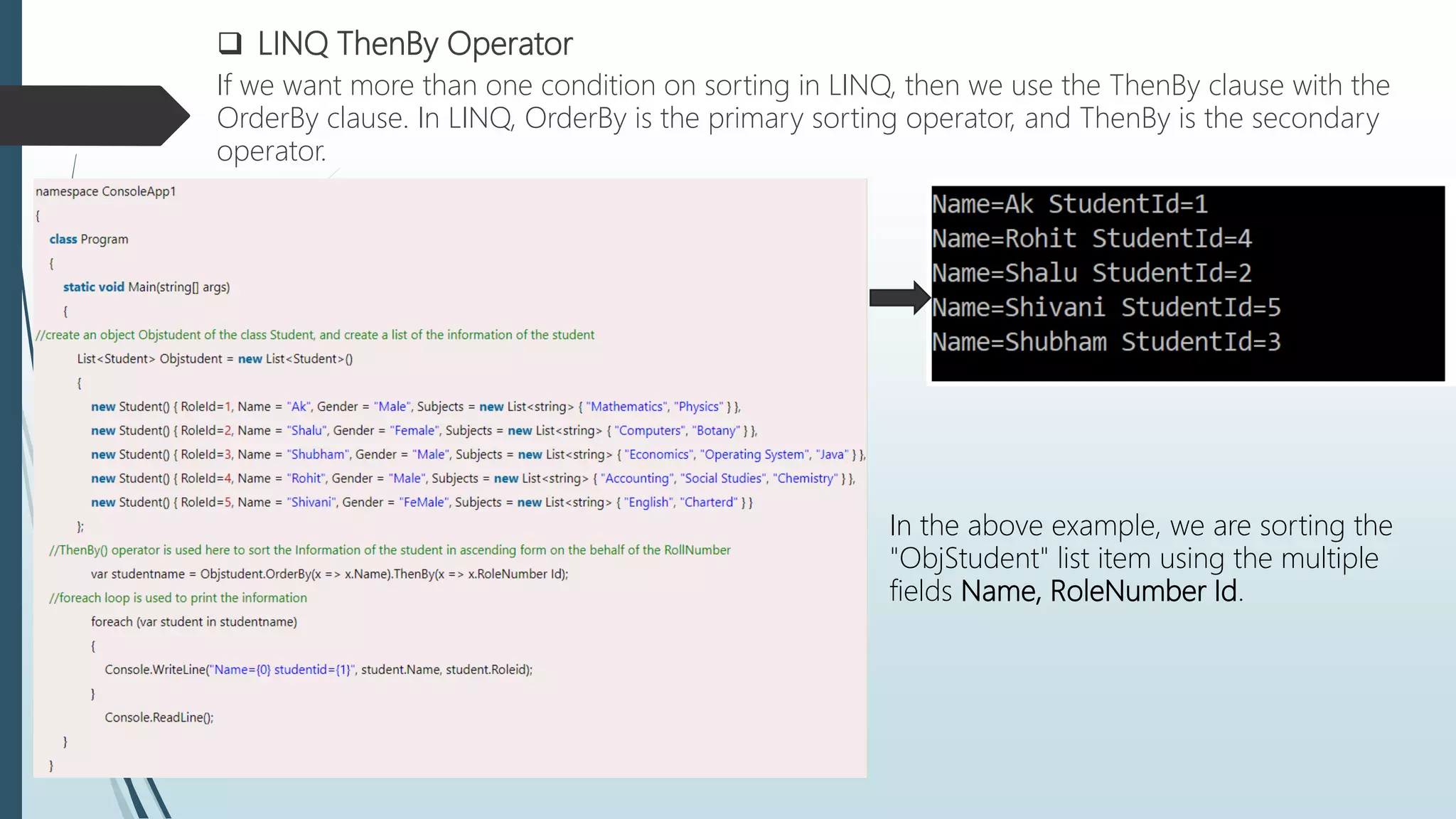
The document discusses Language Integrated Query (LINQ), which introduces a standard query syntax in .NET languages like C# and VB.NET. LINQ allows querying of different data sources like collections, XML documents, and databases. It provides compile-time checking and IntelliSense support. LINQ queries can be reused and reduce code compared to traditional approaches. The document also covers LINQ architecture, advantages, disadvantages, syntax, lambda expressions, and common query operators like filtering, sorting, aggregation, partitioning, and more.





![ Aggregate Functions
LINQ Min() Function and Max() Function
MIN () function of LINQ is useful to get the minimum value from a collection or list whereas Max
() function of LINQ is useful to get the maximum value
int[] a = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 };
int m = a.Min(); or int m = a.Max();
From the above syntax, we are getting the minimum and maximum value from the "a" list using the
LINQ Min () or Max() function.
LINQ Sum() Function
In LINQ sum() function is used to calculate the sum of the items in collections/lists.
int[] a = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 };
int sum = a.Sum();
From the above syntax, we are summing up the items in the “a" list using the LINQ Sum function.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linq-220428054310/75/LINQ-pptx-8-2048.jpg)
![ LINQ Count() function
COUNT () function in LINQ is used to count the number of elements in the list or collection.
int[] a = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 };
int m = a.count();
LINQ Aggregate() Function
int[] Num = { 1, 2, 3, 4 };
double Average = Num.Aggregate((a, b) => a + b);
Output 10 ((1+2)+3)+4 )
in the above syntax, we take two elements 1 and 2 to perform the addition and make 3 then it take
the previous result 3 and next element 3 and perform the addition to make the 6 to the next
4 and result will be 10.
Ex. Now we will calculate the average of the numbers by applying the Aggregate function.
double Average = Num.Aggregate((a, b) => a * b);
Output 362880 ((((((((1*2)*3)*4)*5)*6)*7)*8)*9)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linq-220428054310/75/LINQ-pptx-9-2048.jpg)

![Take() and TakeWhile()
In LINQ, Take Operator is used to get the specified number of elements in sequence from the
list/collection. The LINQ takes the Operator will return the specified number of elements from the
starting of collection or list.
Ex. string[] countries = { "India", "USA", "Russia", "China", "Australia", "Argentina" };
IEnumerable<string> result = countries.Take(3);
foreach (string s in result) Console.WriteLine(s);
LINQ, TakeWhile Operator is used to get the elements from the list/collection of the data source as
long as the specified condition is holding the expression or until the condition is false.
Ex. string[] countries = { "India", "USA", "Russia", "China", "Australia", "Argentina" };
IEnumerable<string> result = (from x in countries select x).TakeWhile(x => x.StartsWith("U"));
foreach (string s in result) Console.WriteLine(s);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linq-220428054310/75/LINQ-pptx-15-2048.jpg)
![LINQ SKIP OPERATOR
In LINQ, the Skip operator is used to skip the specified number of elements from the list/collection
and return the remaining elements
Ex. string[] countries = { "India", "USA", "Russia", "China", "Australia", "Argentina" };
IEnumerable<string> result = countries.Skip(3);
foreach (string s in result) Console.WriteLine(s);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linq-220428054310/75/LINQ-pptx-16-2048.jpg)